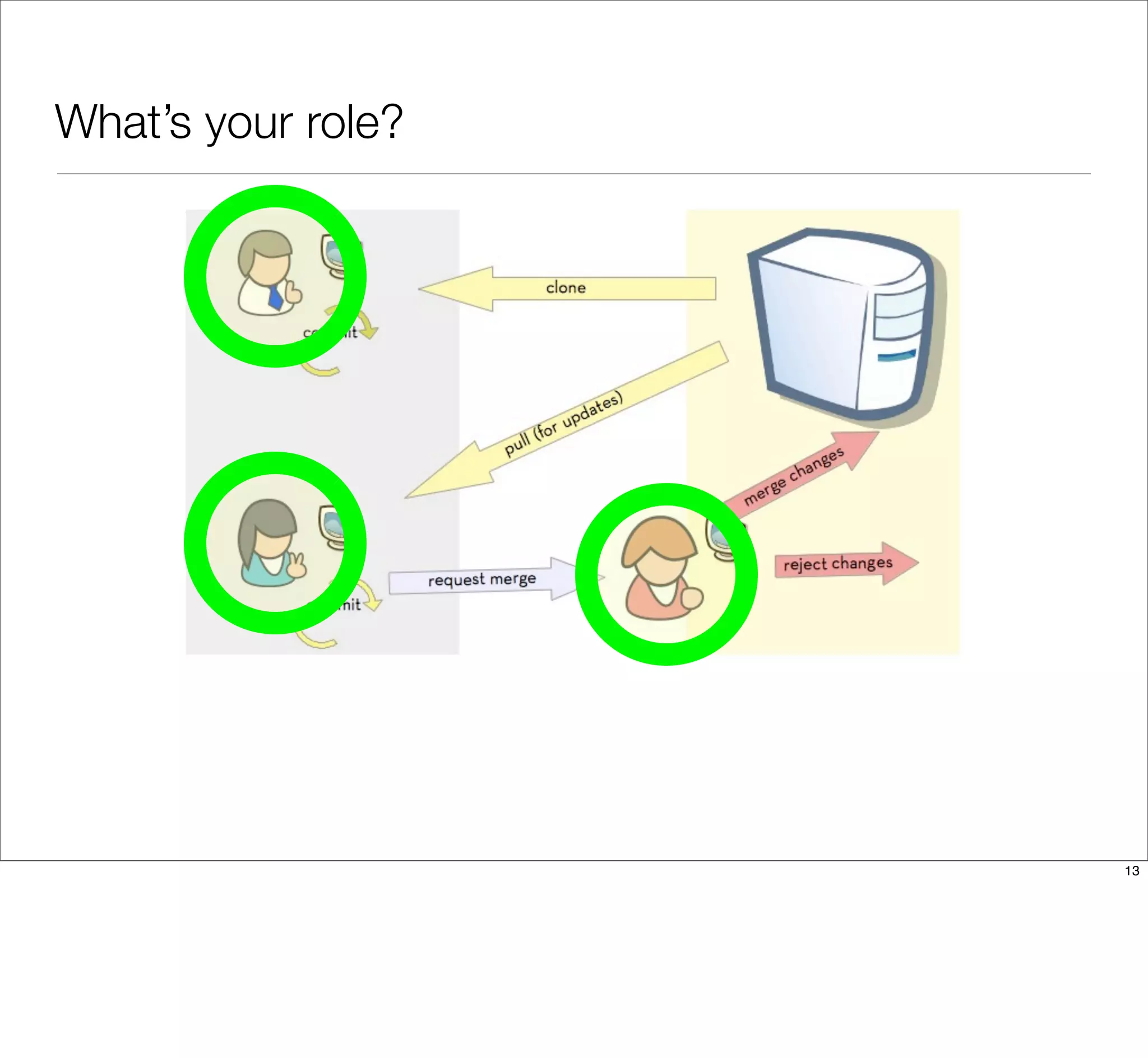
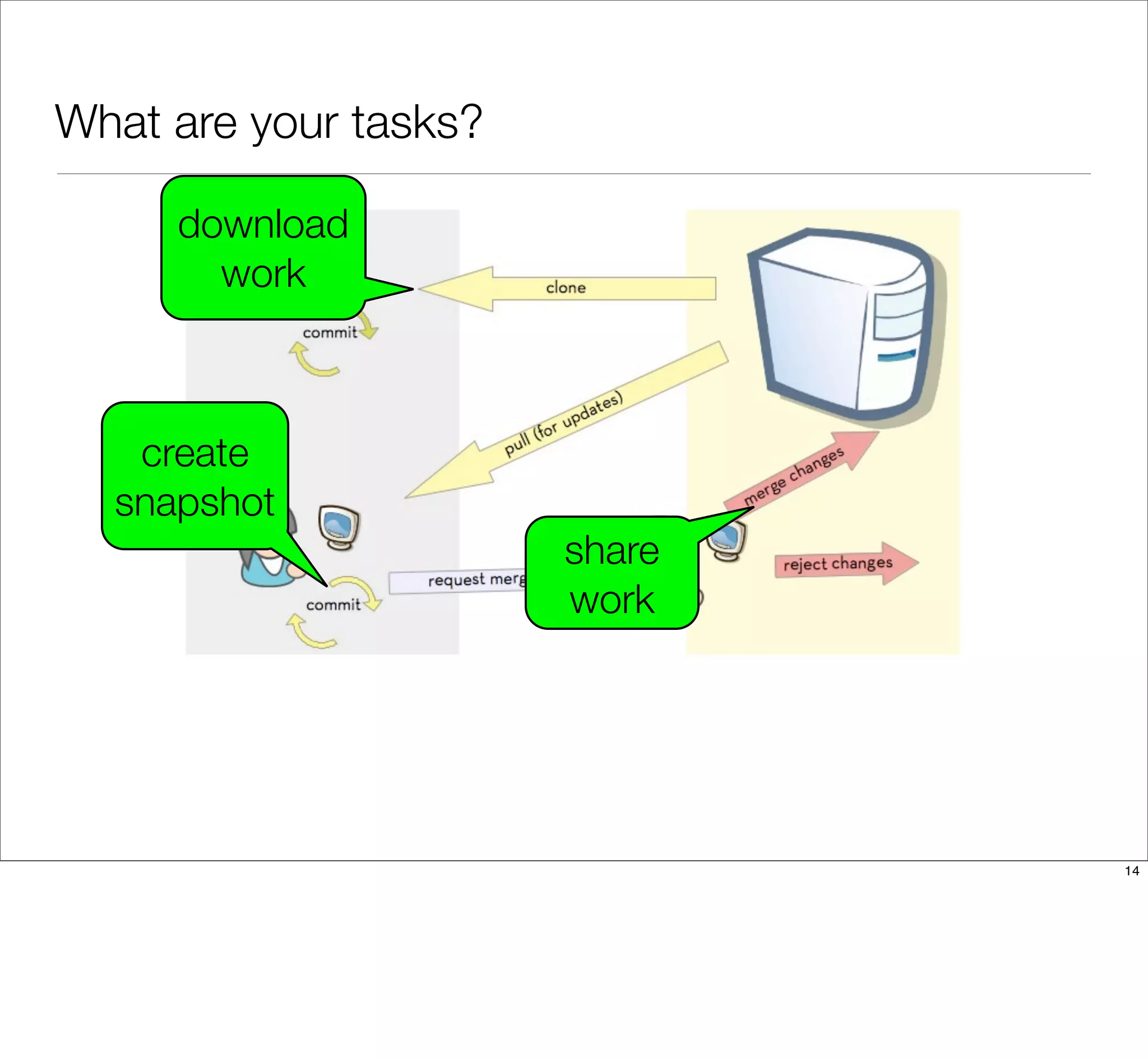
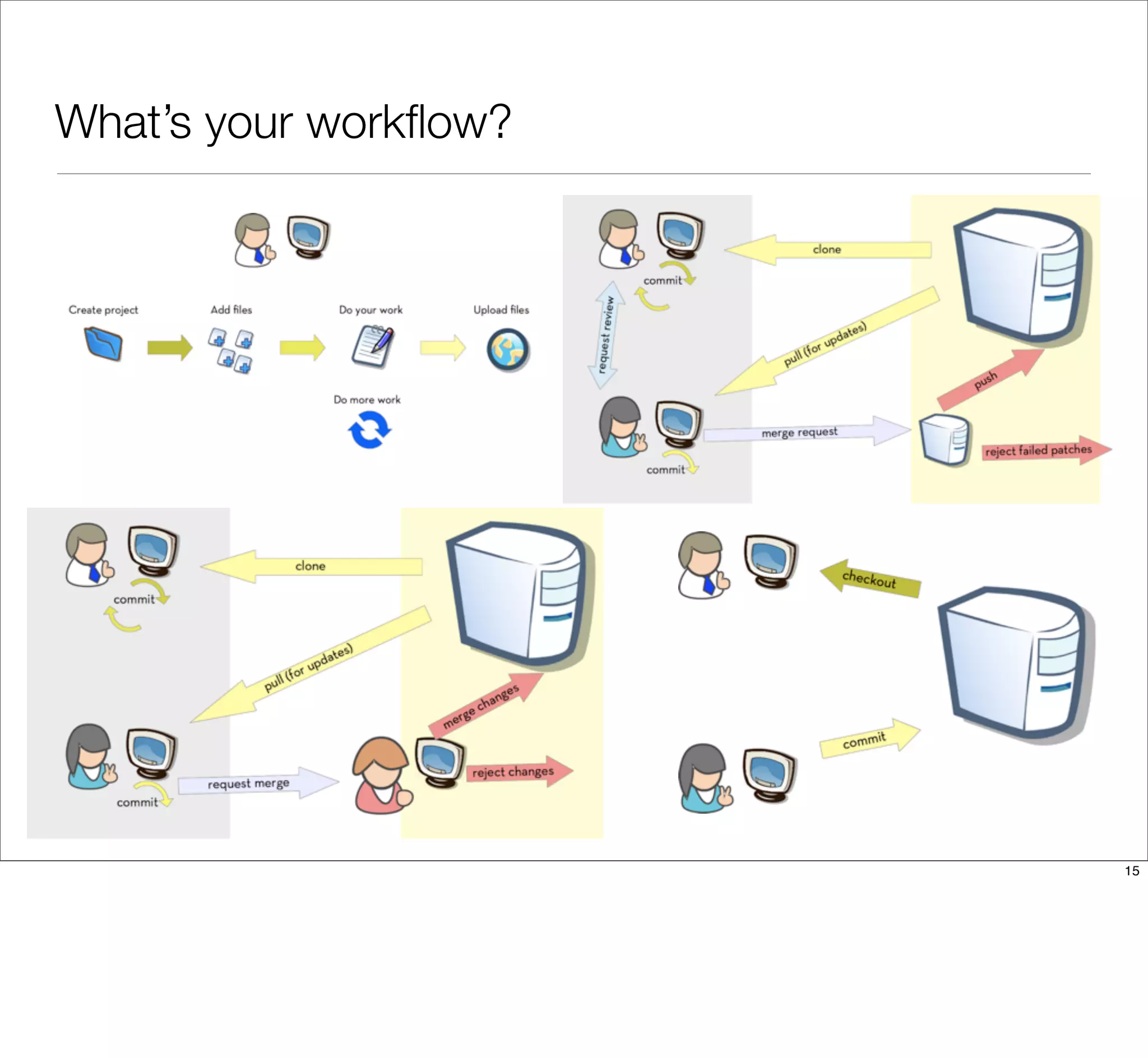
