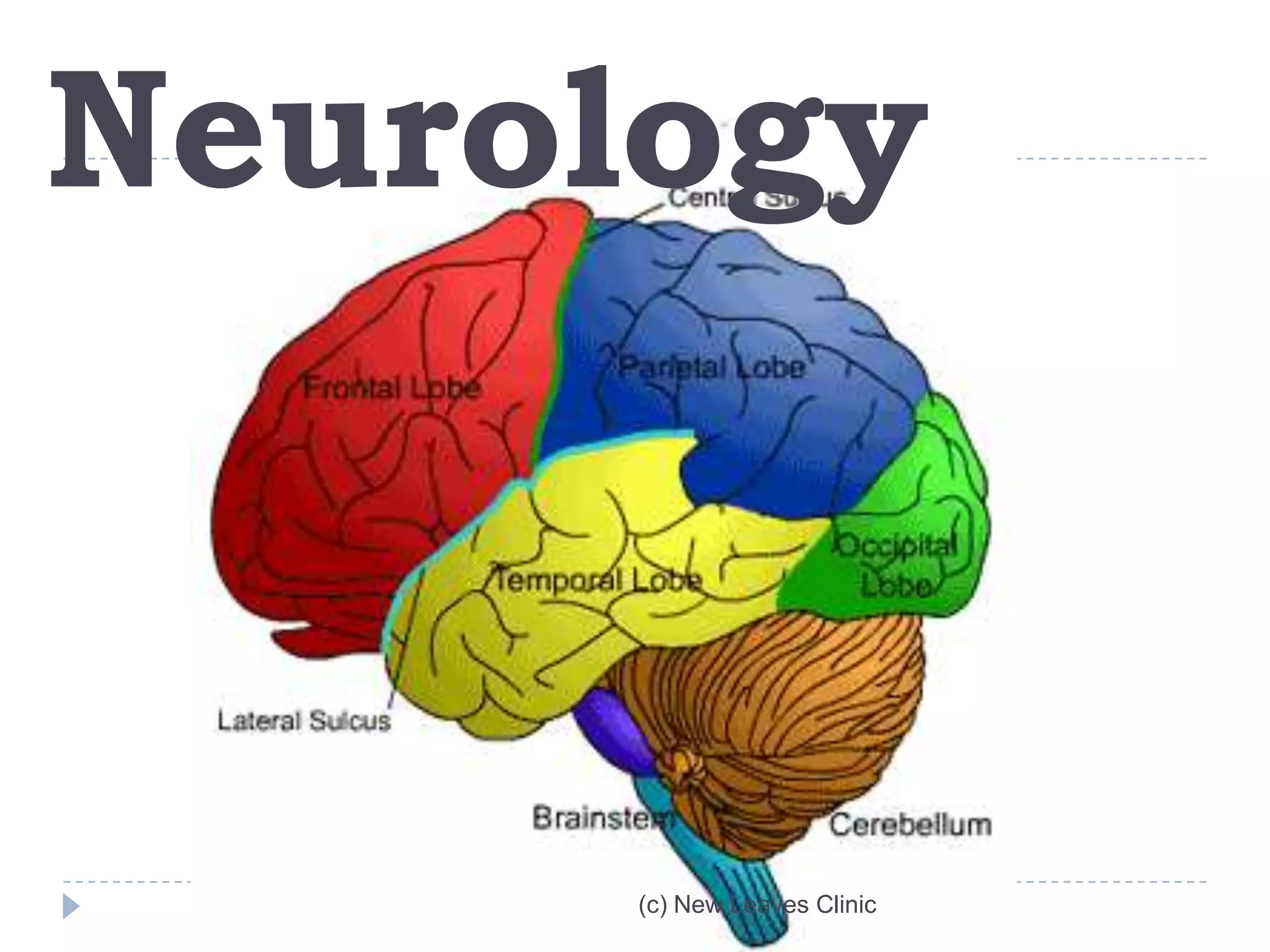
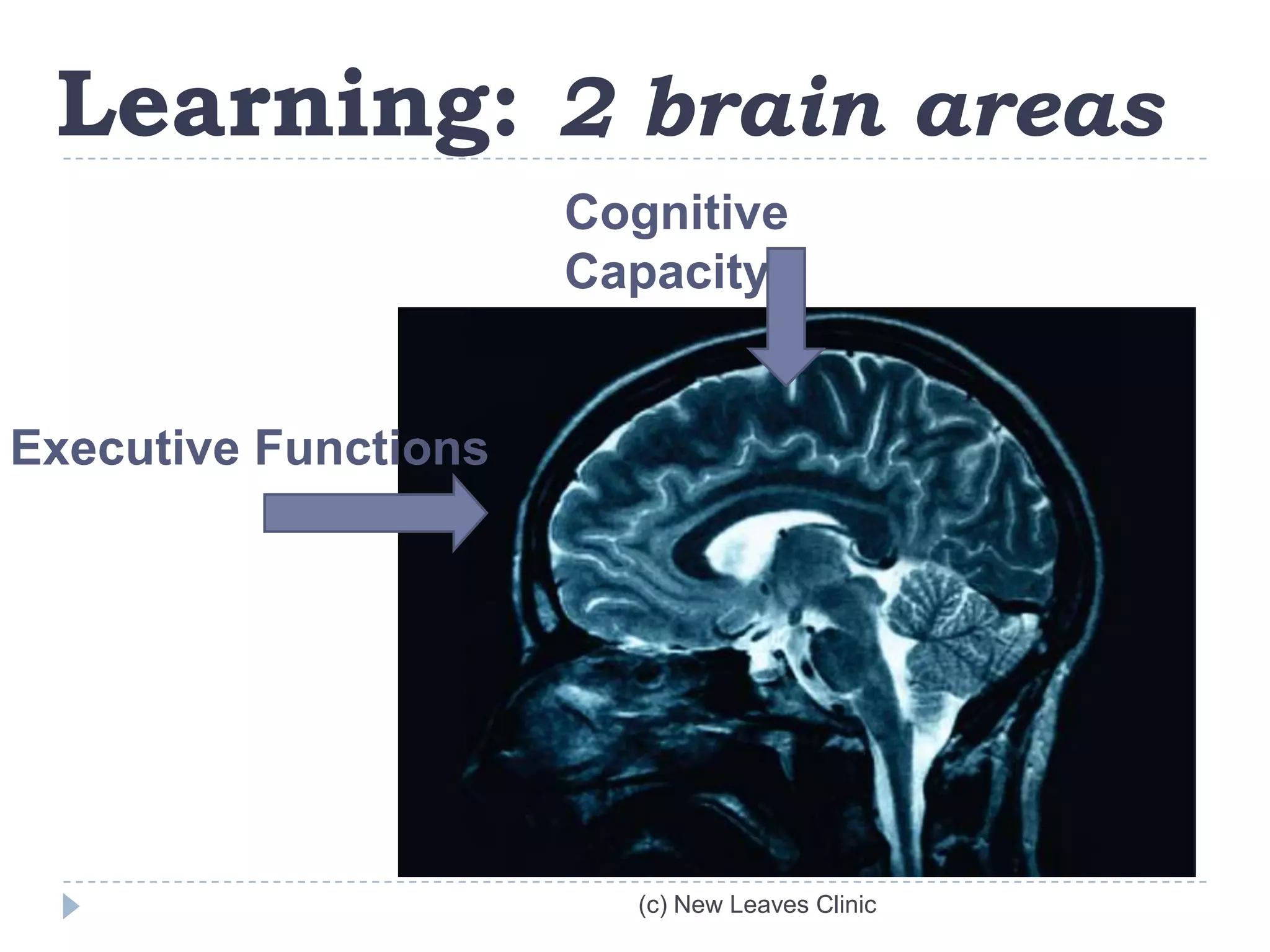
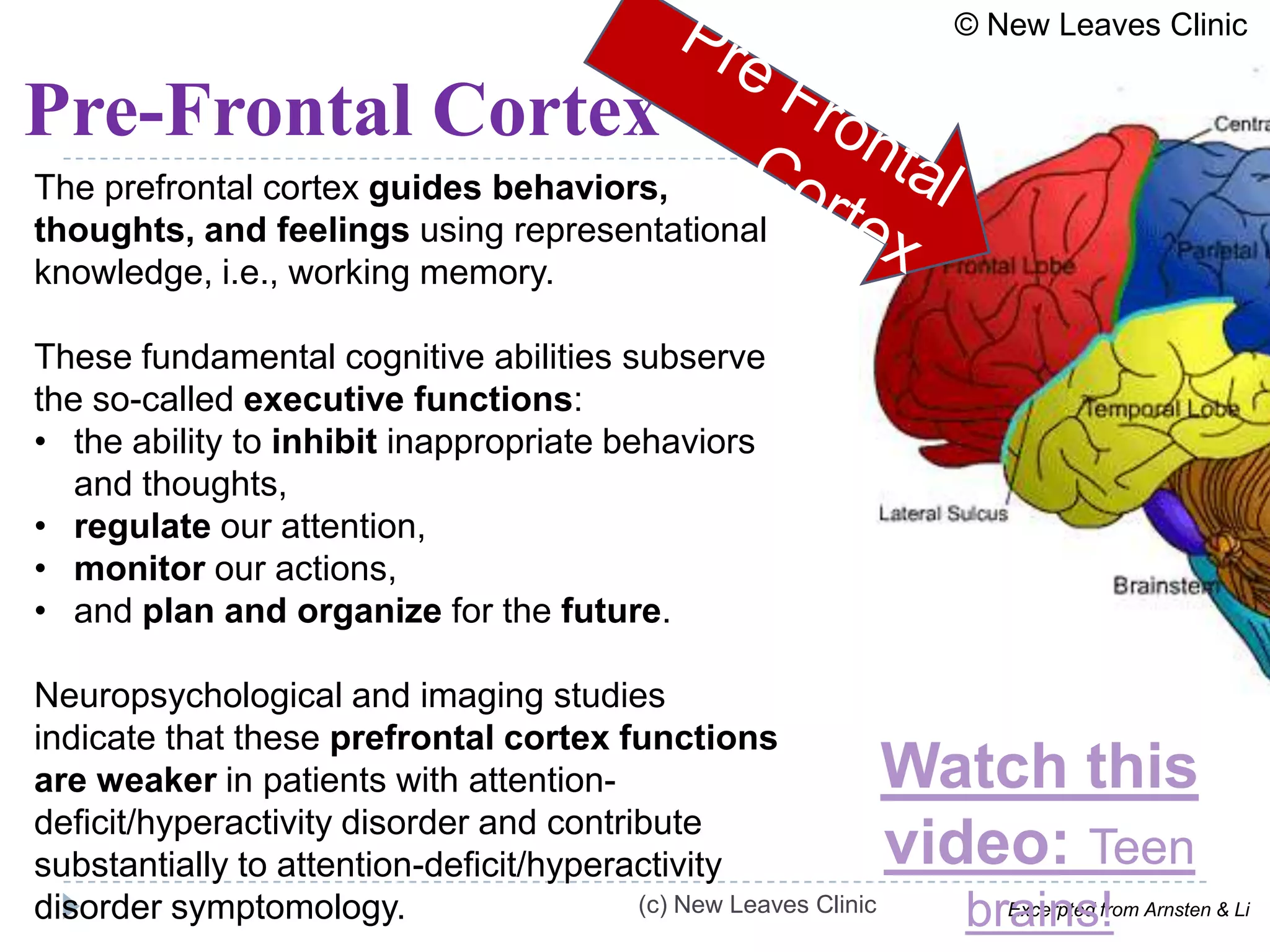
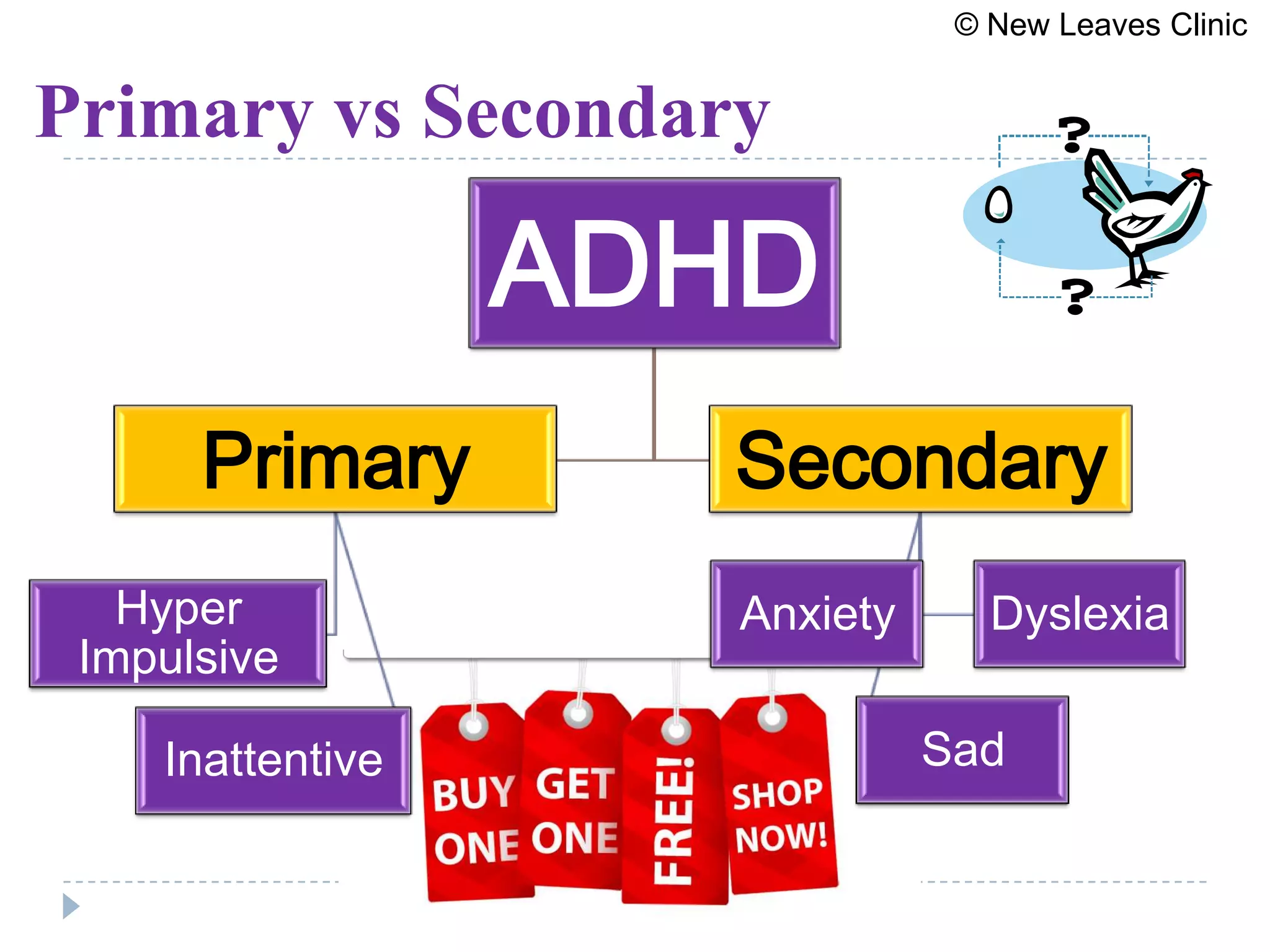
