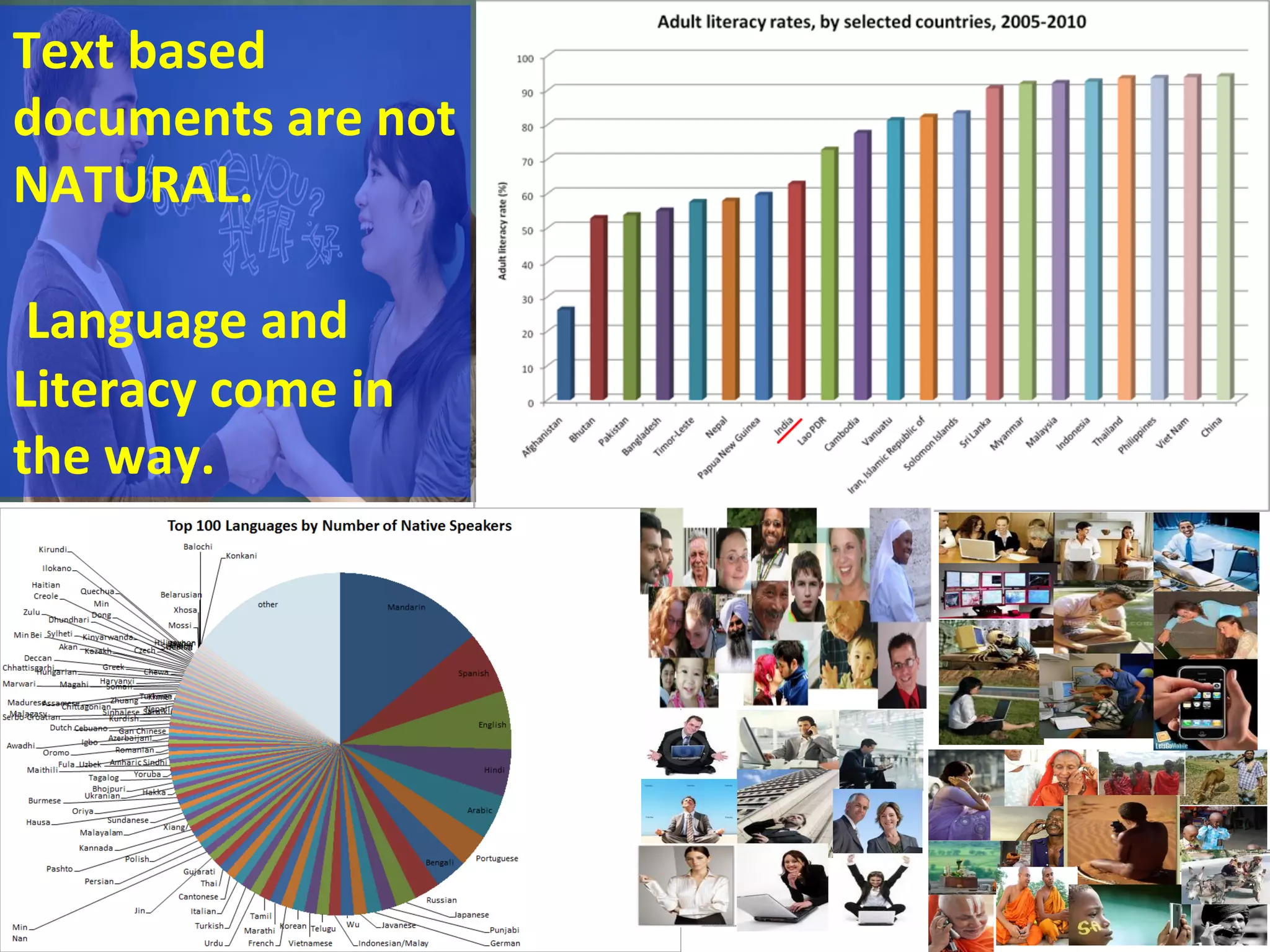
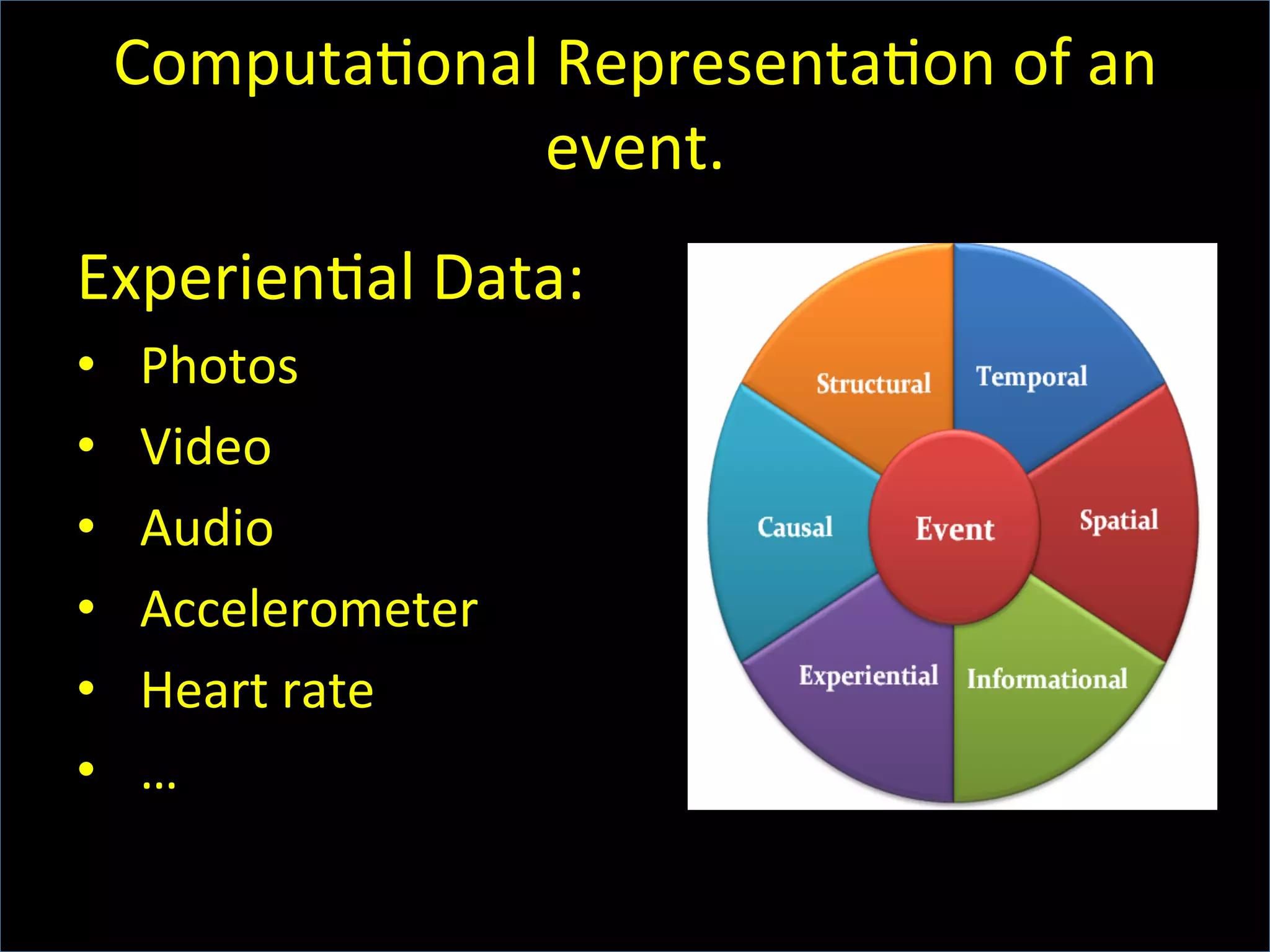
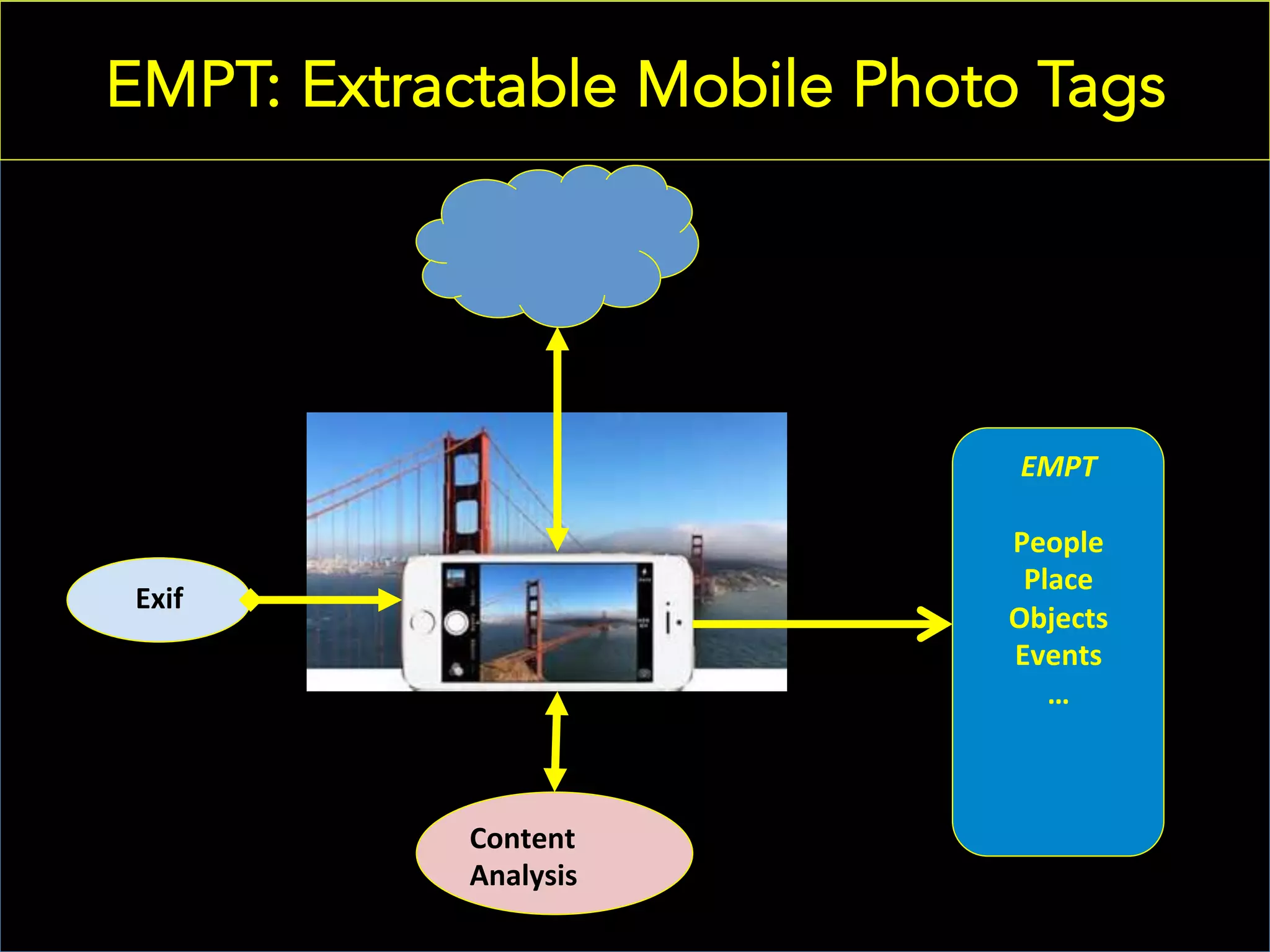
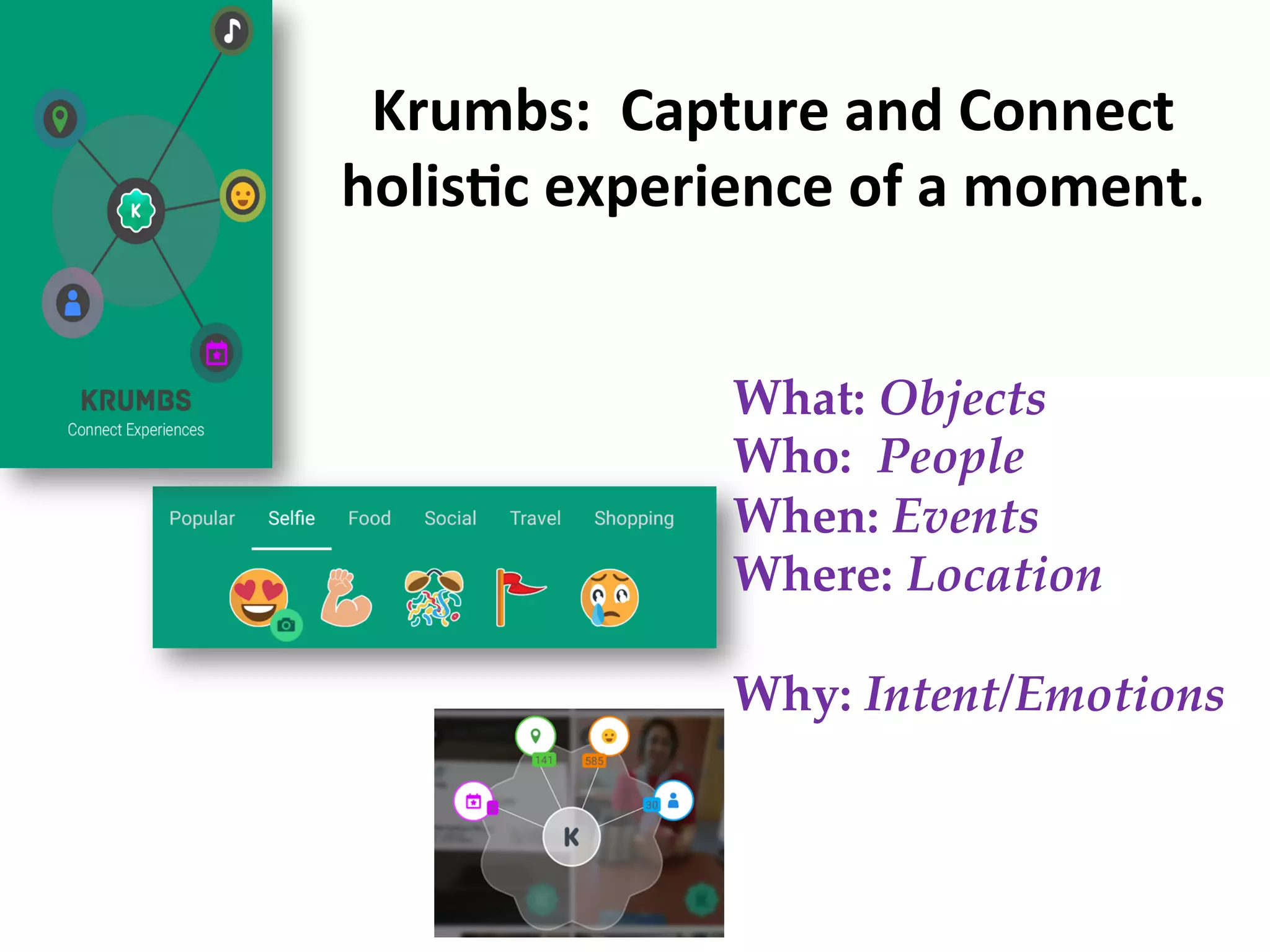