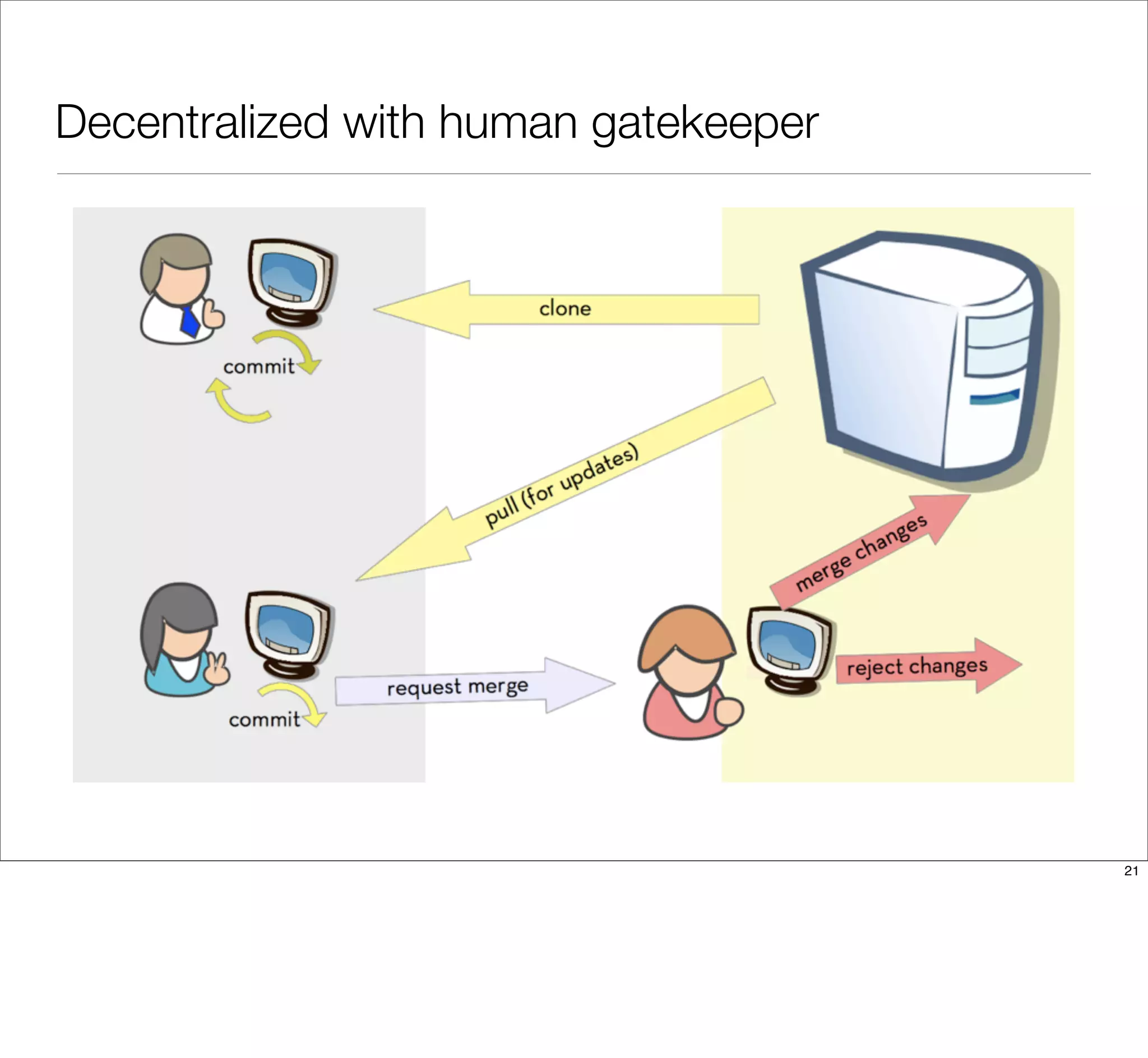
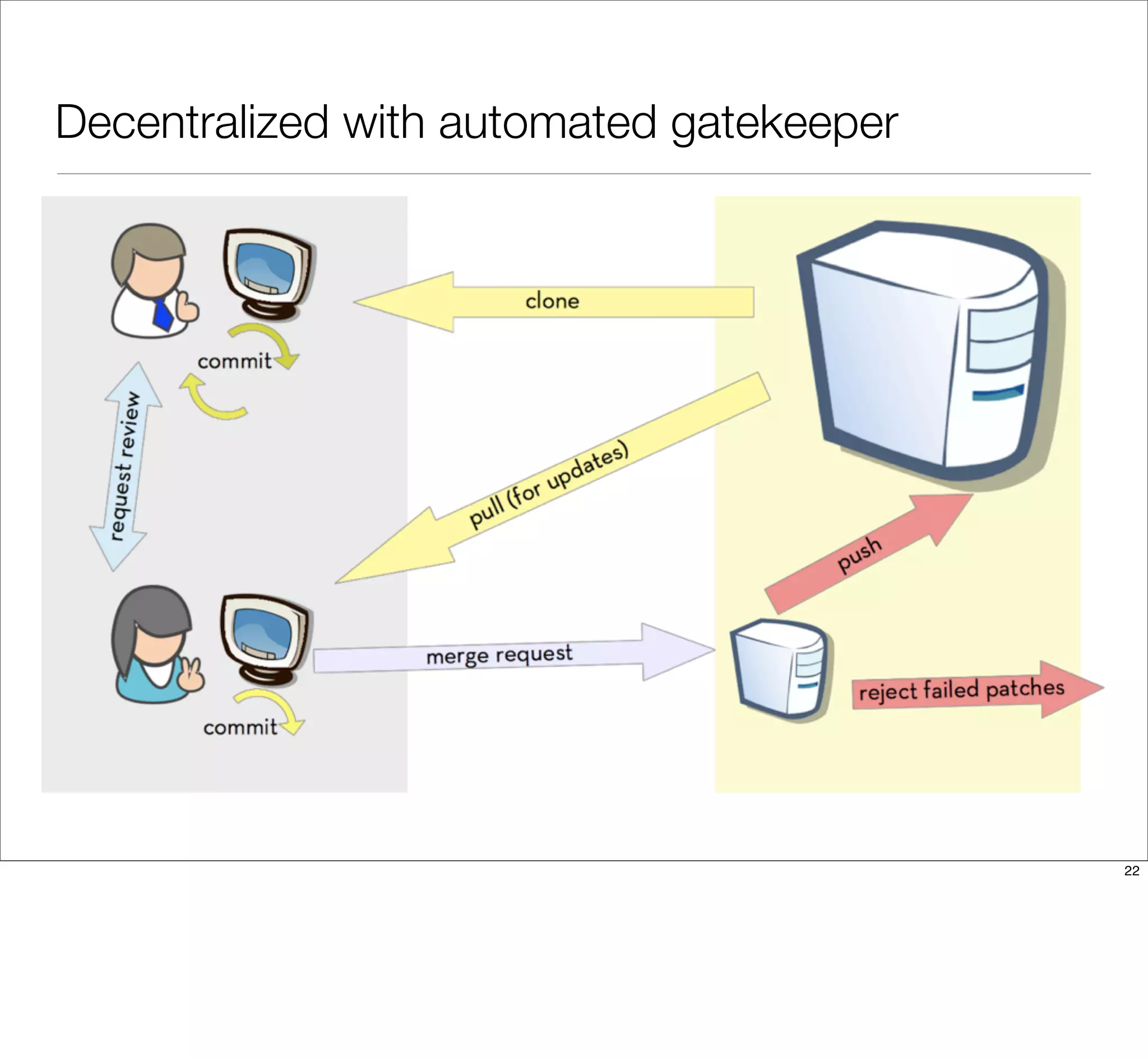
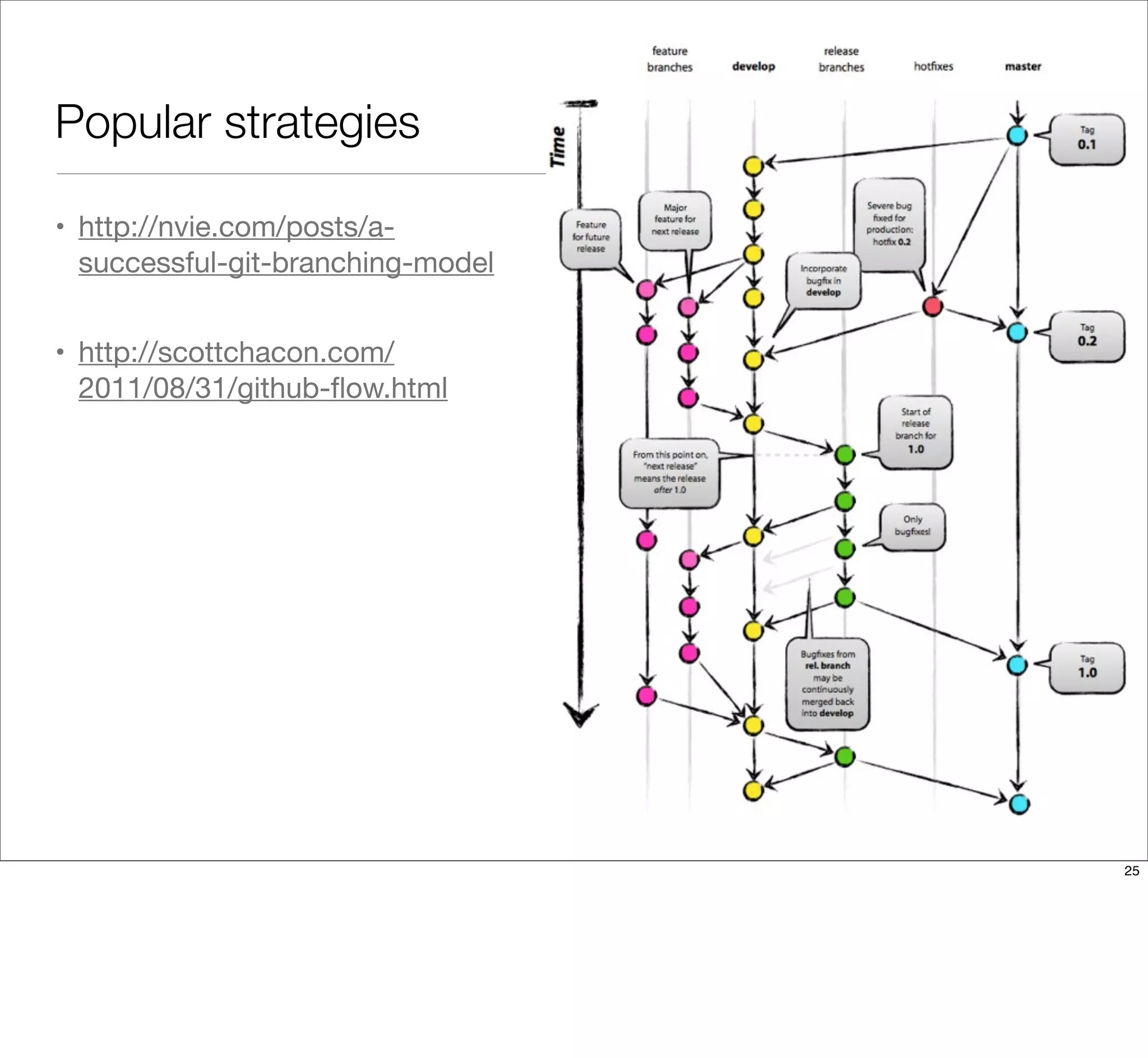
