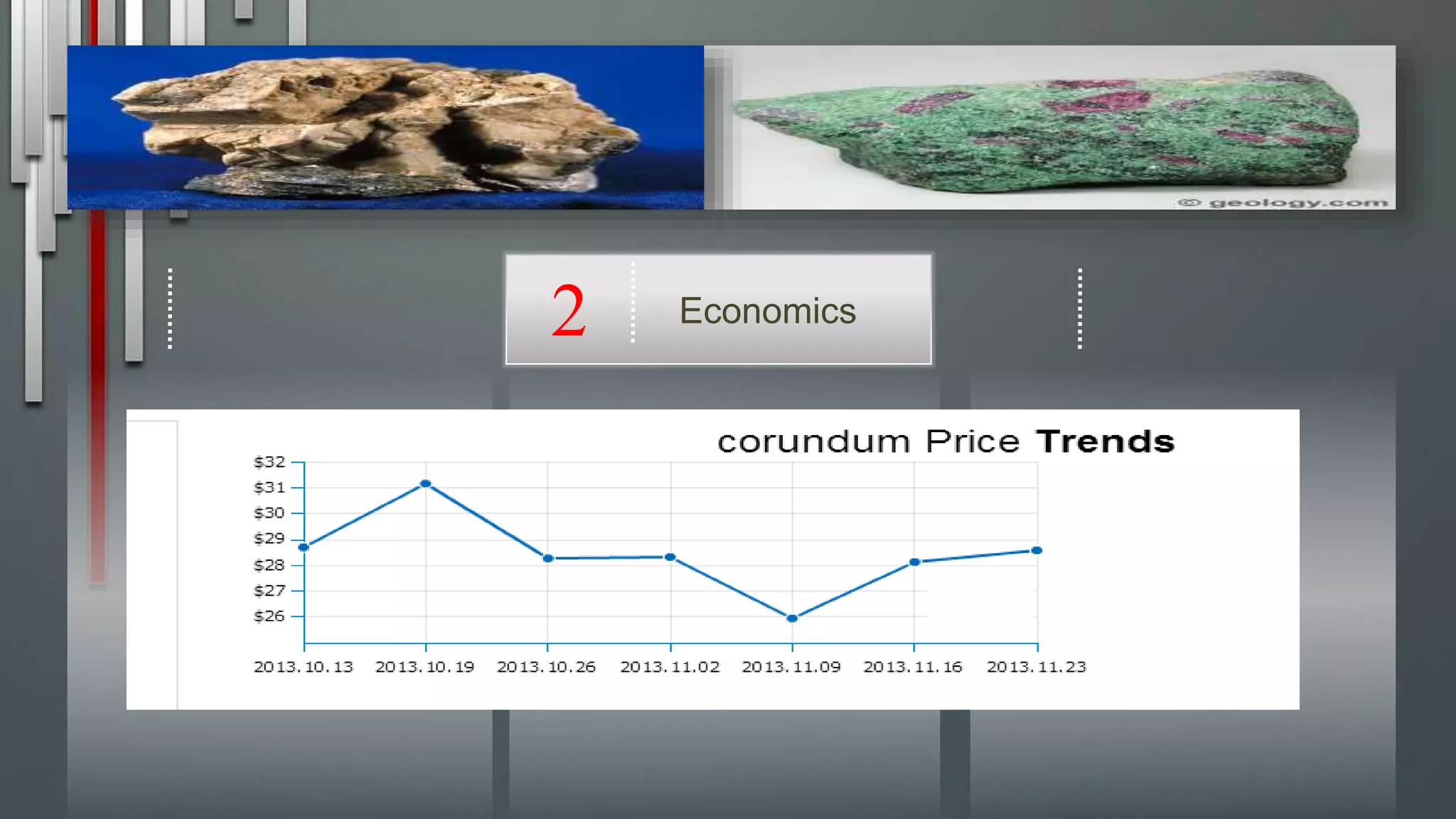
Corundum is a crystalline form of aluminum oxide that occurs naturally in various colors depending on impurity levels. It is the second hardest mineral after diamond. Synthetic corundum is produced from bauxite and is of high quality and cost competitive with natural sources. Rubies and sapphires, gemstone forms of corundum, are rarely mined from host rocks and are instead concentrated in stream deposits through weathering. Corundum is used for both its hardness as an abrasive and when clear, as a gemstone.