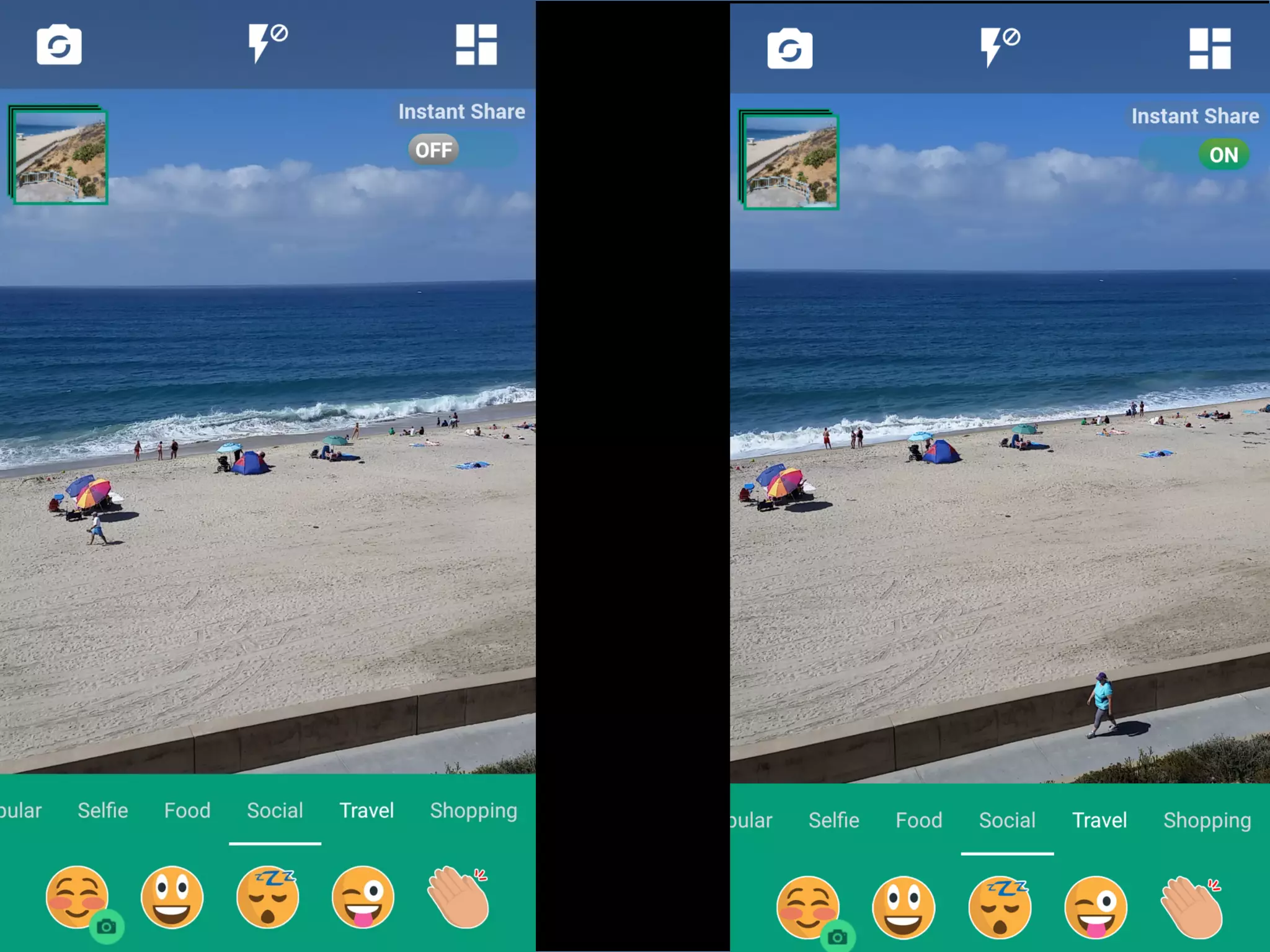
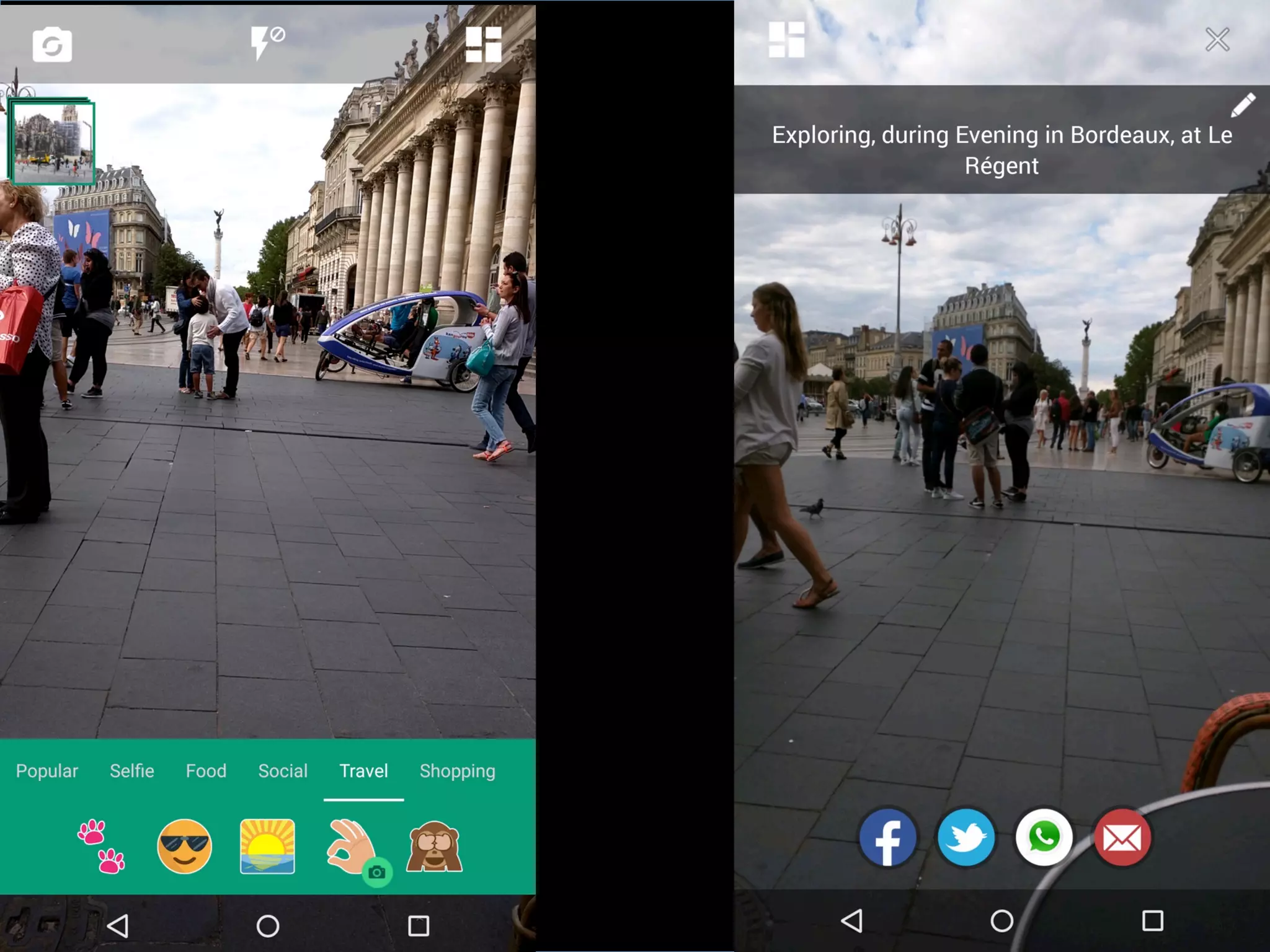
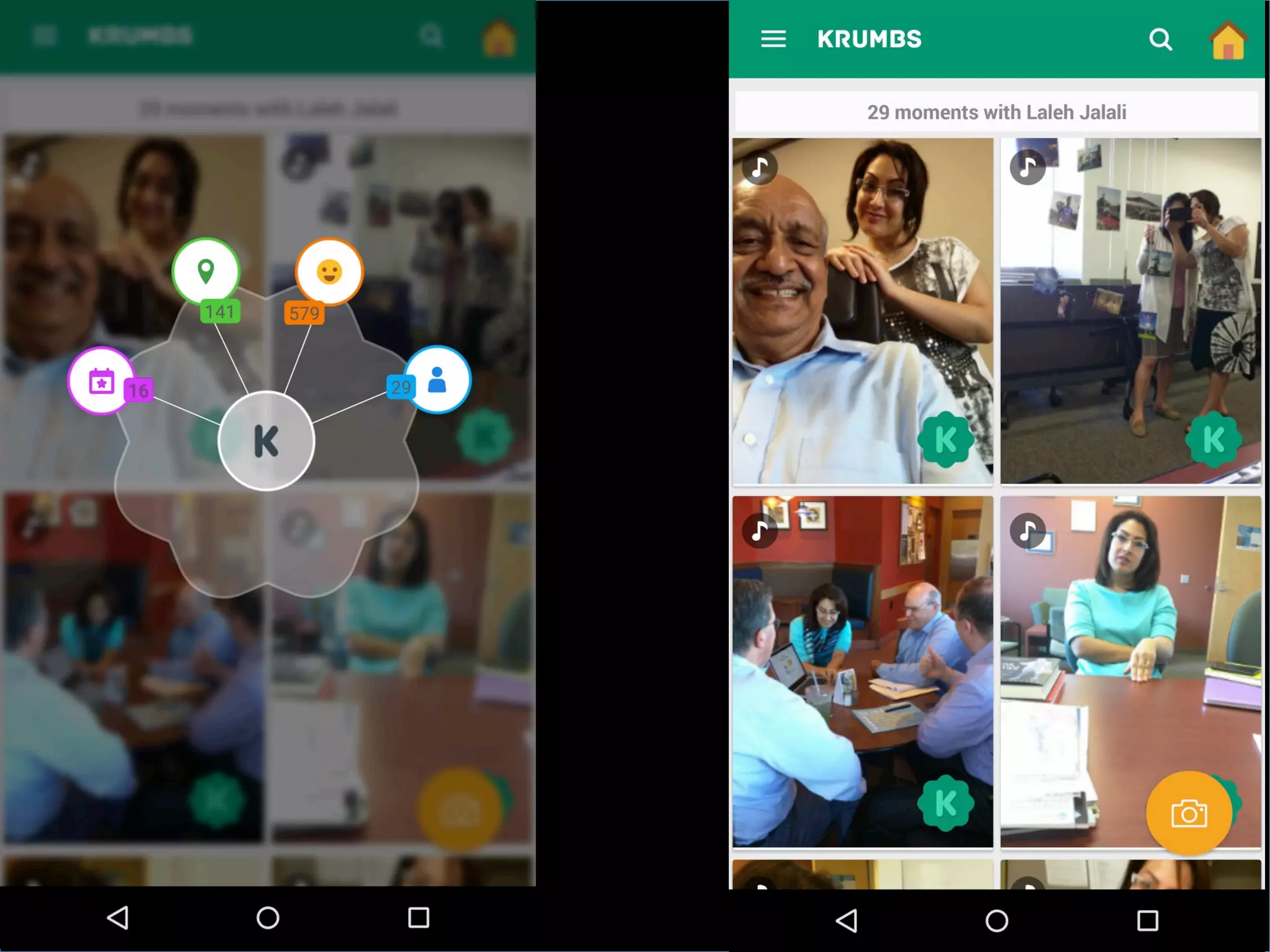
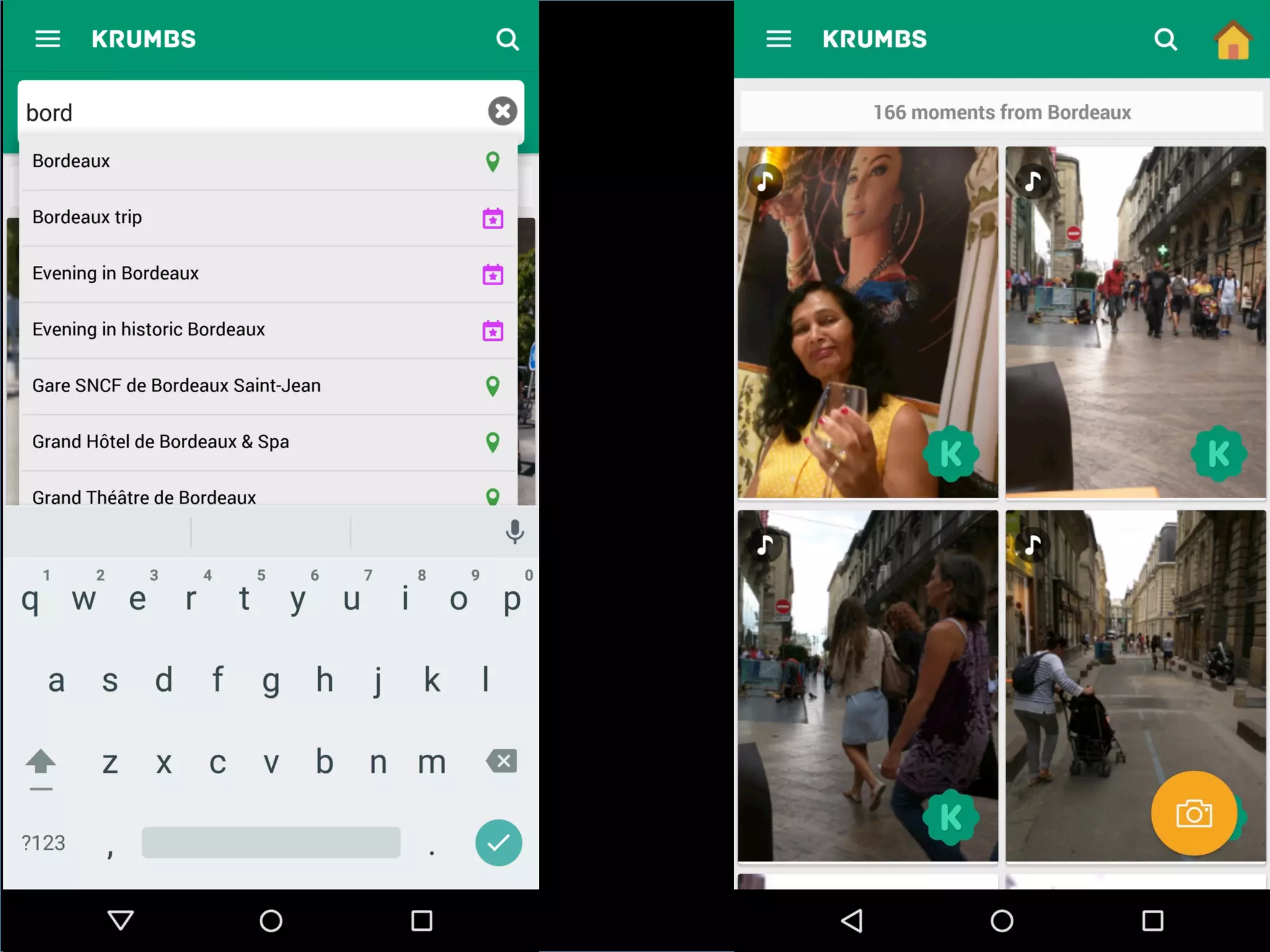