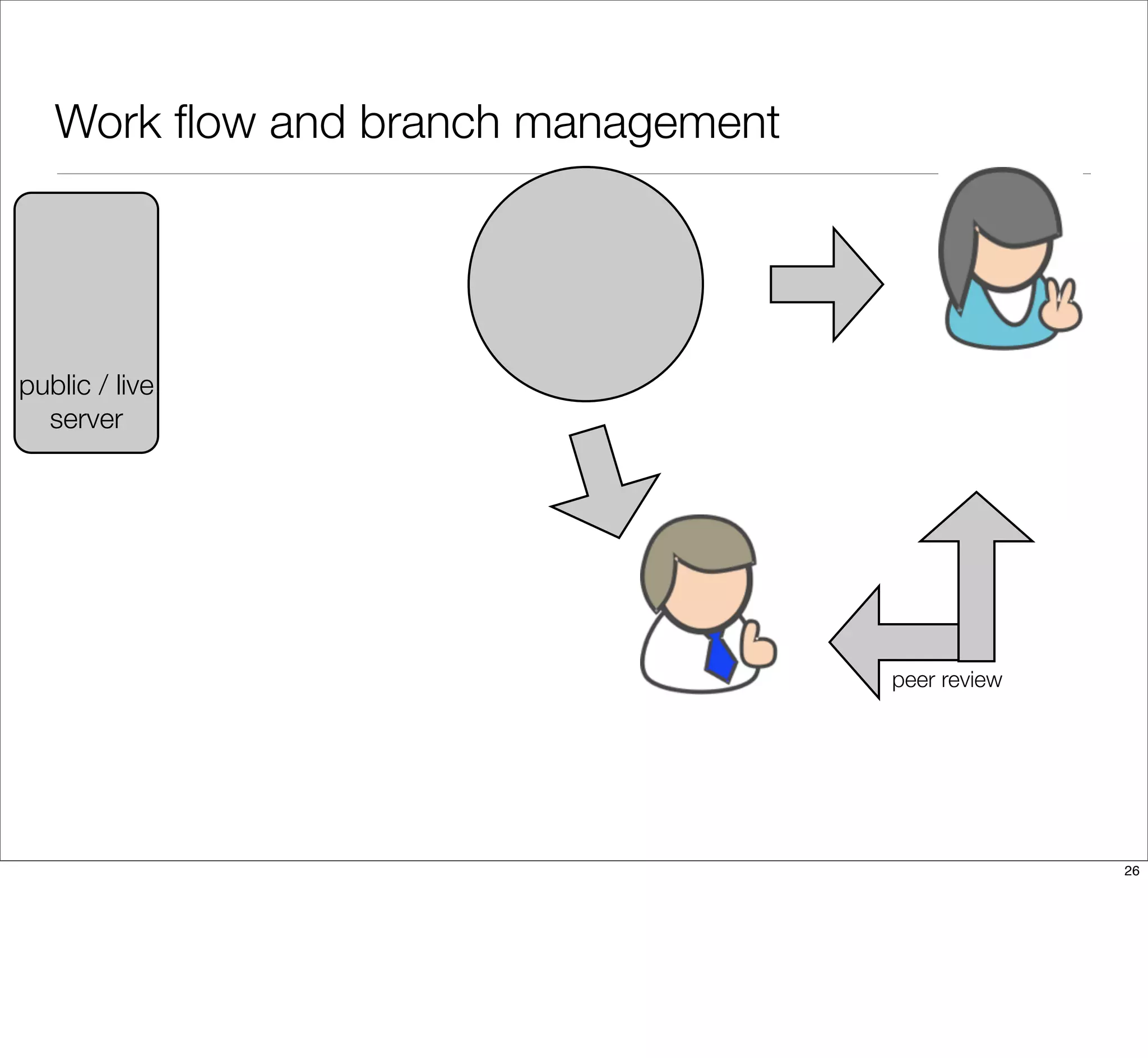
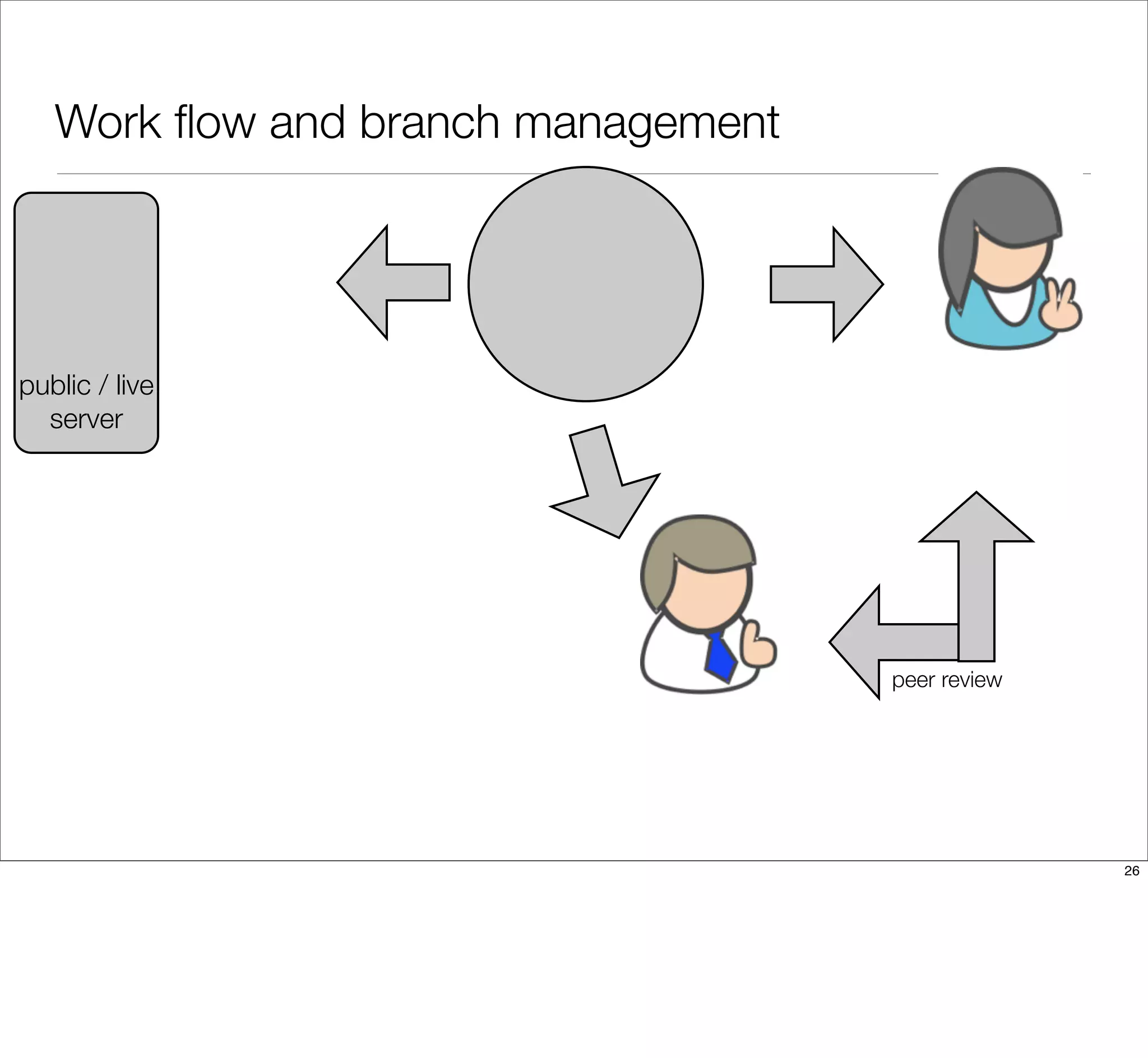
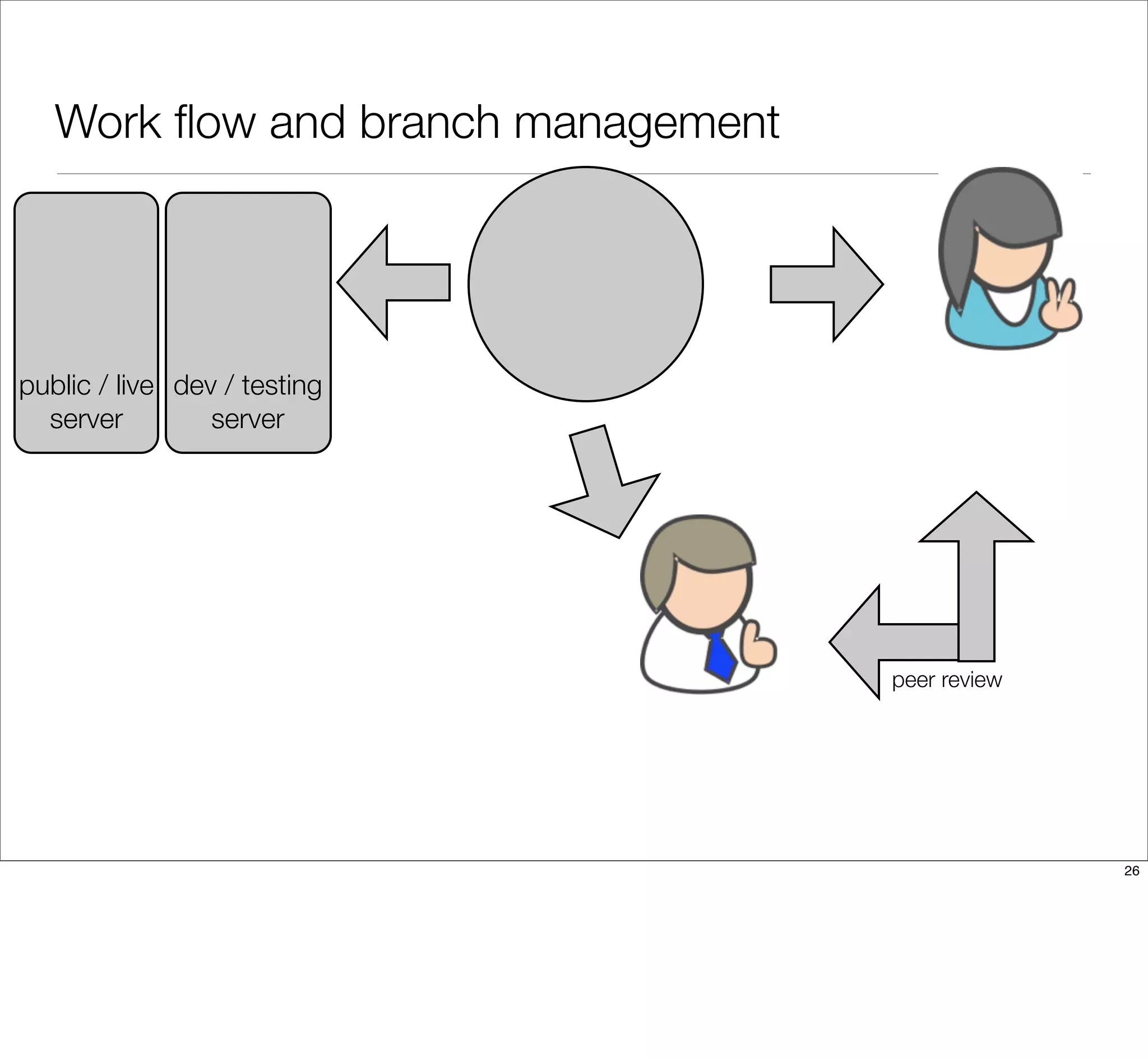
