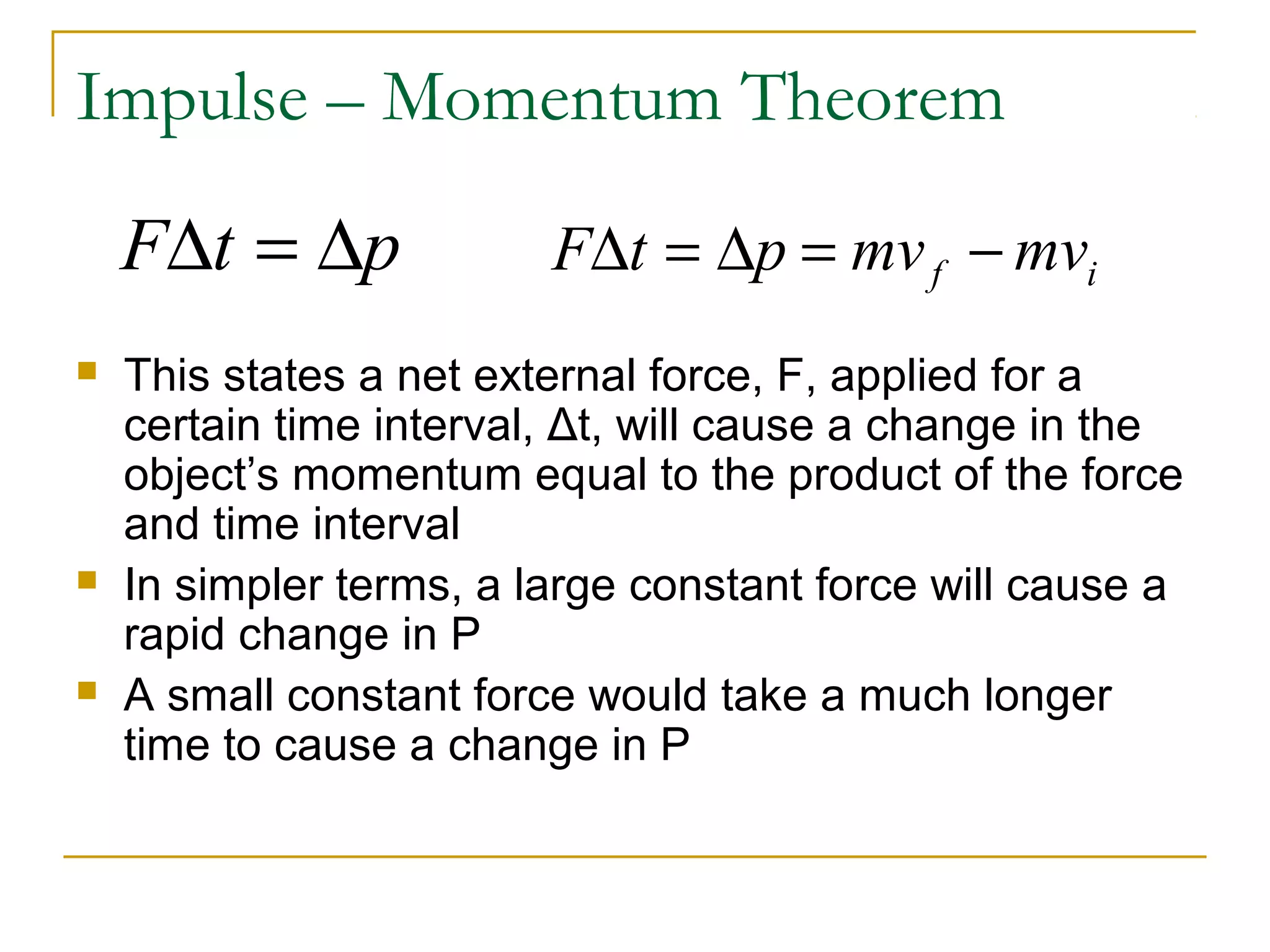
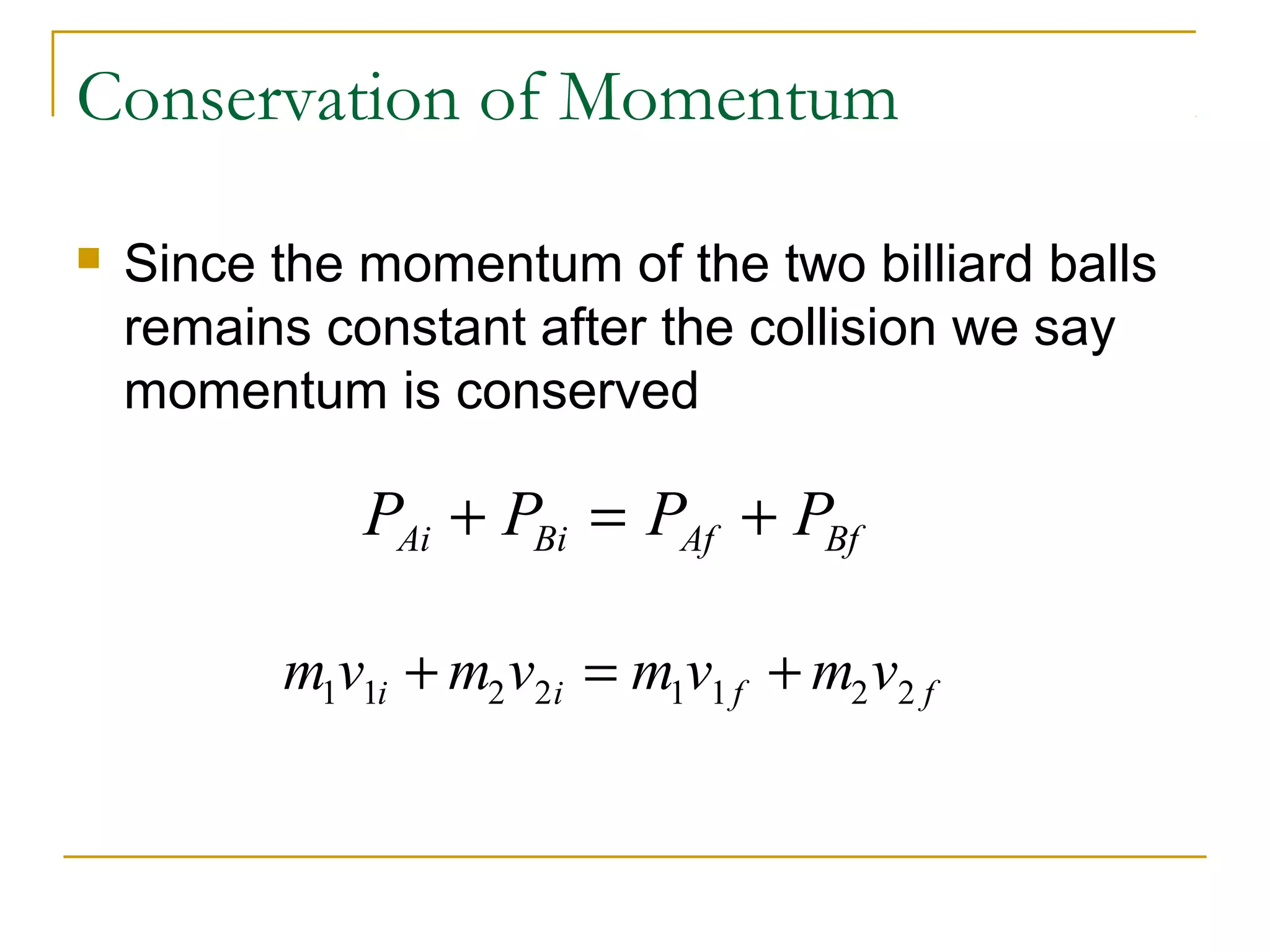
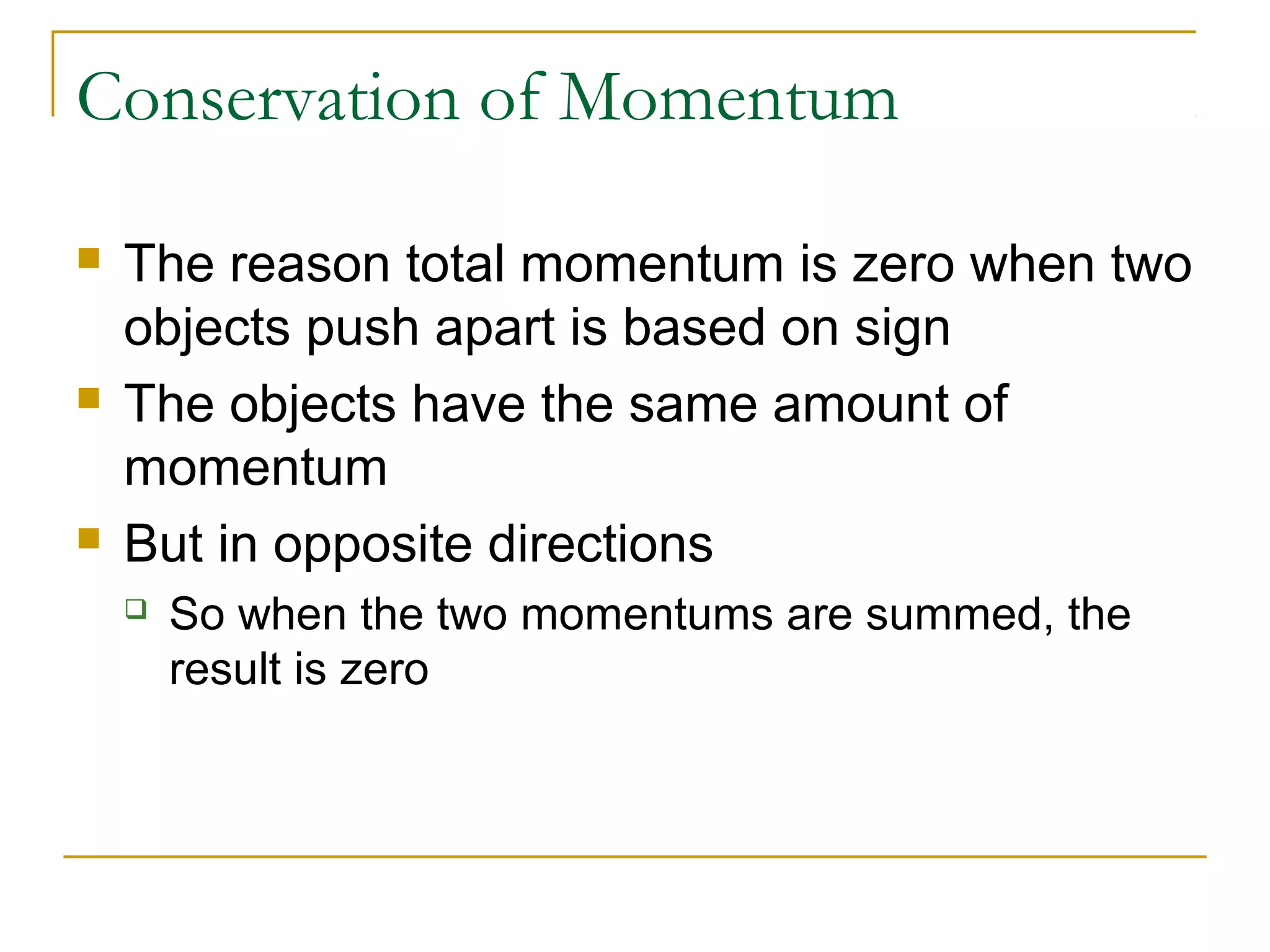
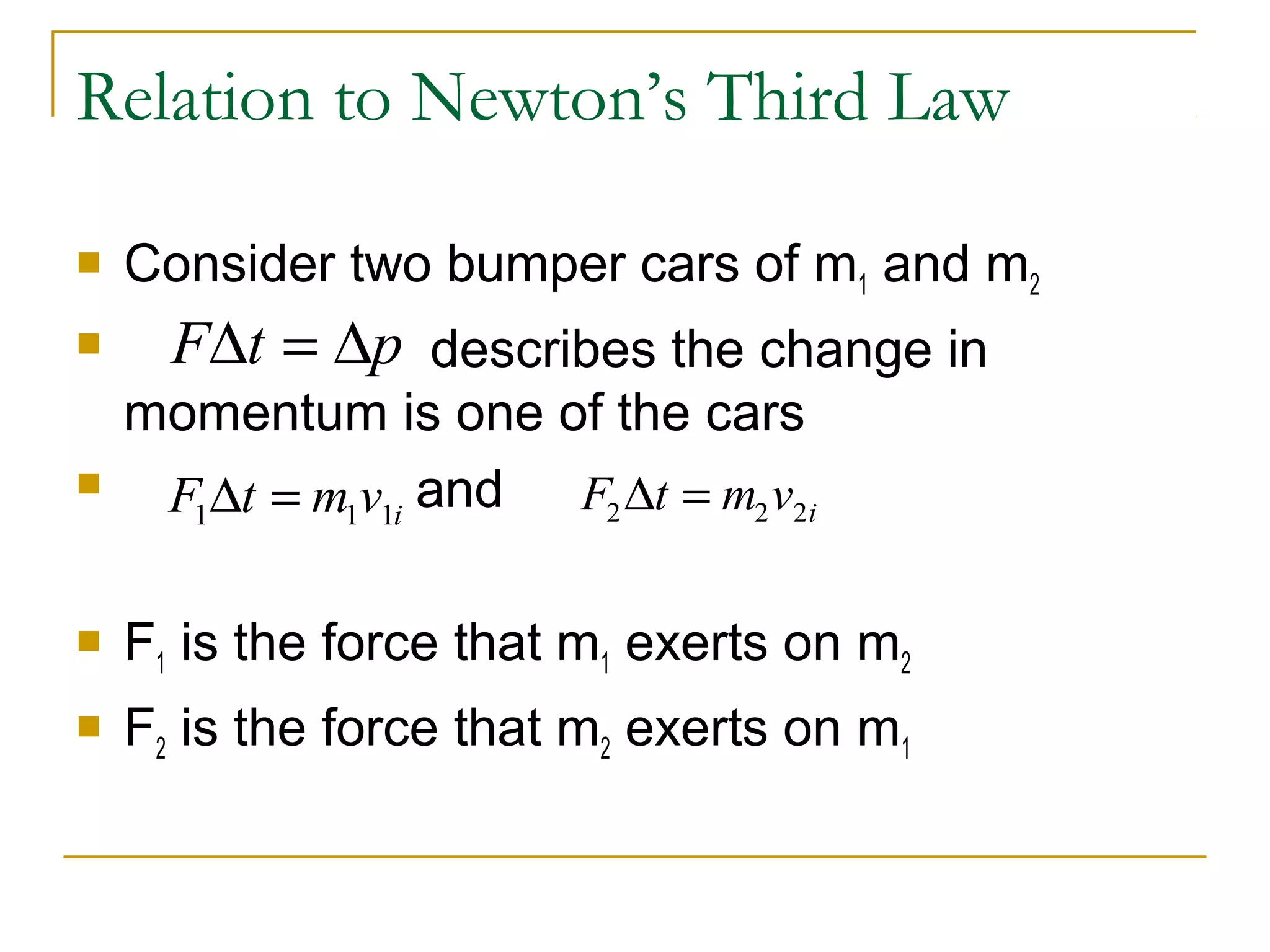