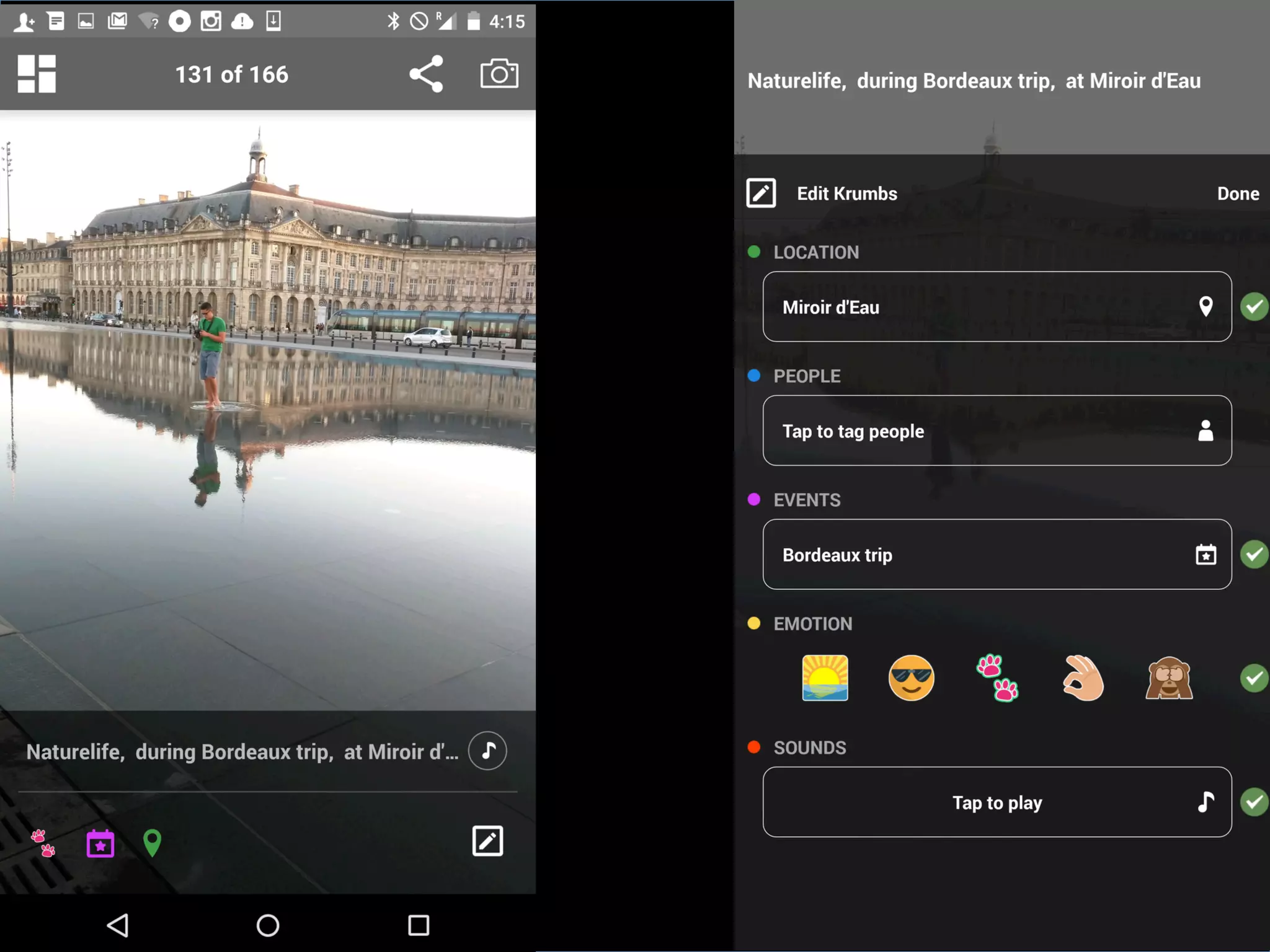
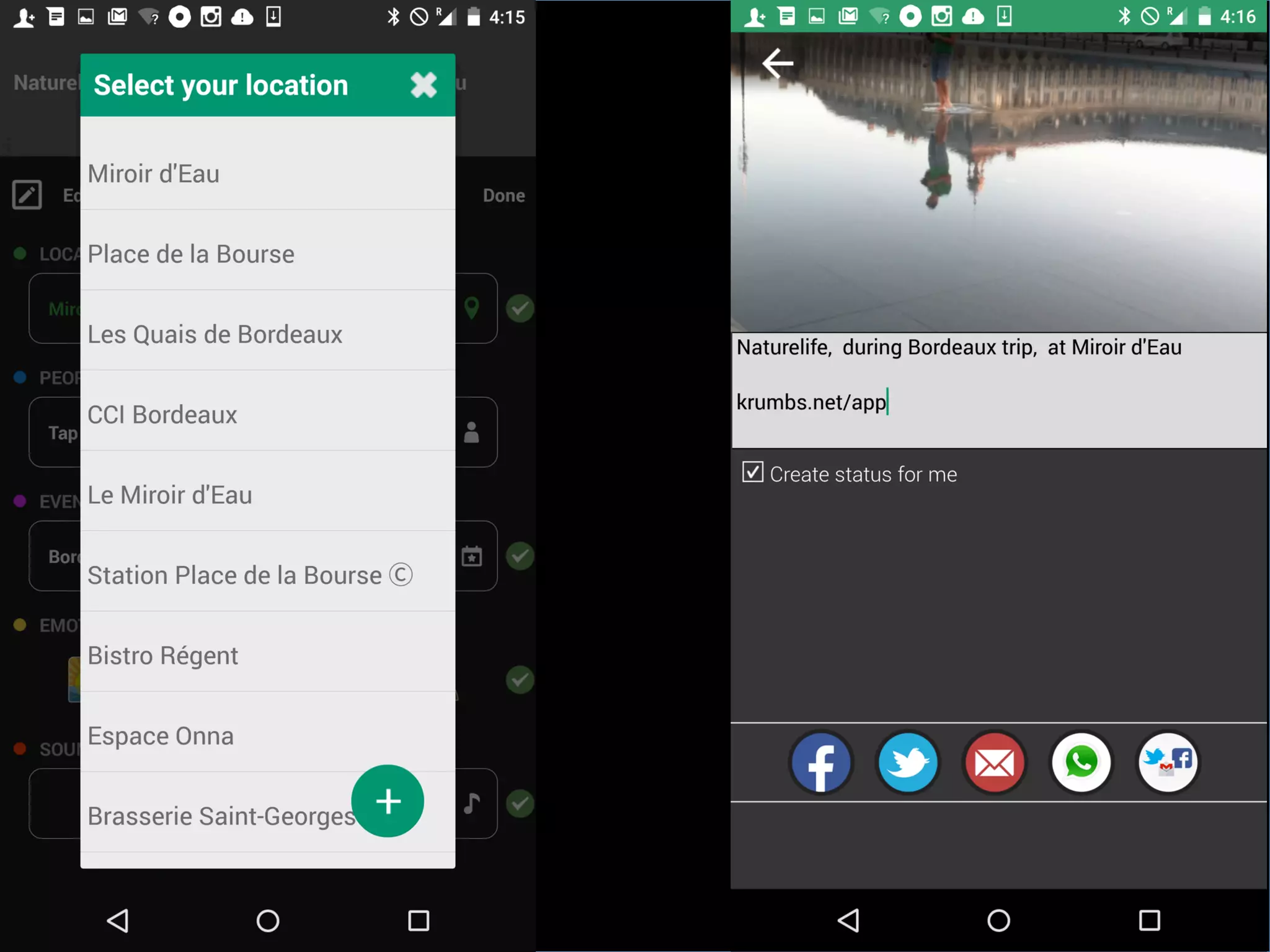
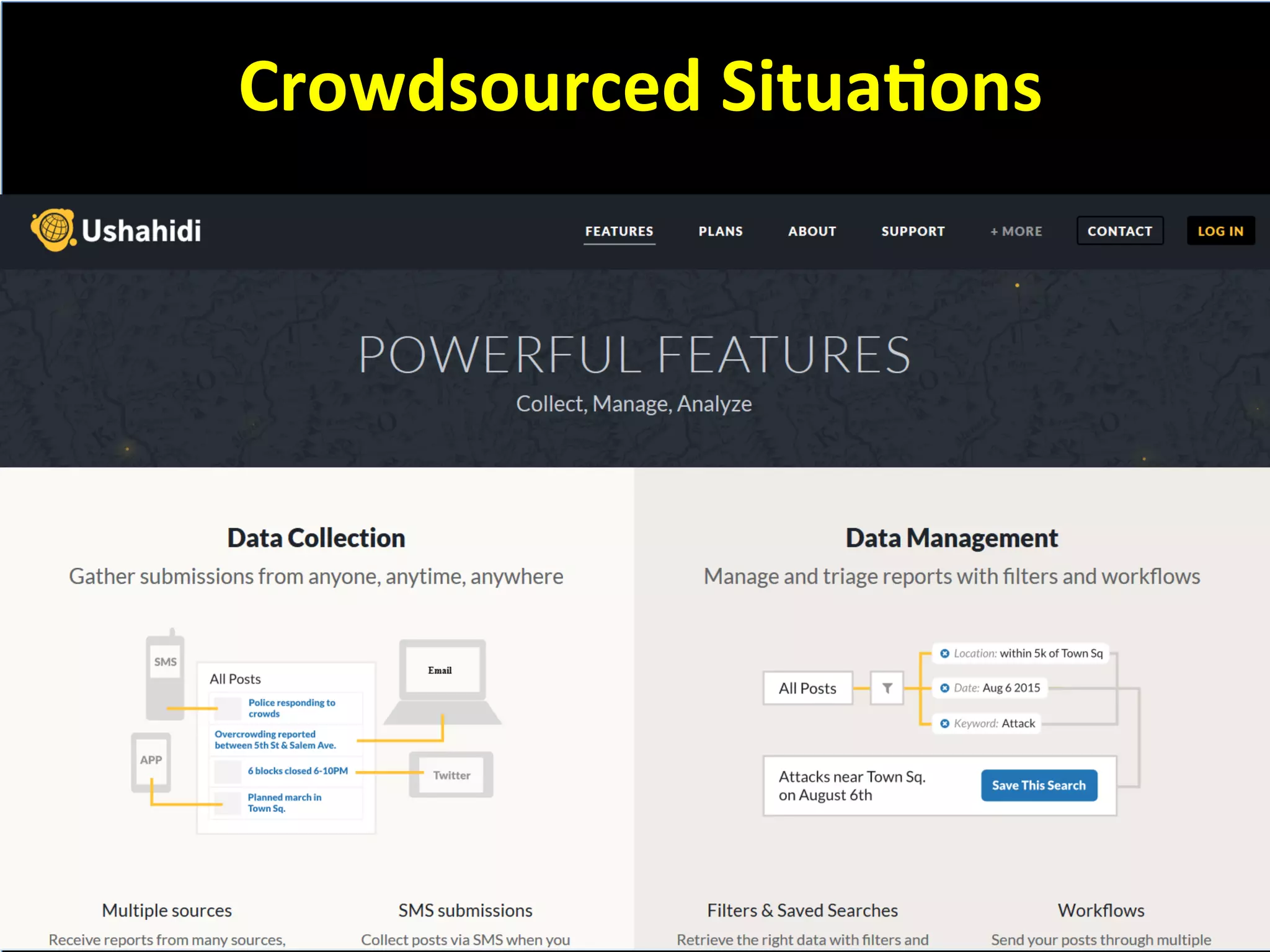
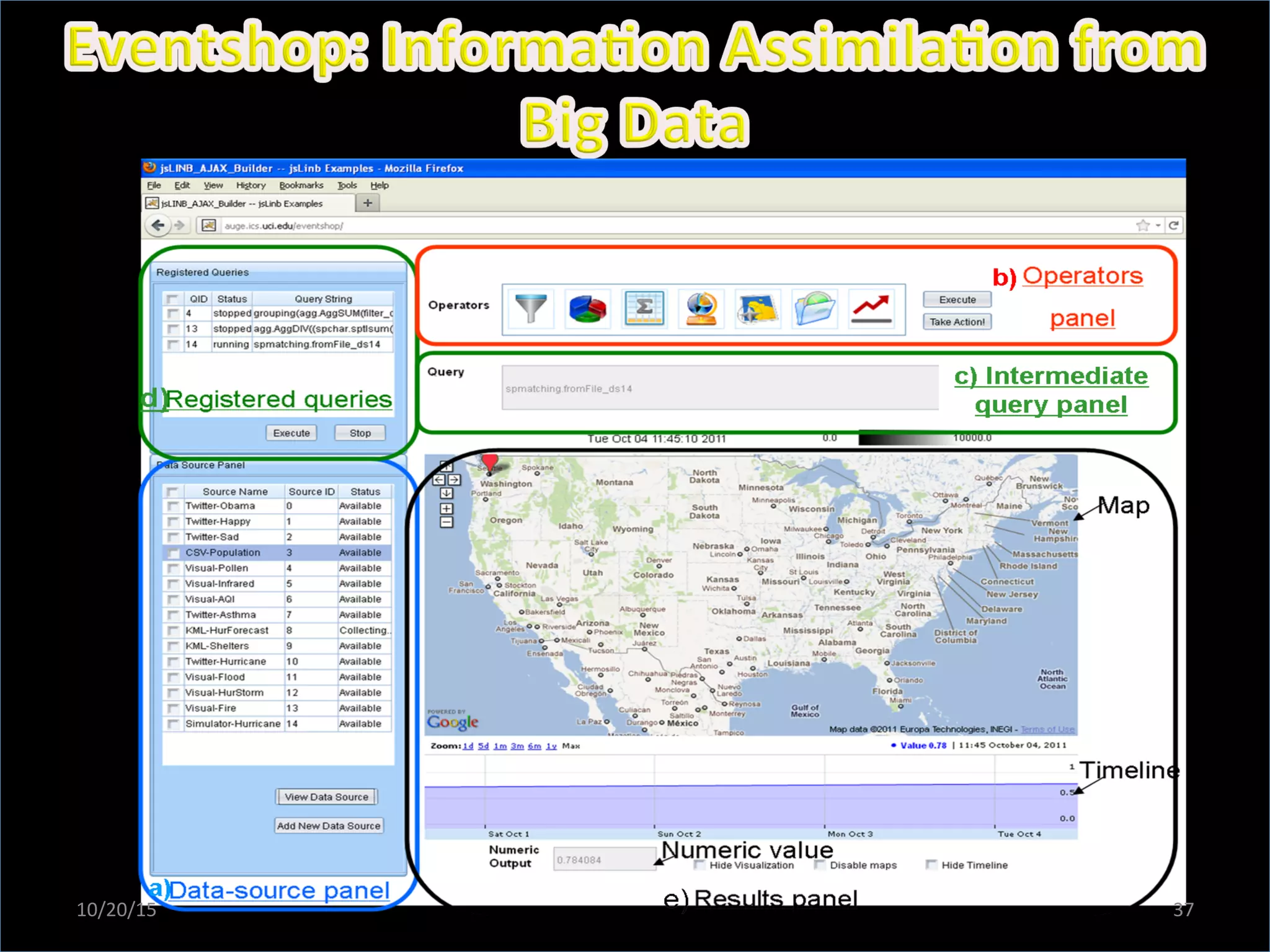
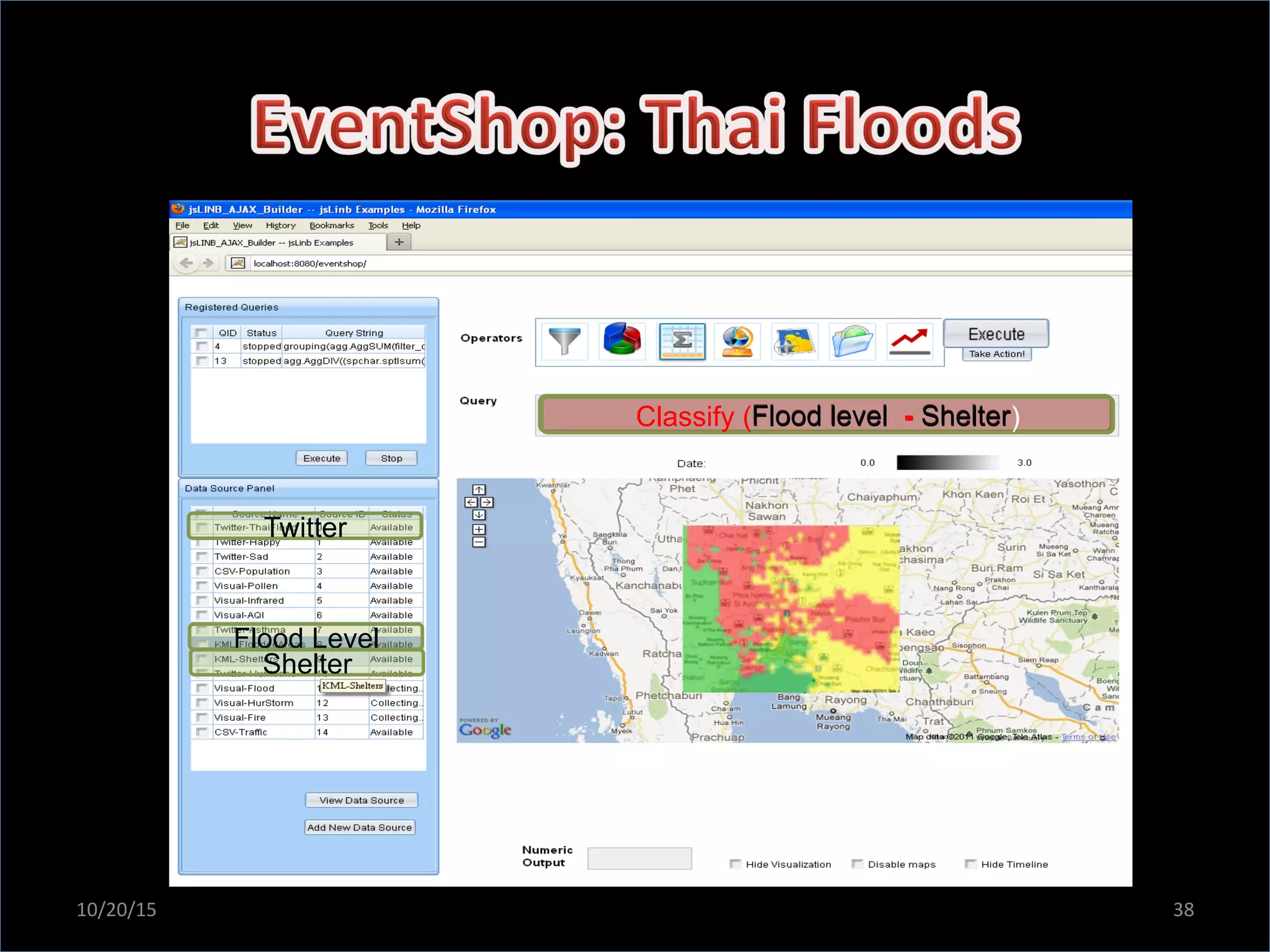
