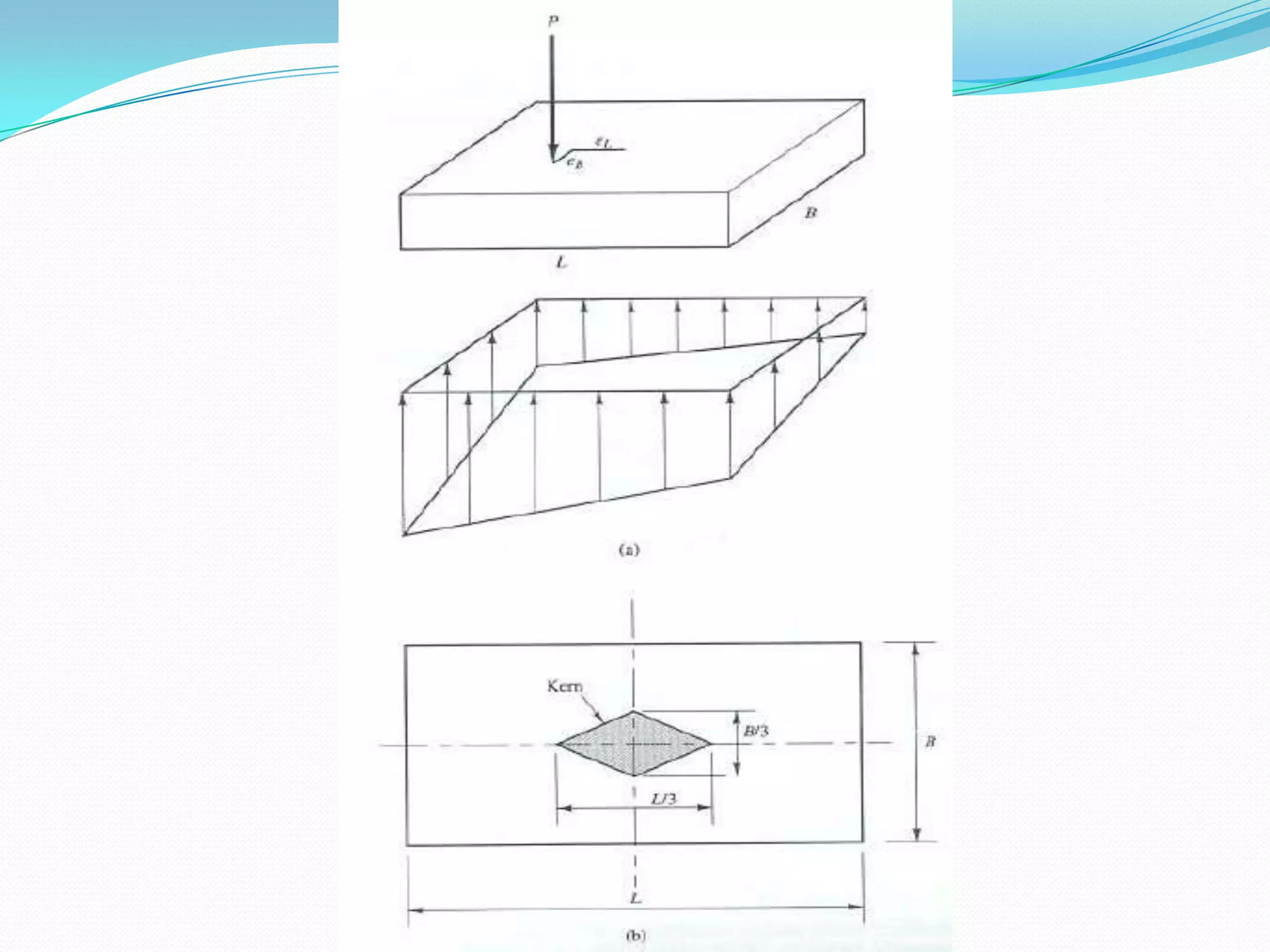