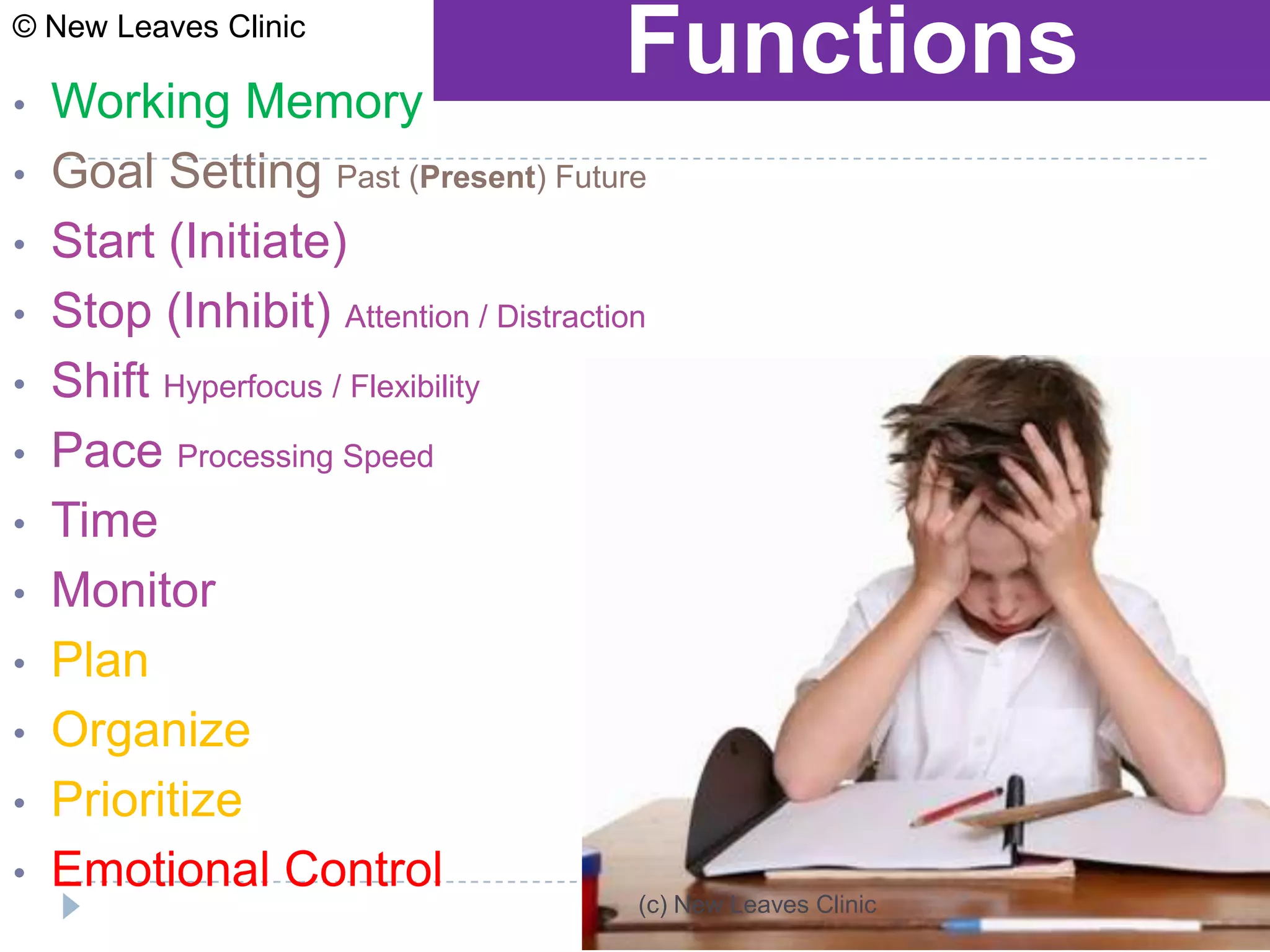
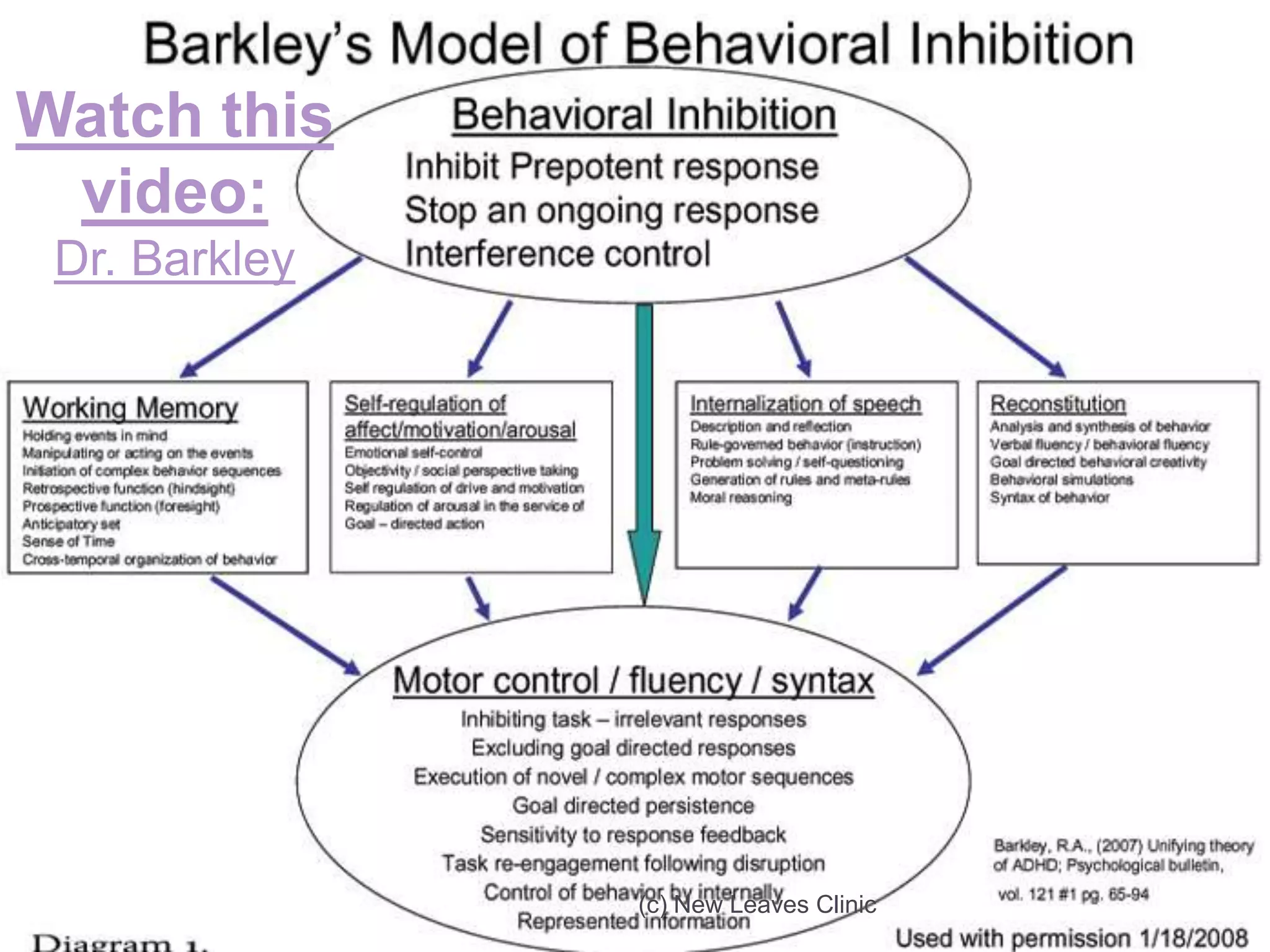
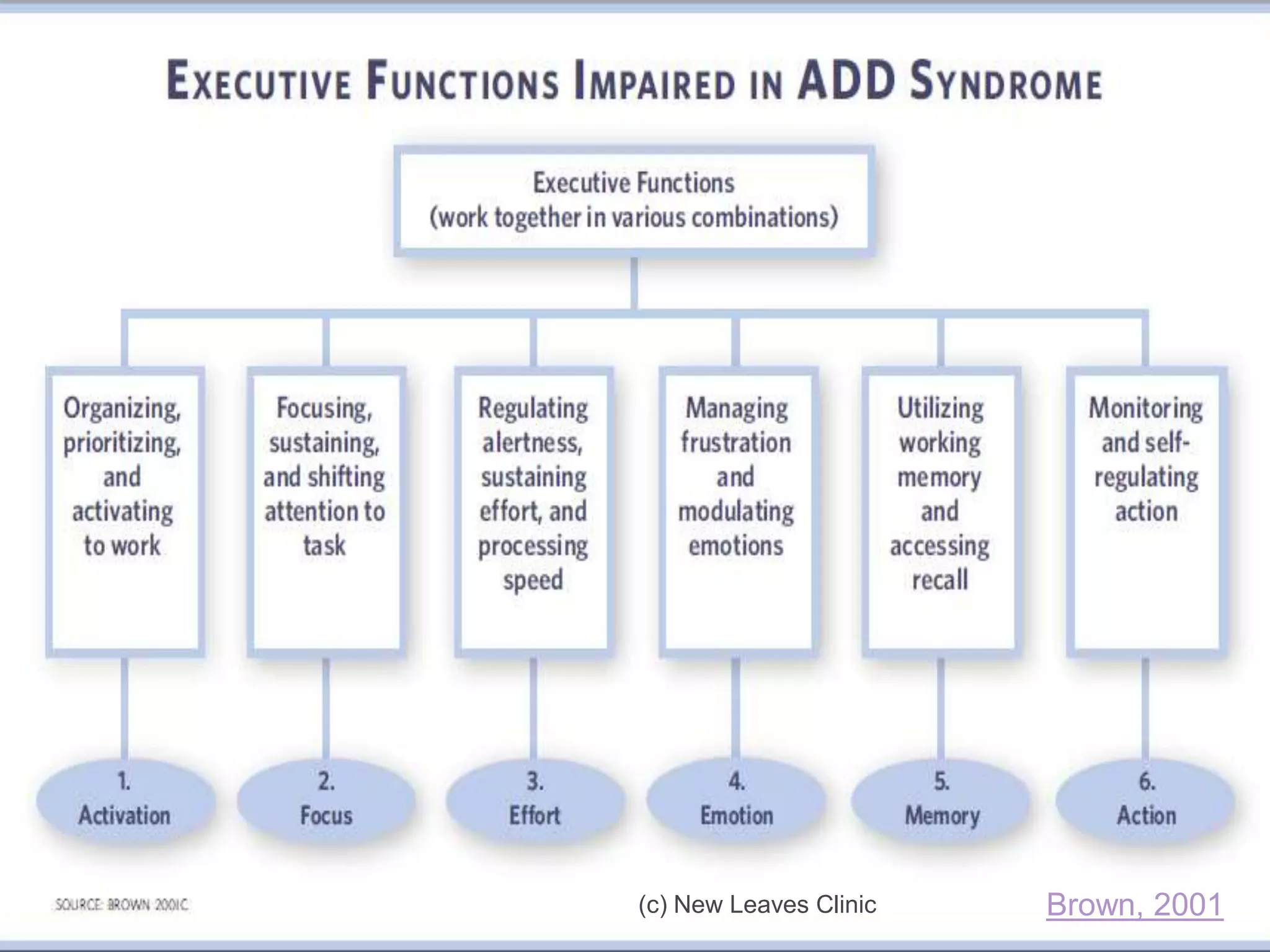