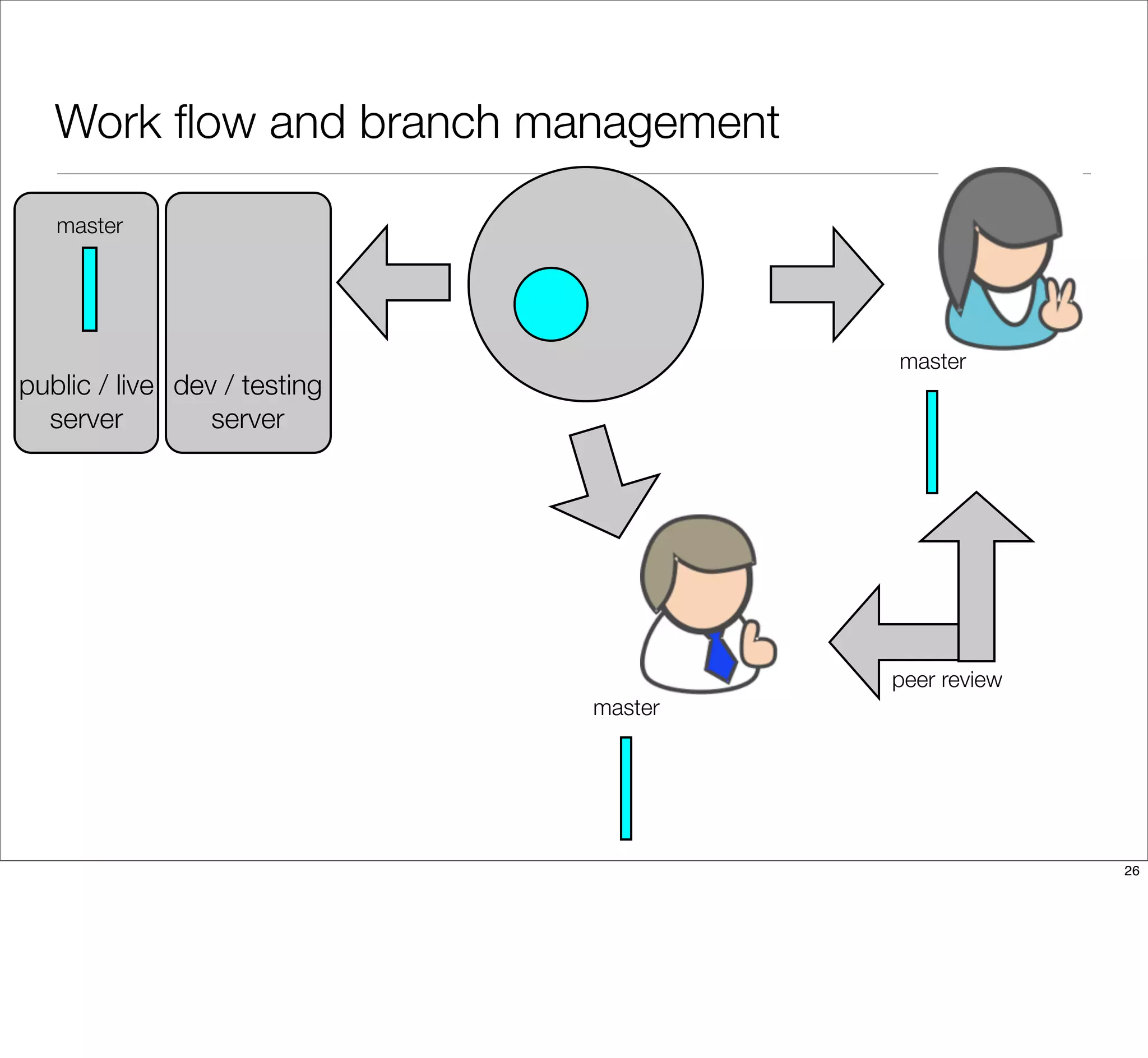
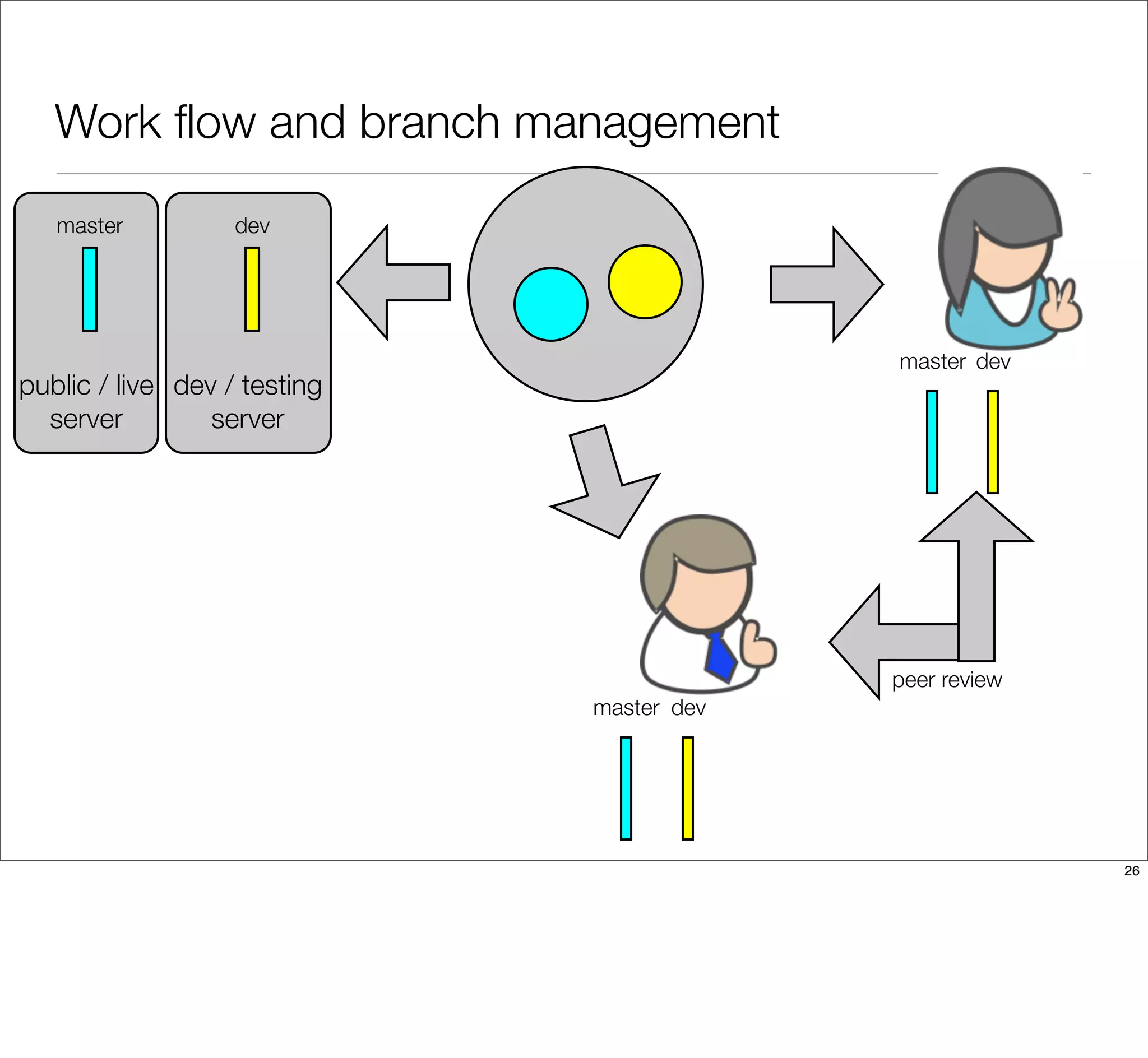
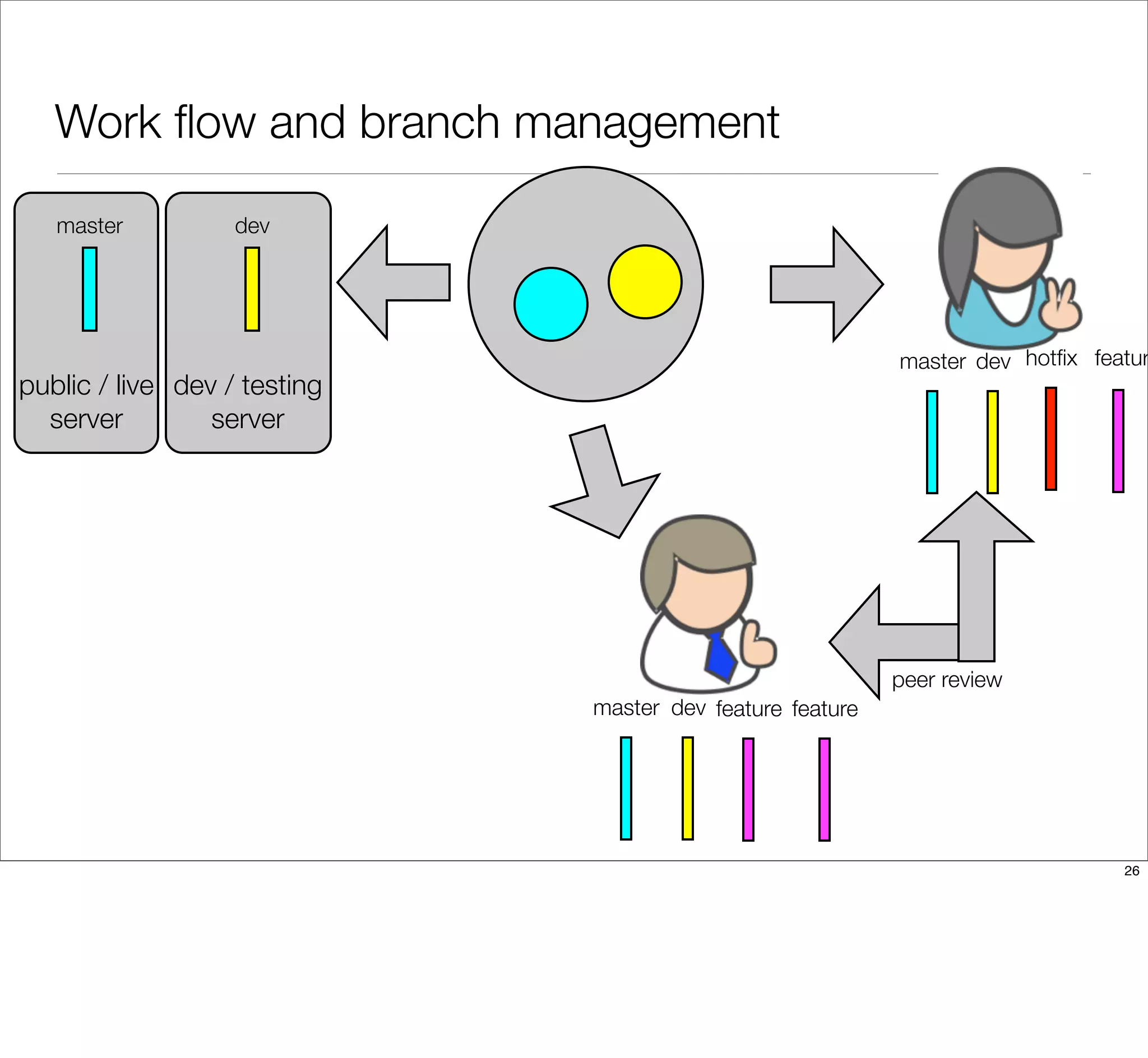