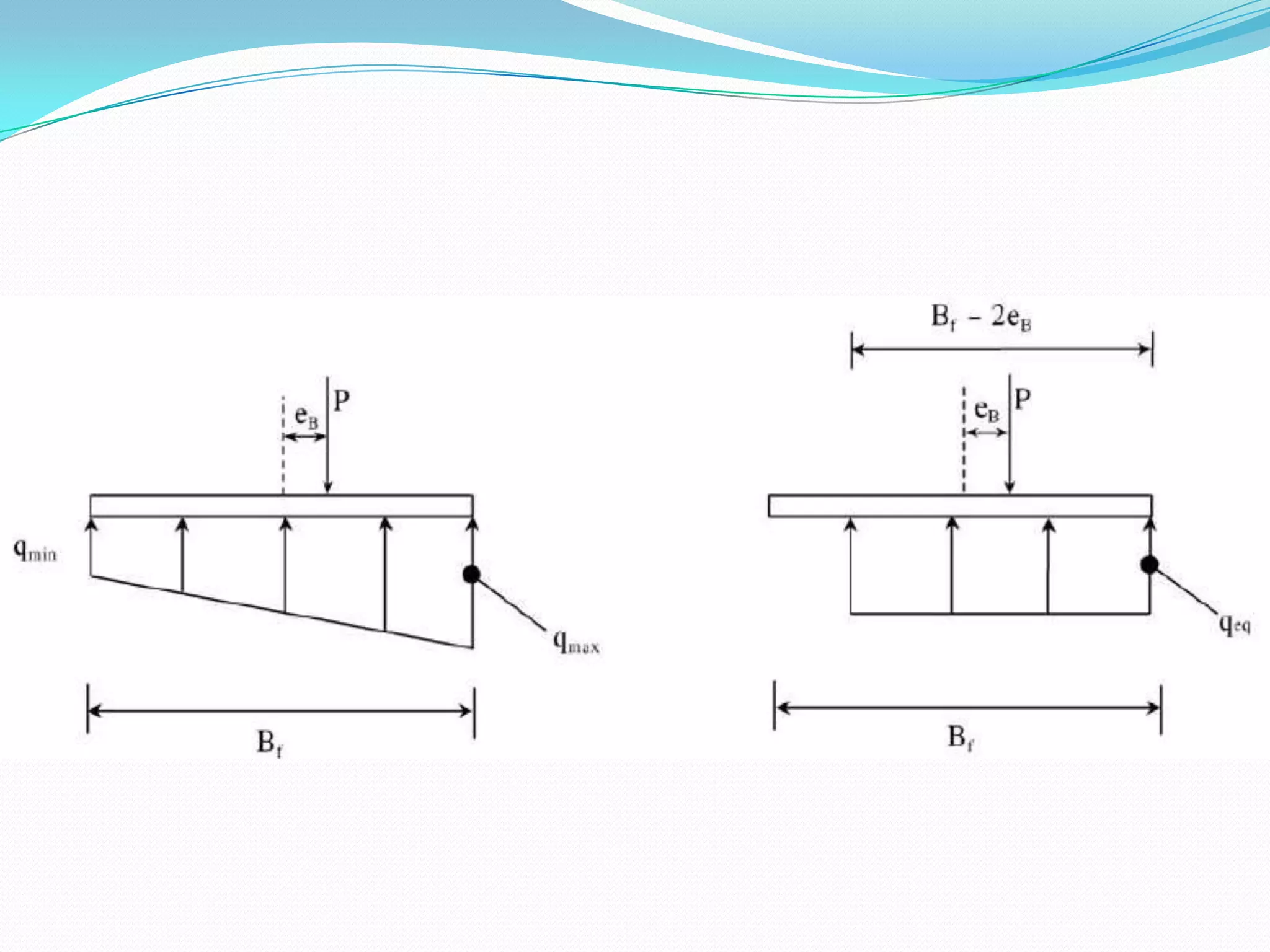