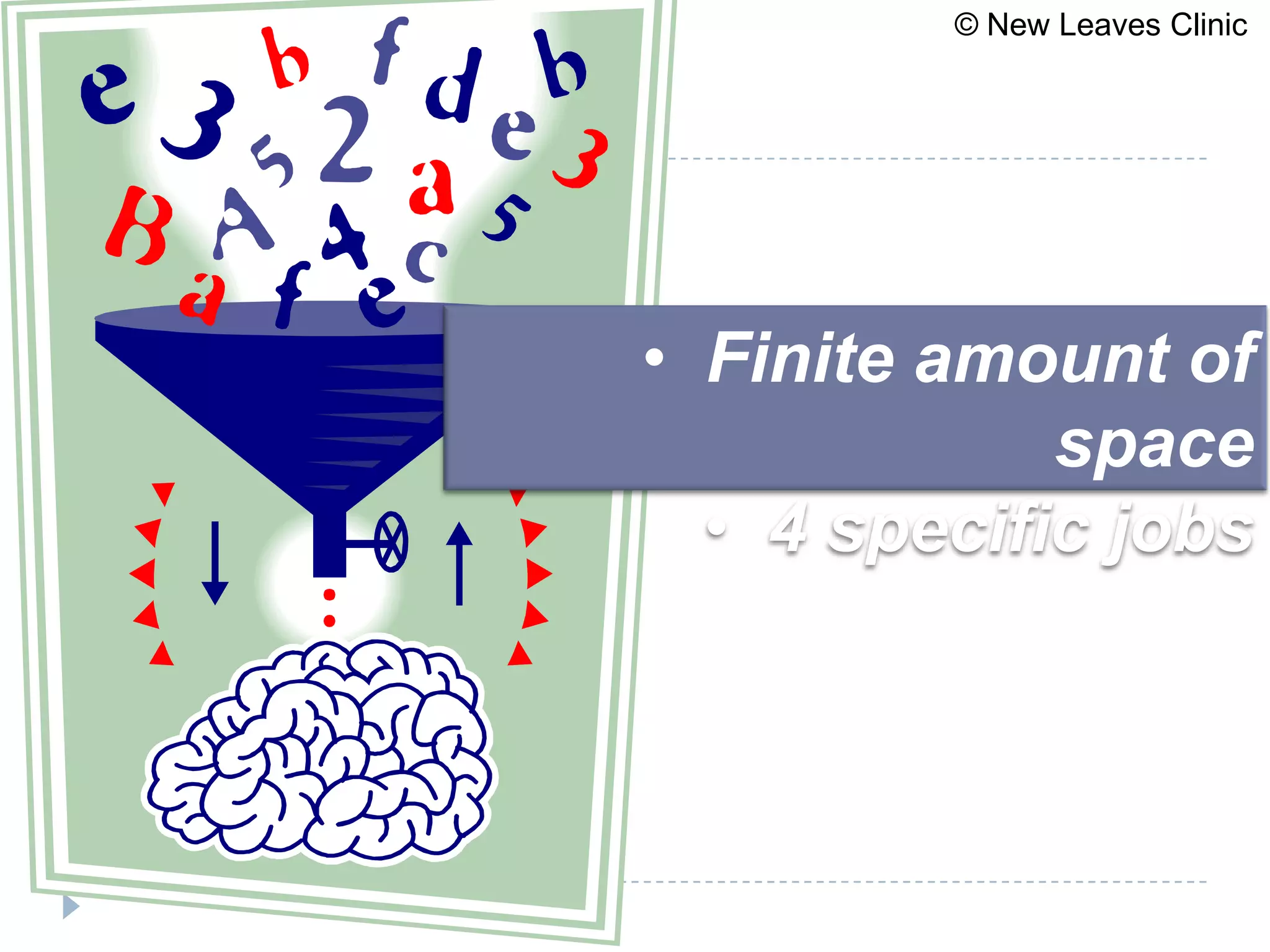
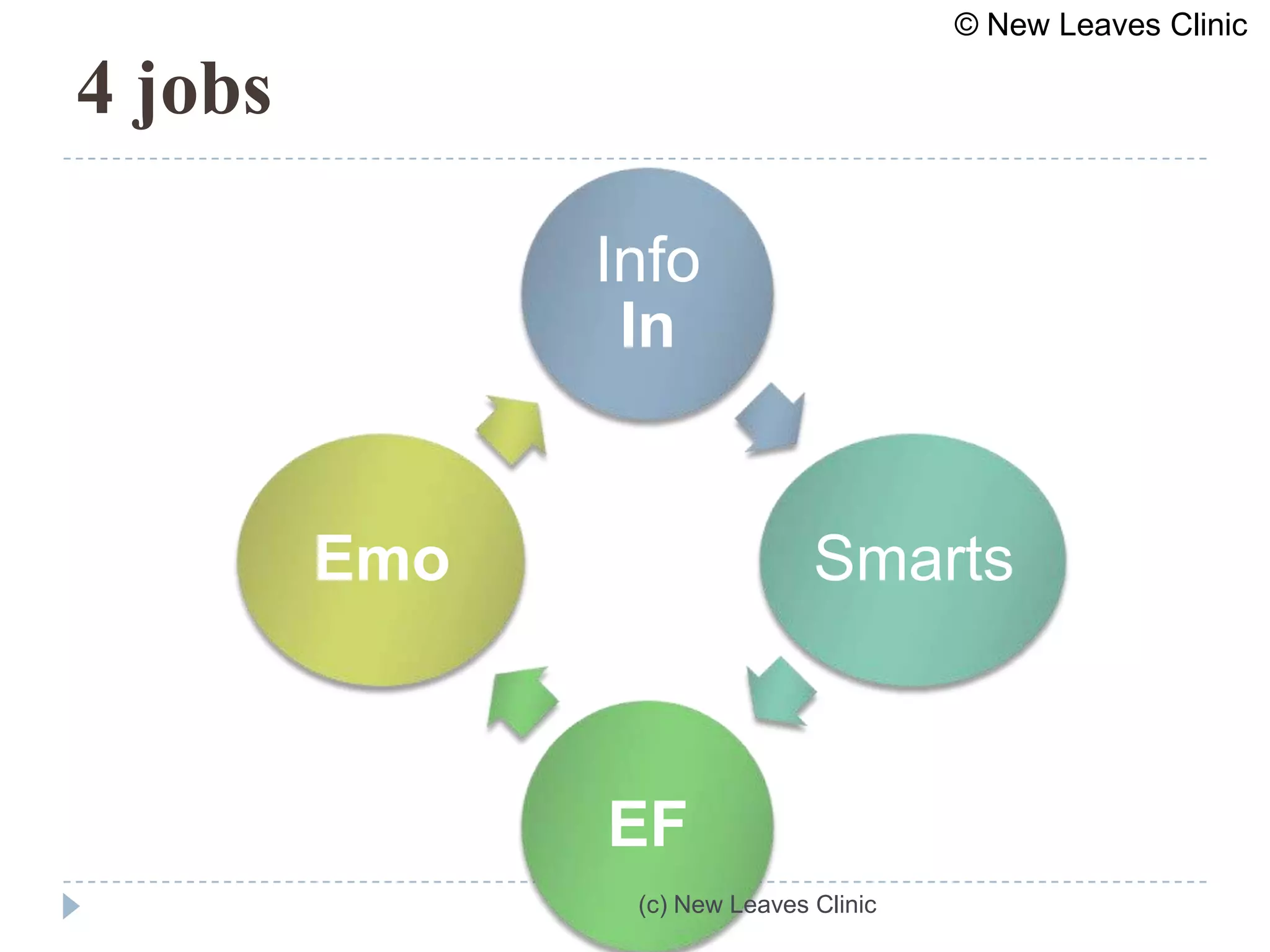
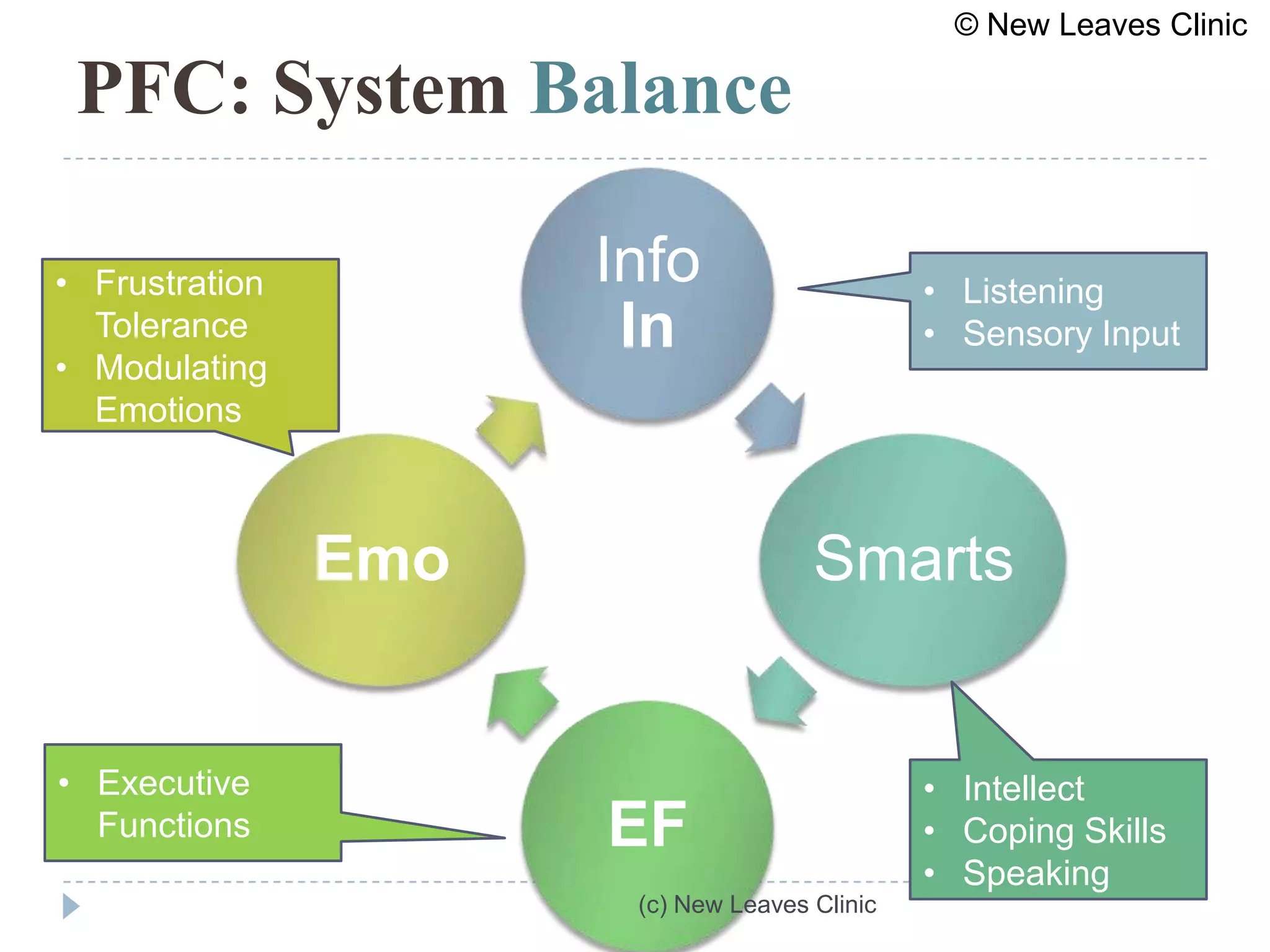
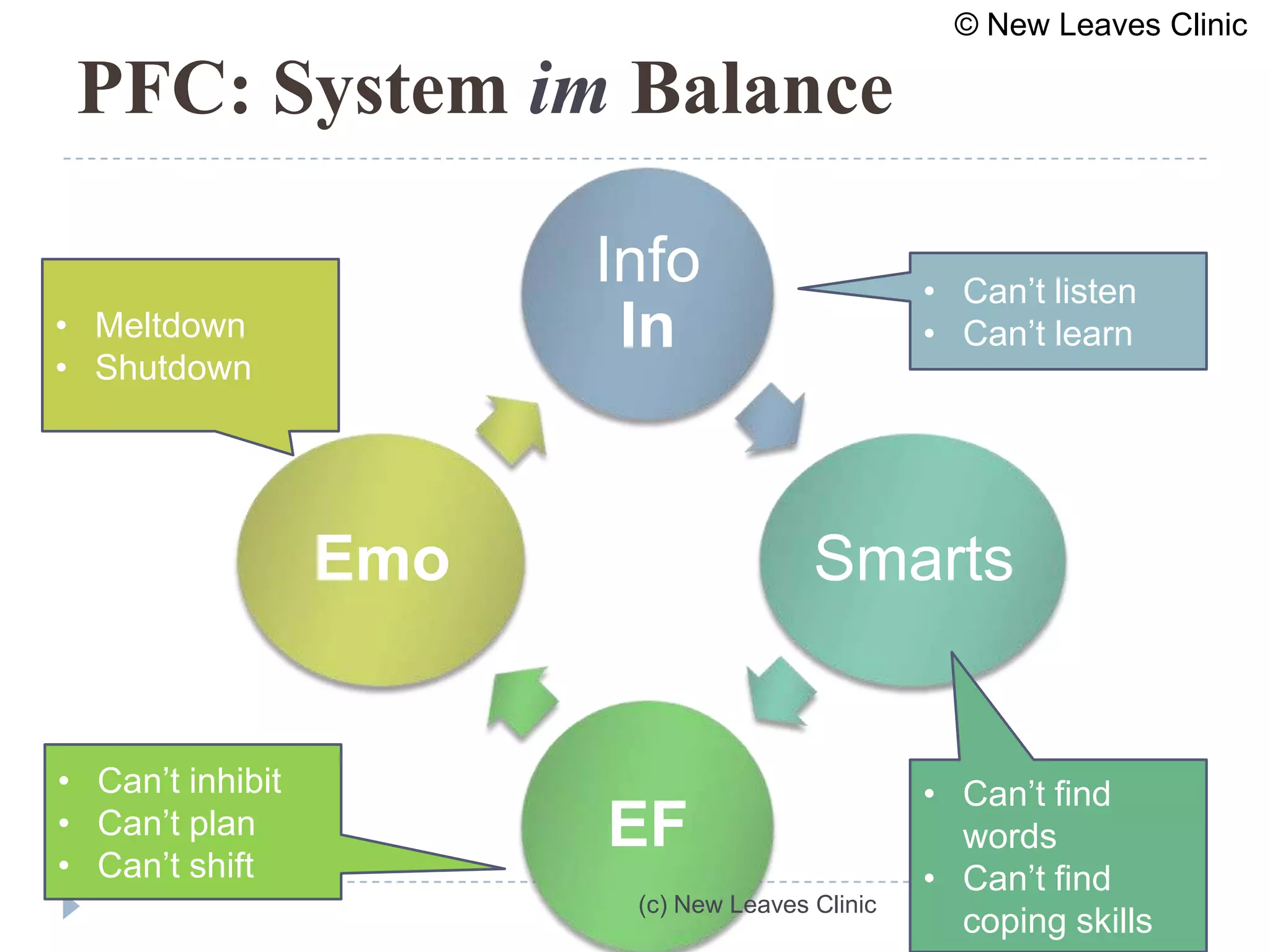