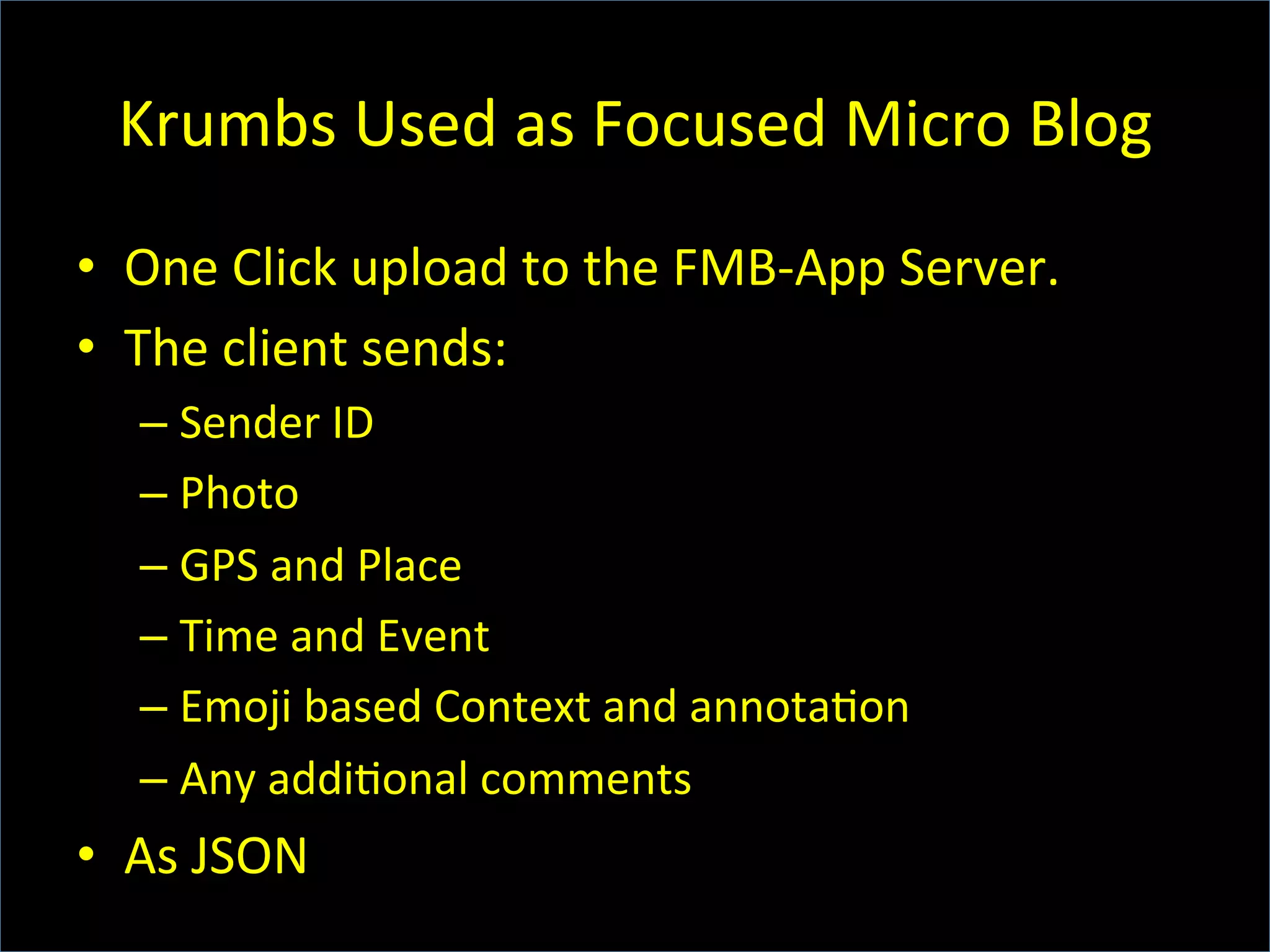
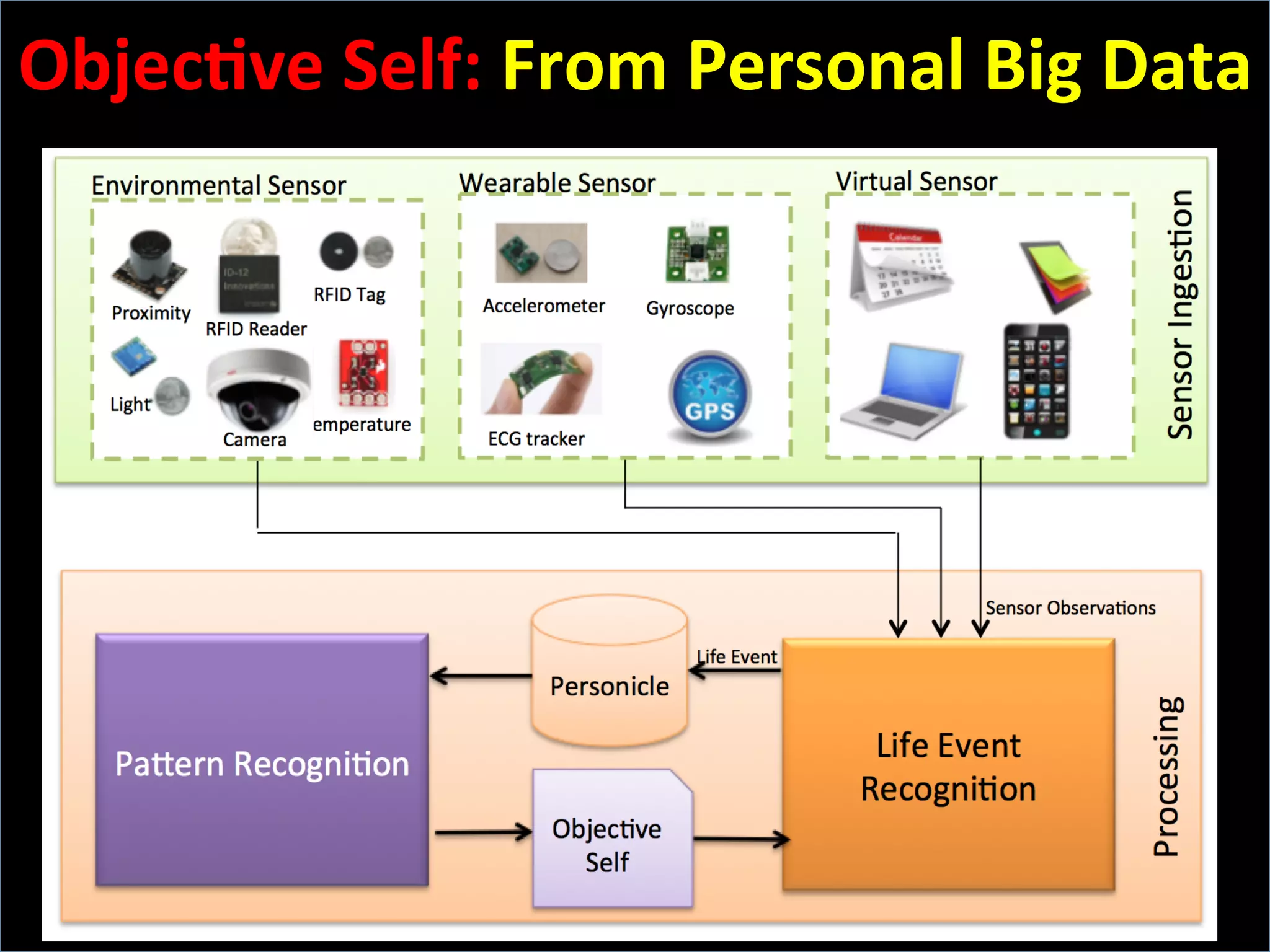
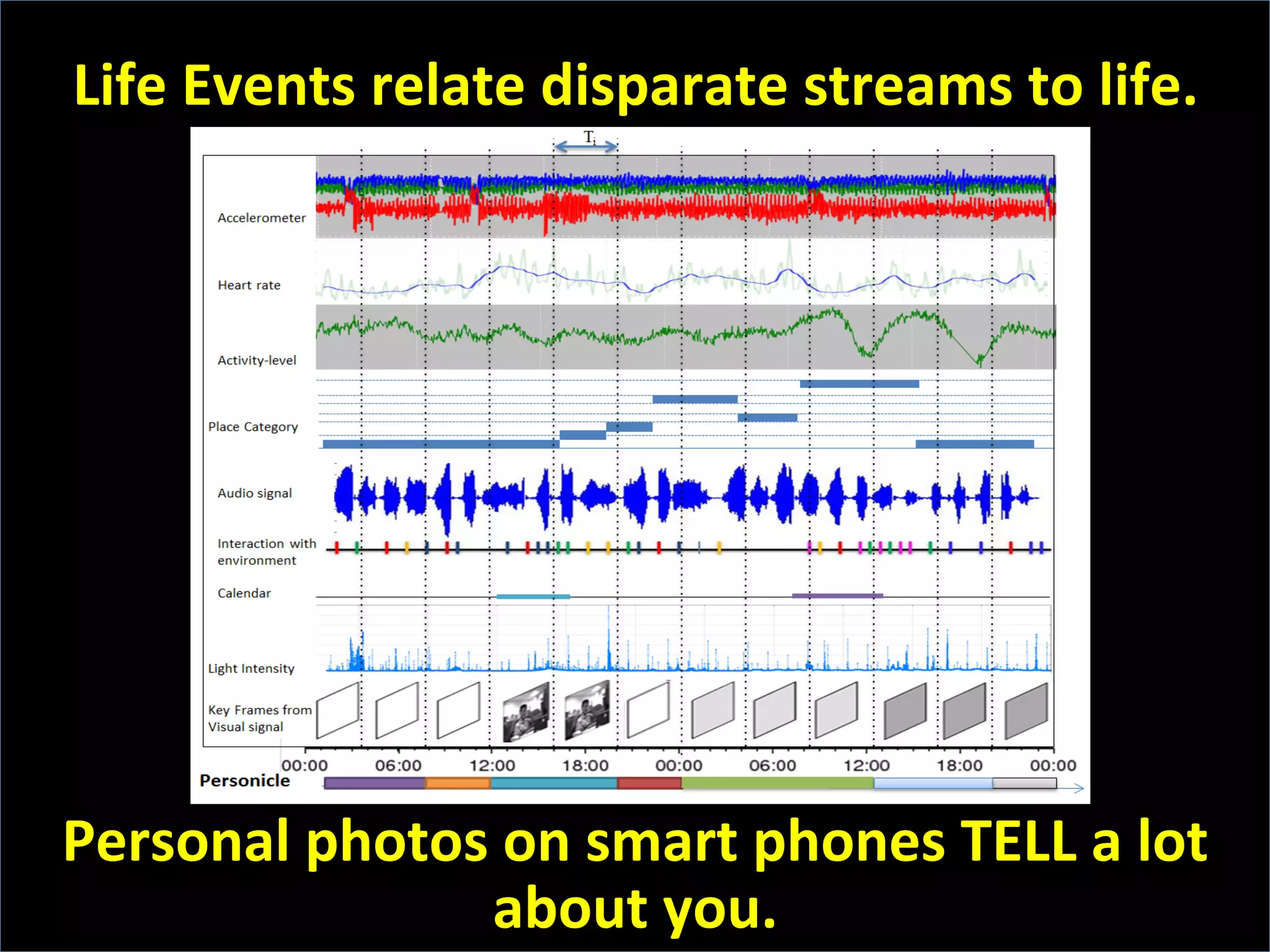
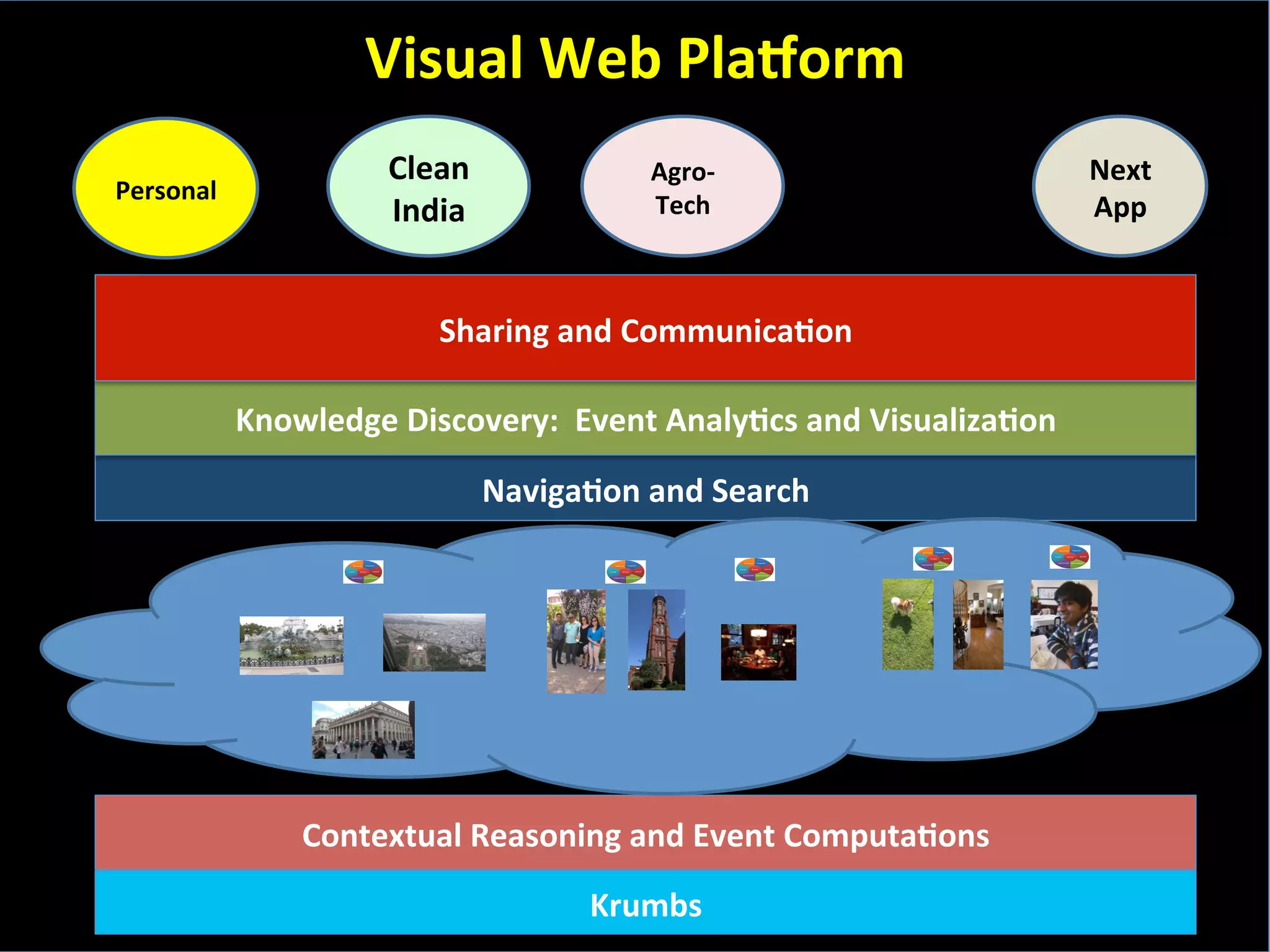