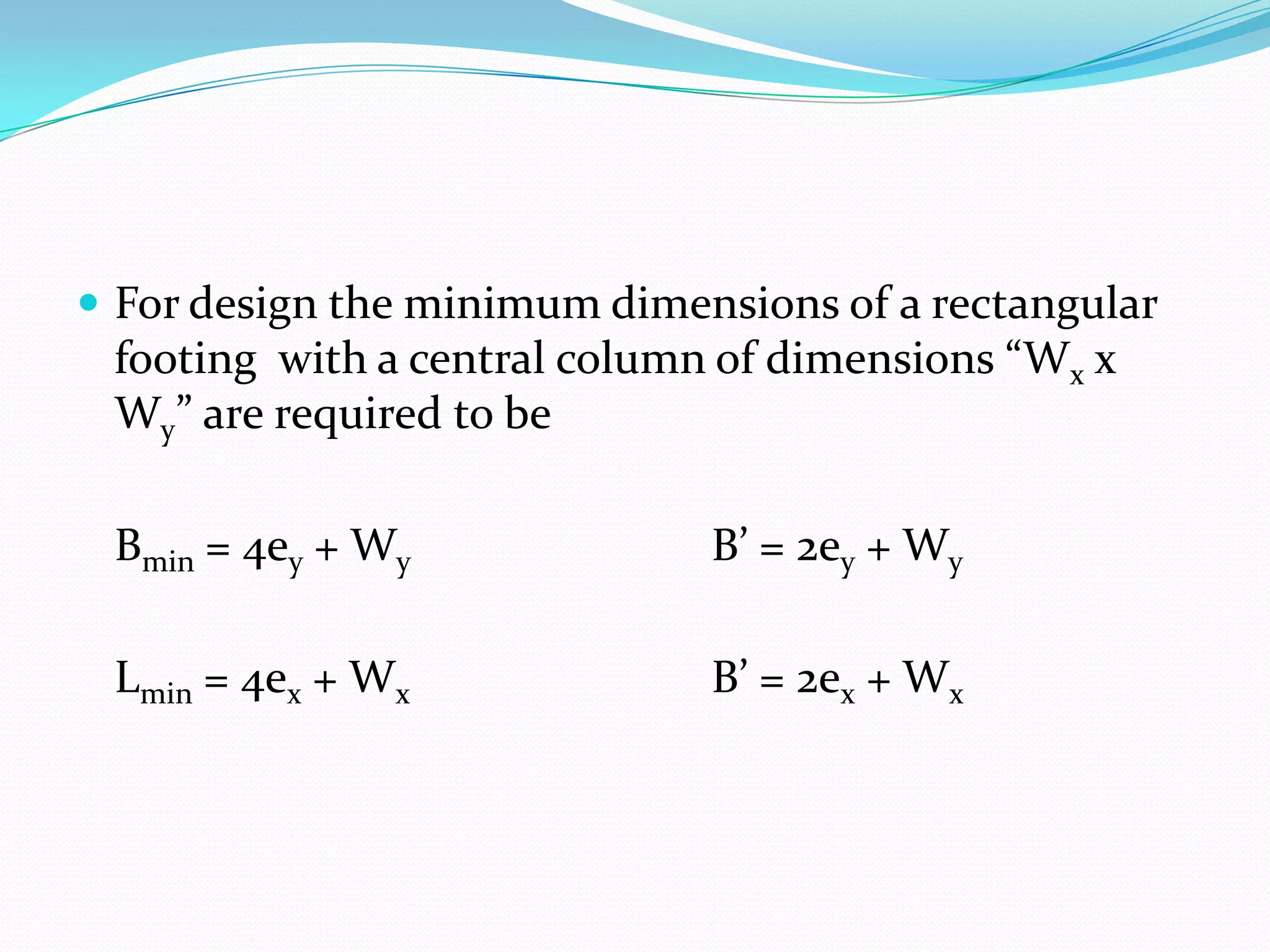