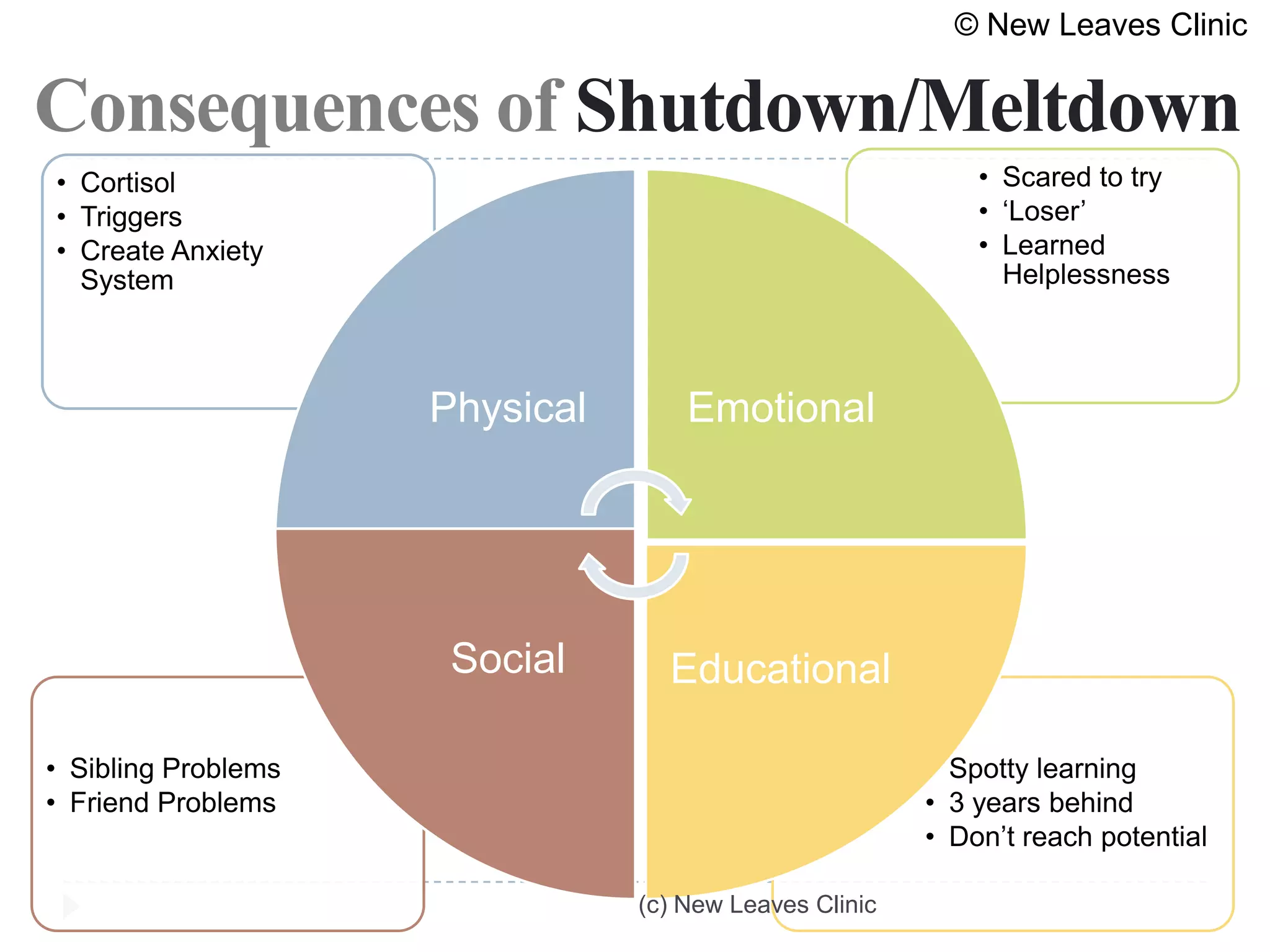
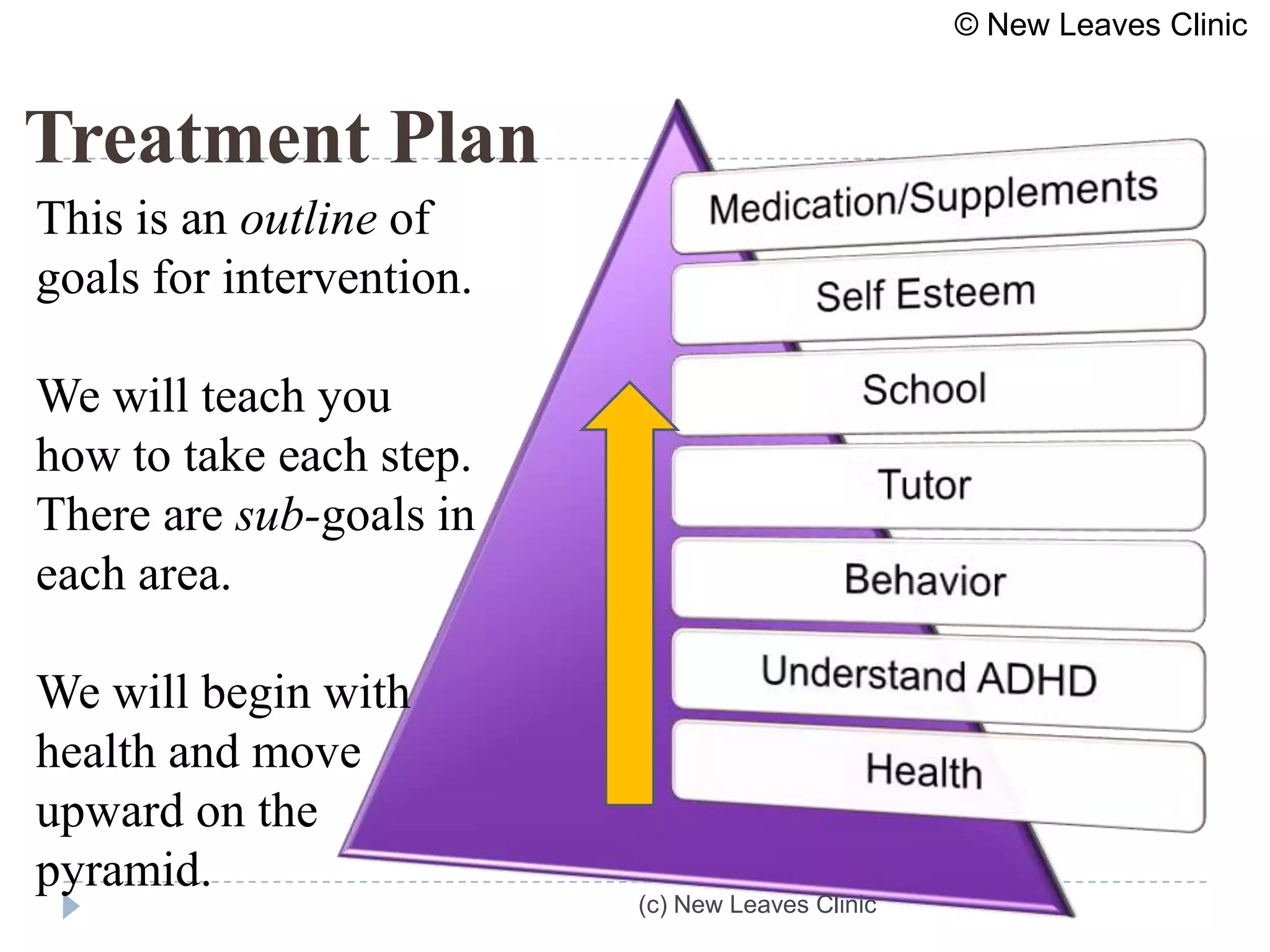
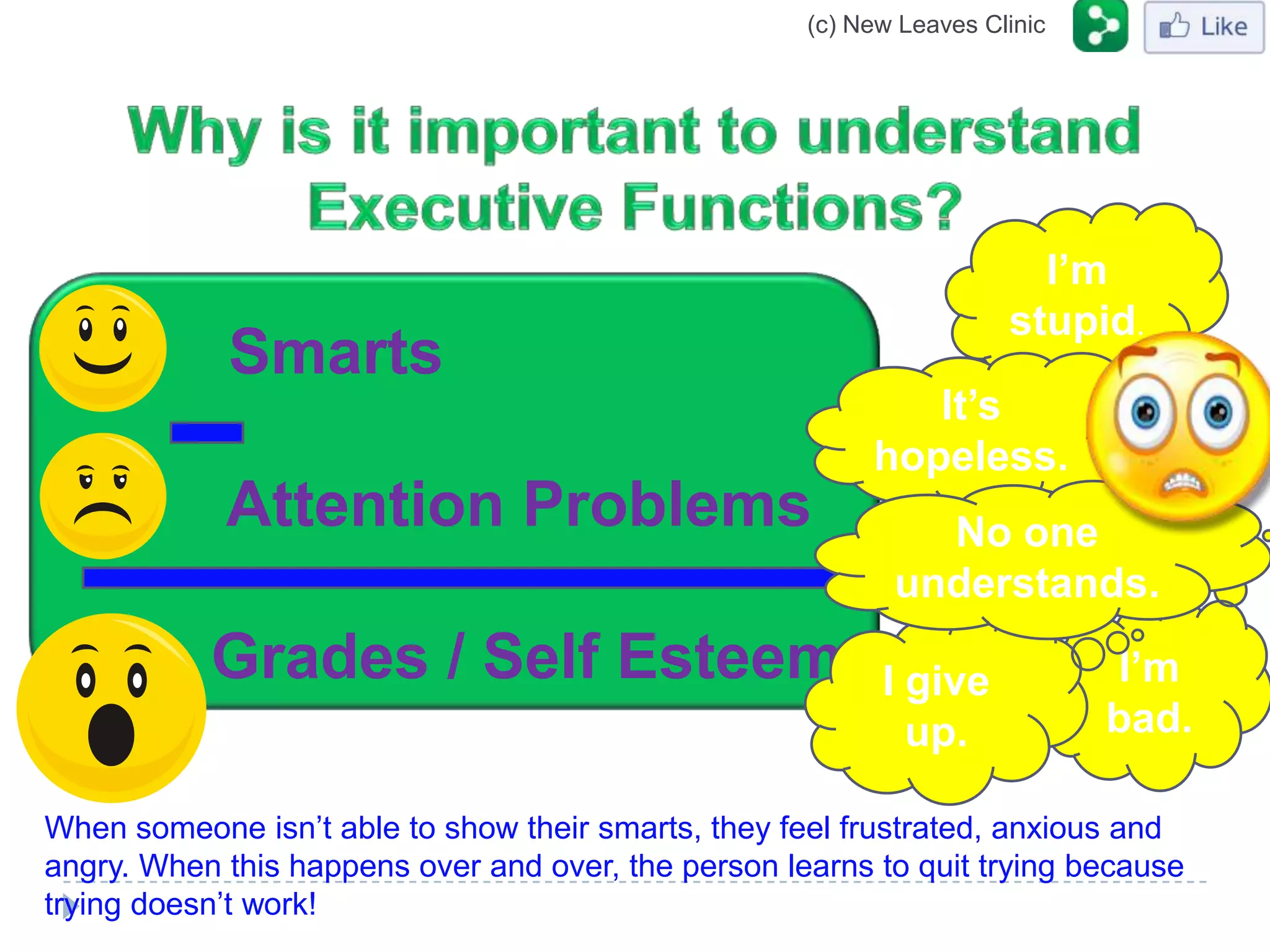
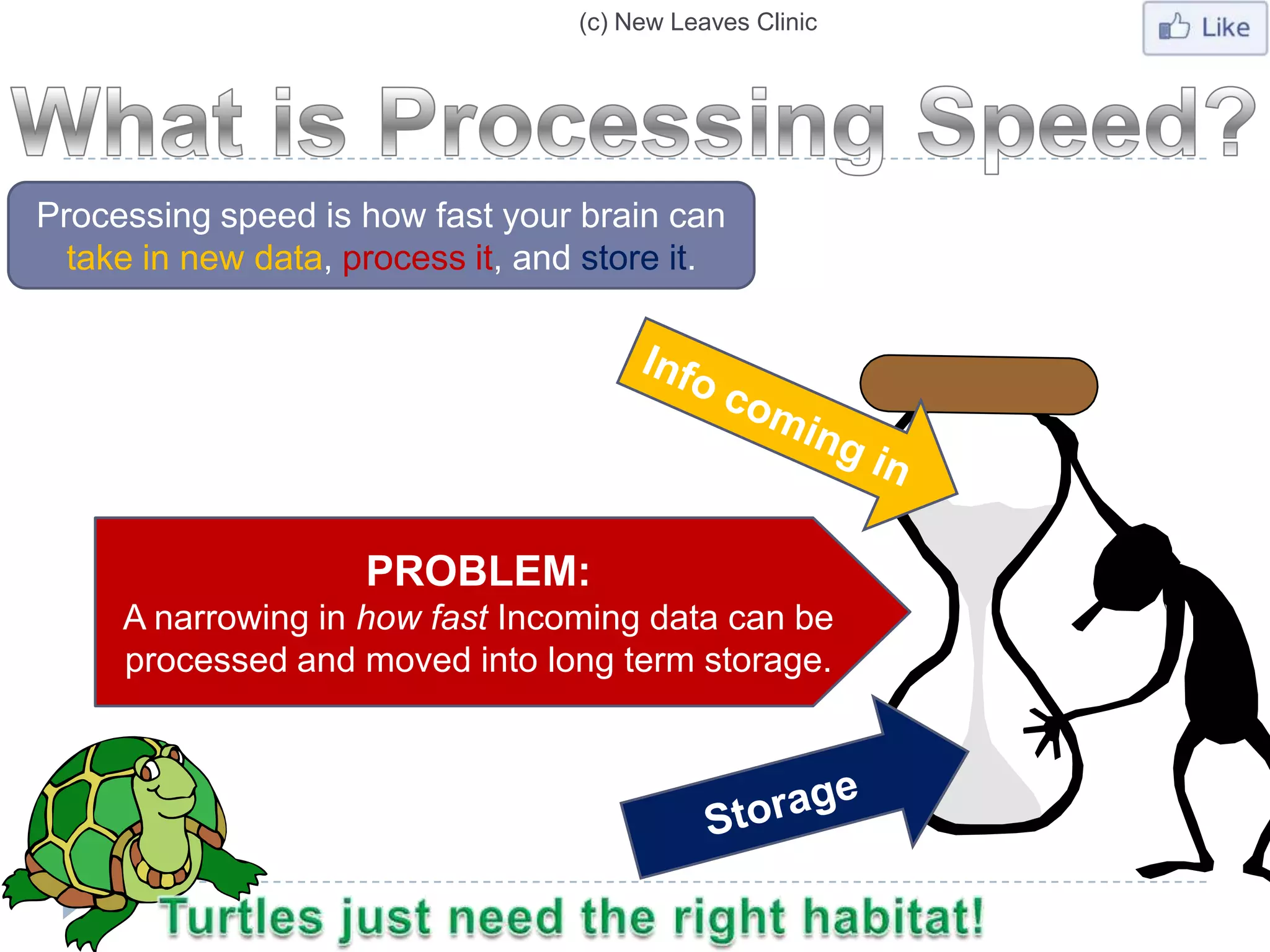