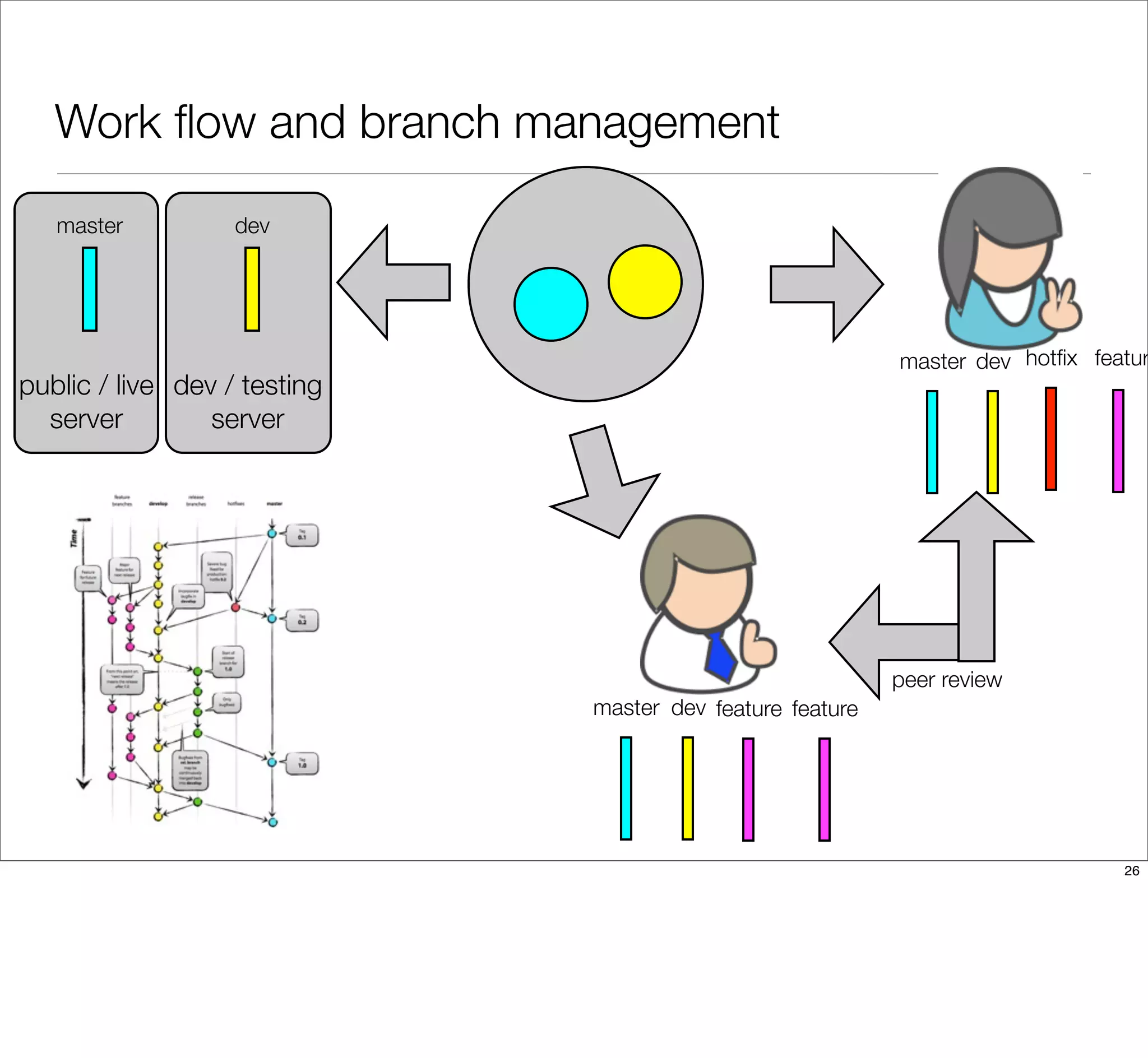
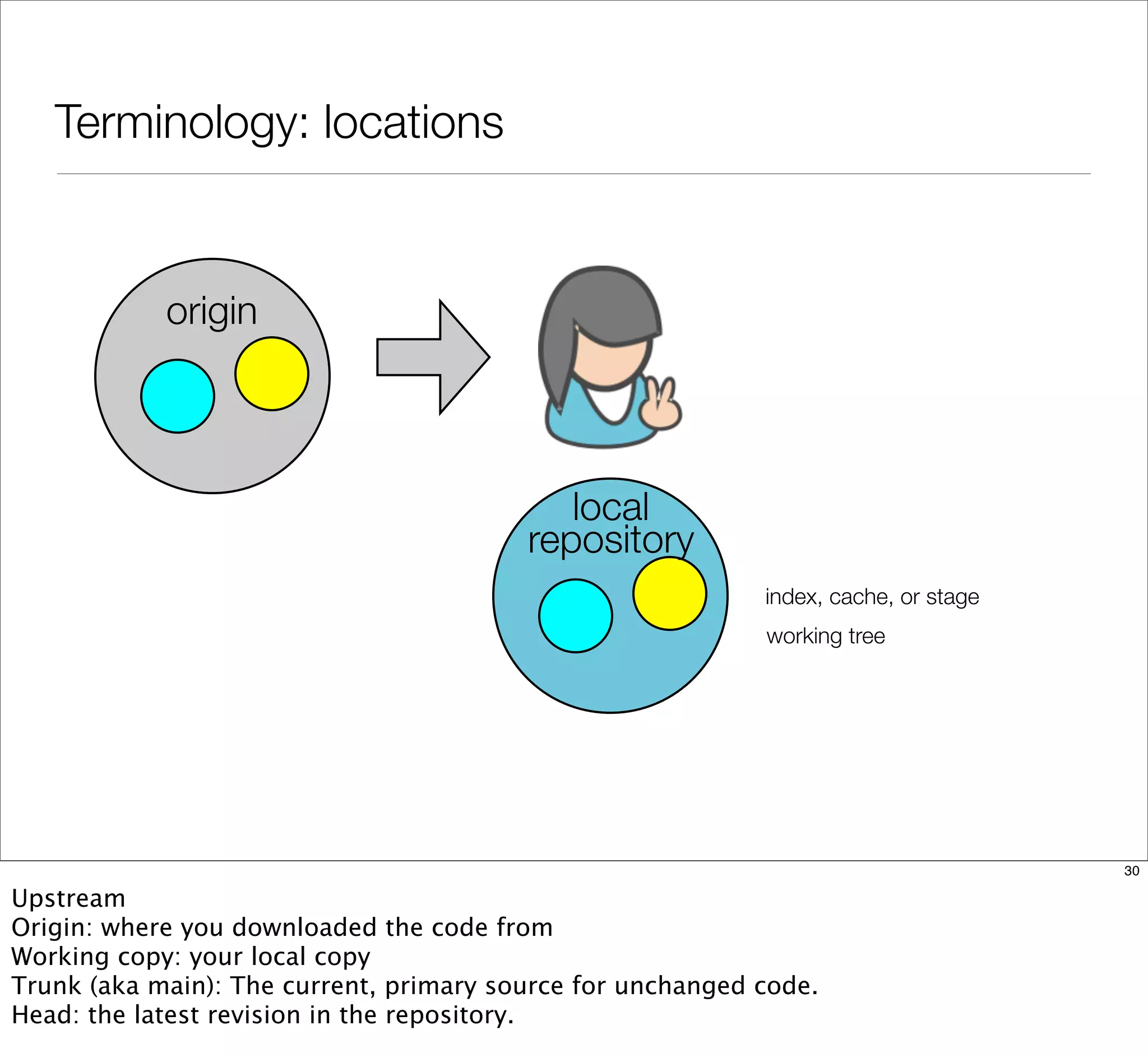
The document discusses the challenges of learning Git, emphasizing that traditional teaching methods often misalign with adult education principles. It encourages understanding the context of problems, collaborating with team members, and adopting workflows that include social dynamics. It also provides guidance on branch management and code workflow strategies in Git.