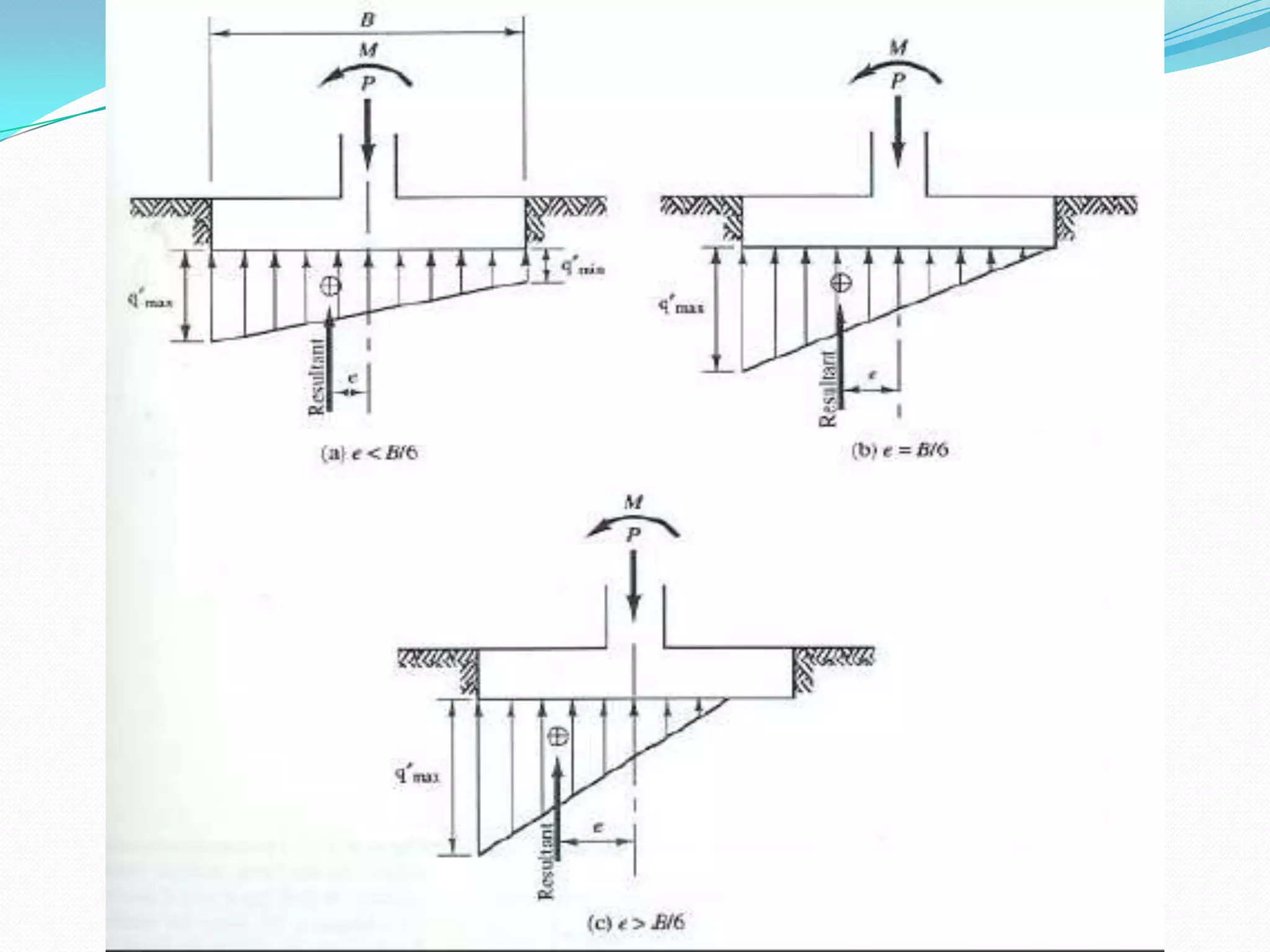