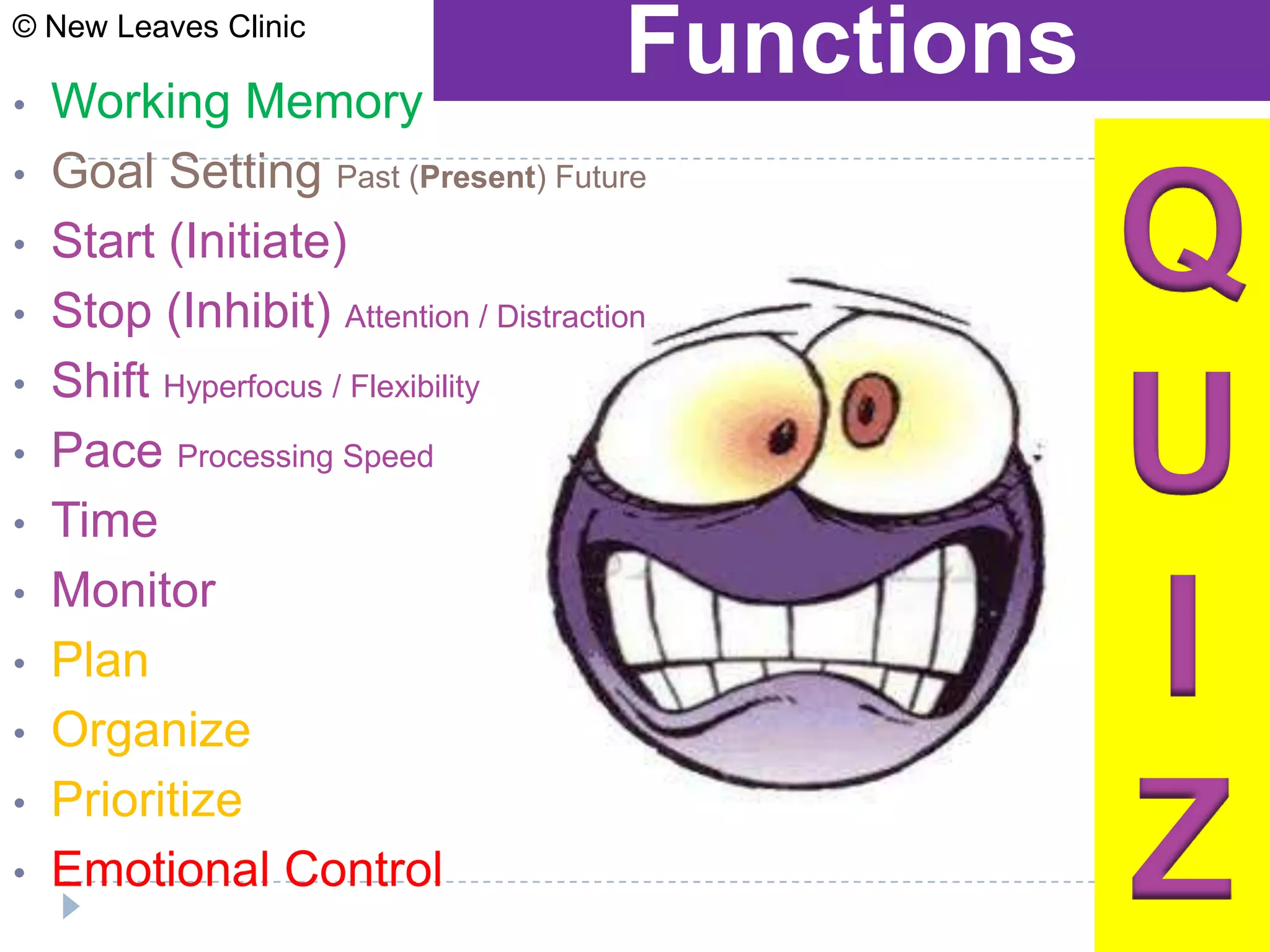
This document provides information from a presentation on executive functions and ADHD. It includes sections on the prefrontal cortex and its role in executive functions like working memory, inhibition, attention regulation, and planning. It discusses different types of ADHD and compares primary vs secondary causes. Slides define the different executive functions and provide assessment tools and treatment strategies like the Pomodoro technique. Resources for further learning include books, videos and websites from experts in the field.