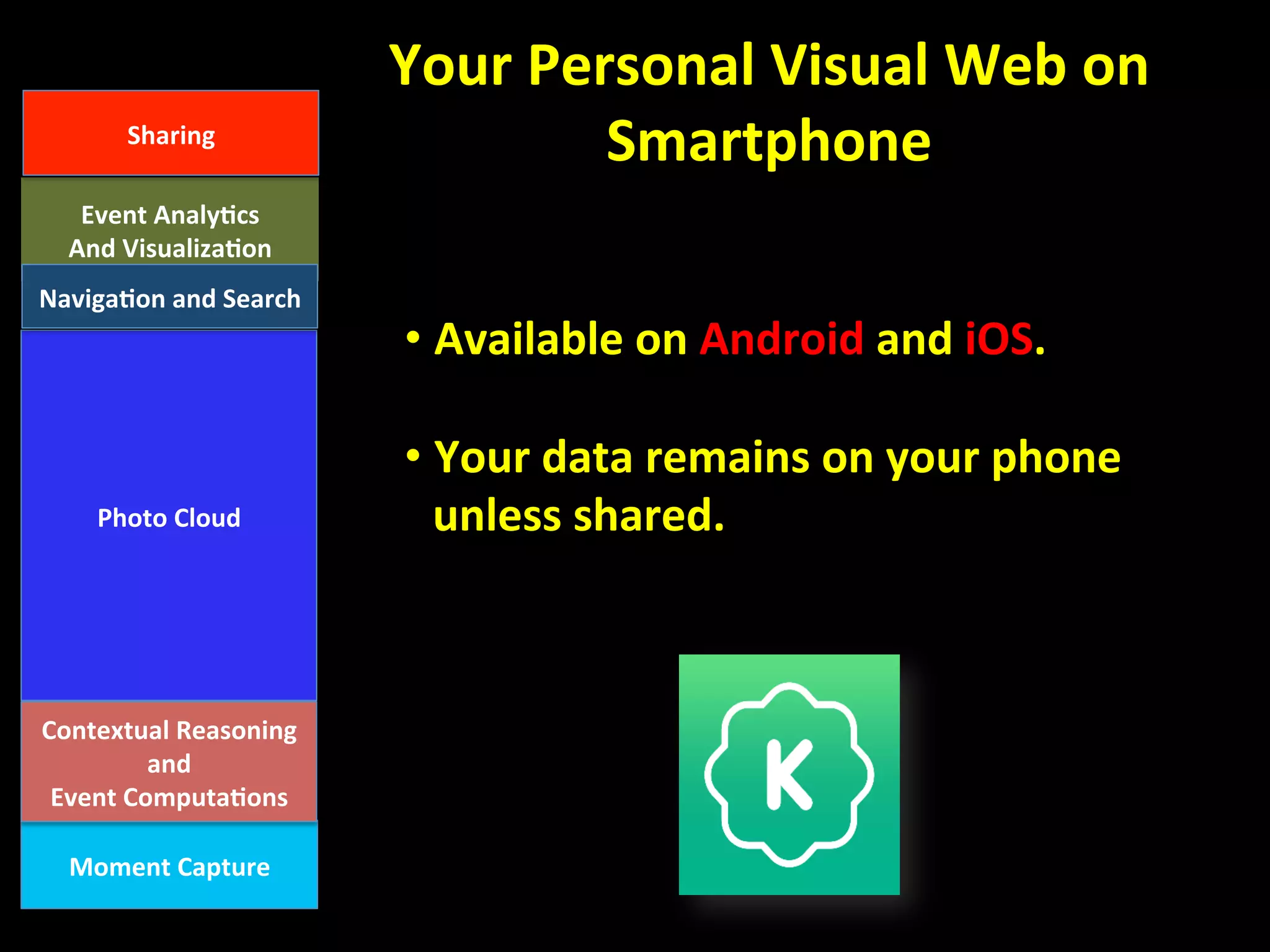
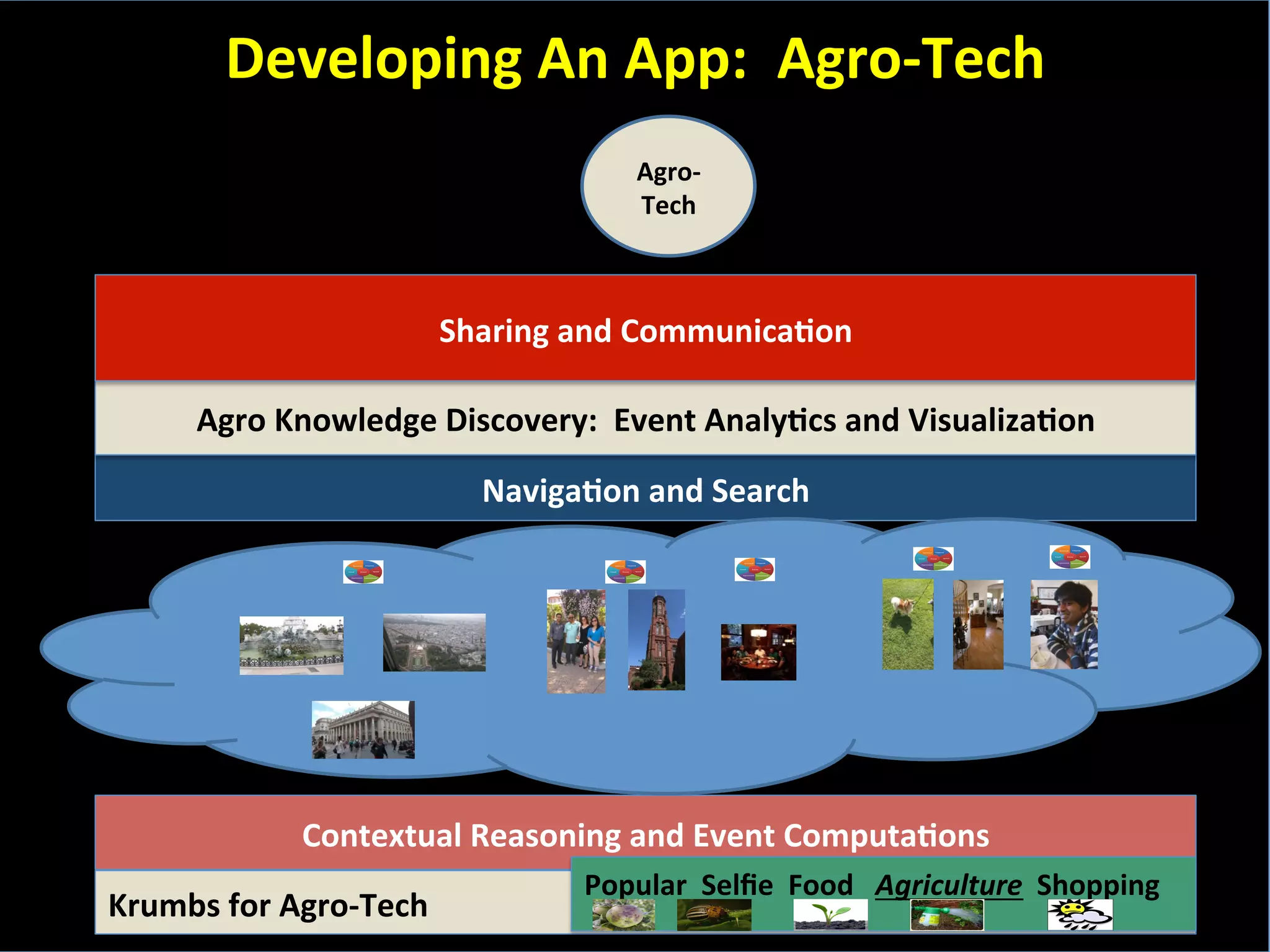
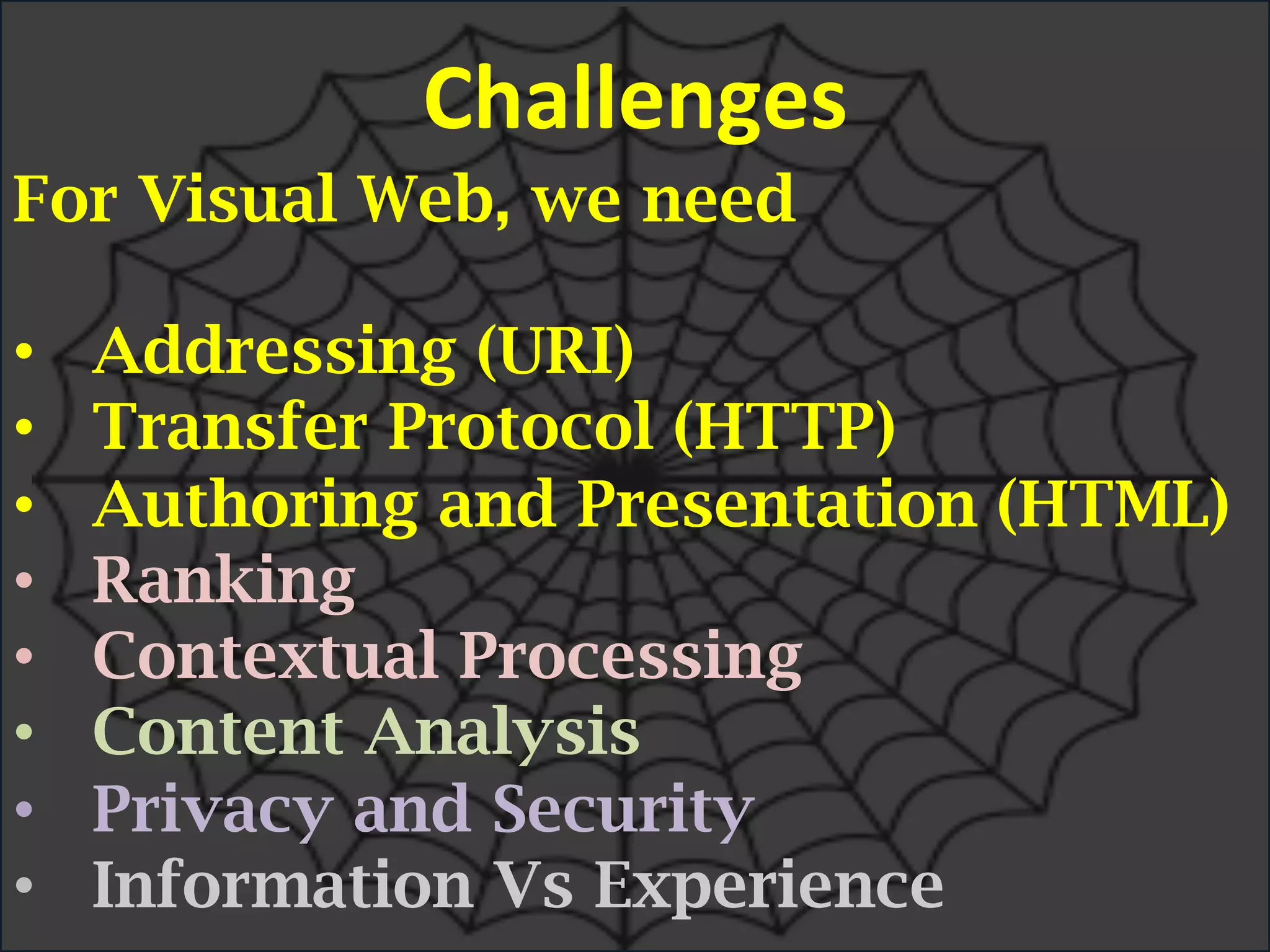
This document discusses the evolving role of photos from memories to sources of information. It argues that photos, when connected to associated metadata and context, can form the basis of a "visual web" that allows for more natural searching and knowledge sharing compared to a text-based web. The author envisions apps that can automatically extract context from photos using sensors and tags to organize all photos into a personal visual web for each user and enable new types of crowdsourced information through "focused microblogging" with photos.