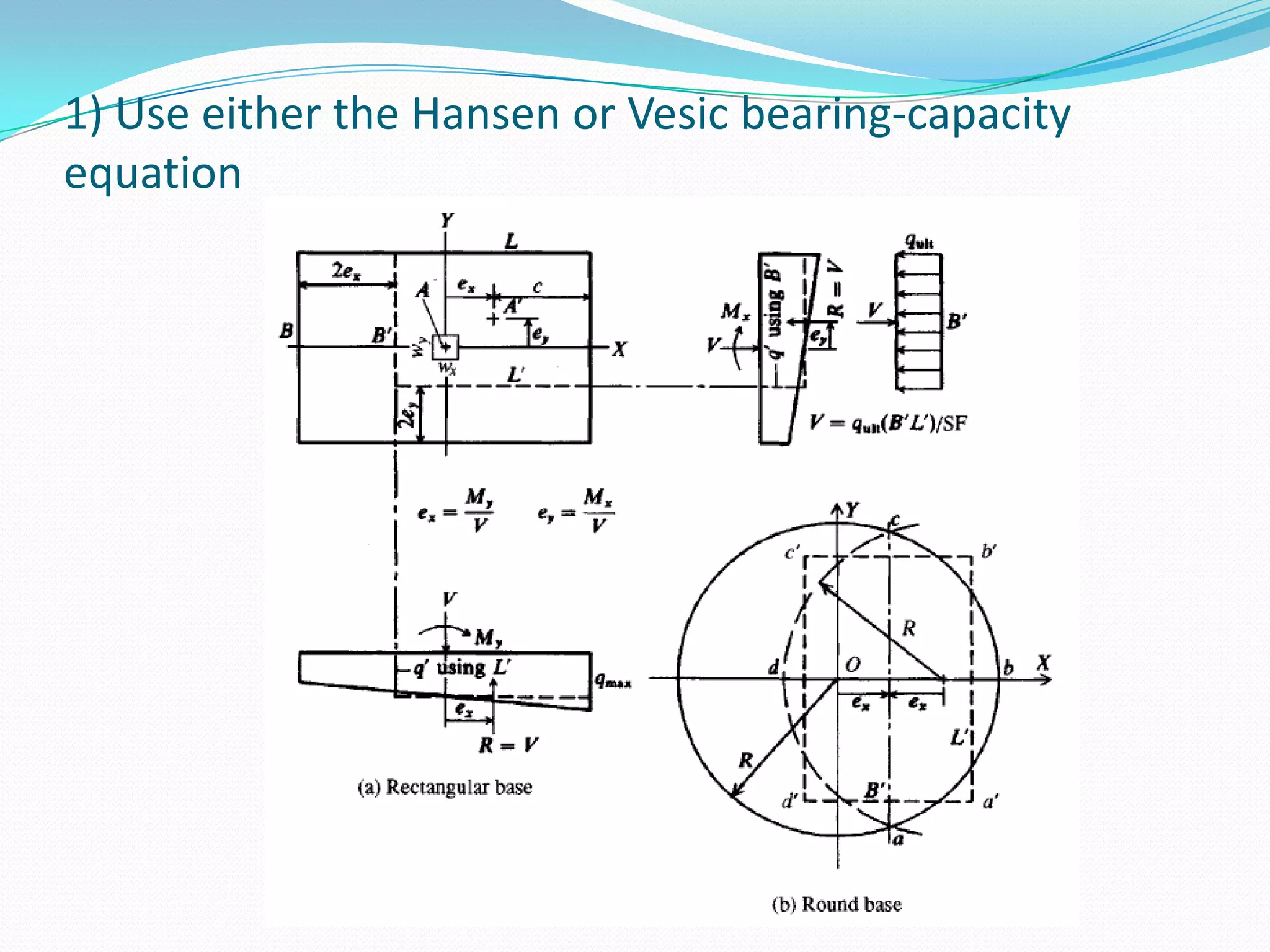