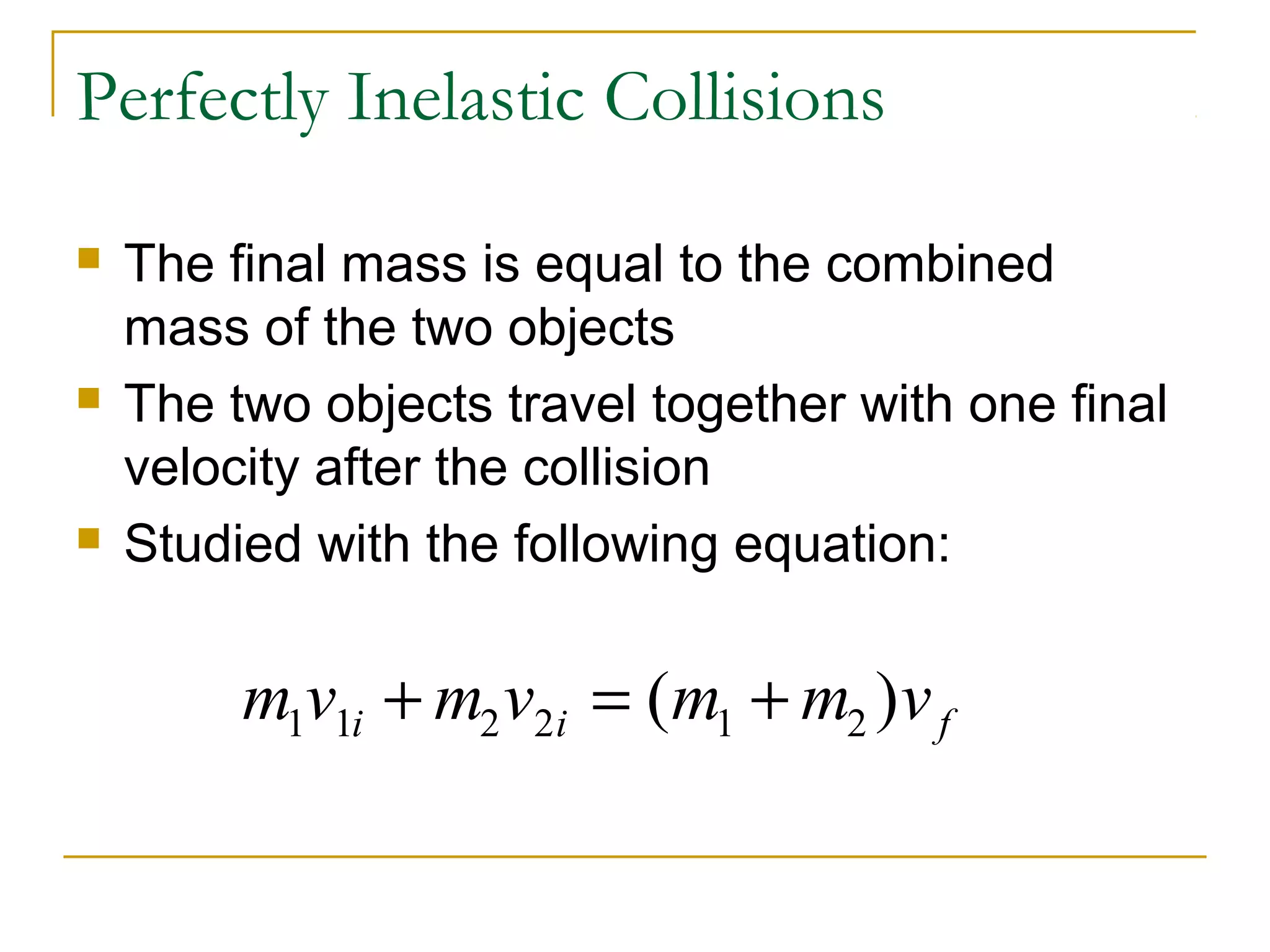
This document provides an overview of linear momentum and impulse. It defines momentum as the product of an object's mass and velocity (p=mv) and describes how momentum is a vector quantity. Impulse is defined as the change in momentum over time due to an external force (Impulse=Force x Time). The document explains how momentum is conserved in collisions and how the impulse-momentum theorem can be used to analyze collisions. It also distinguishes between perfectly elastic, perfectly inelastic, and inelastic collisions in terms of the objects' motions and changes to their kinetic energy before and after the collision.