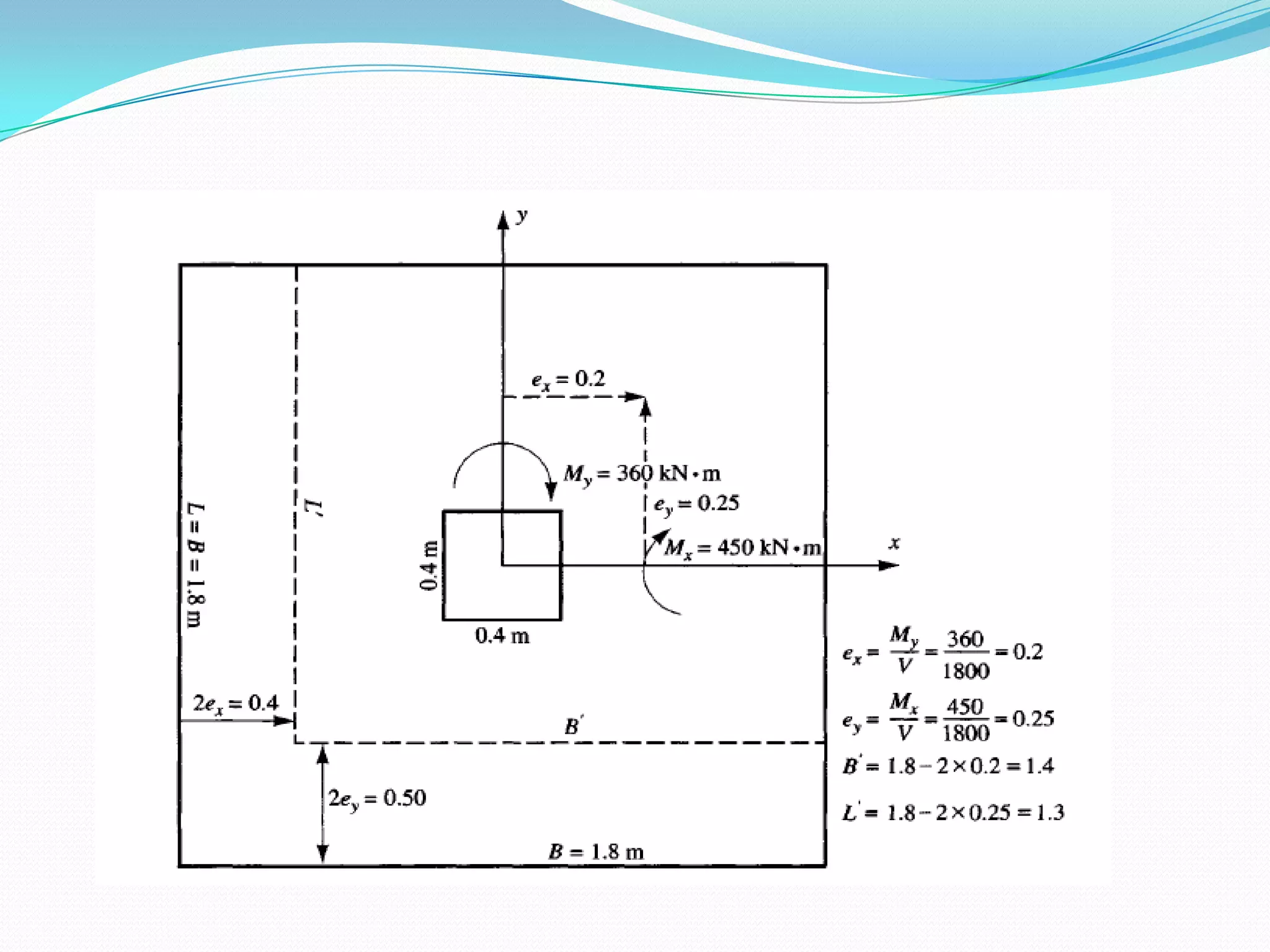
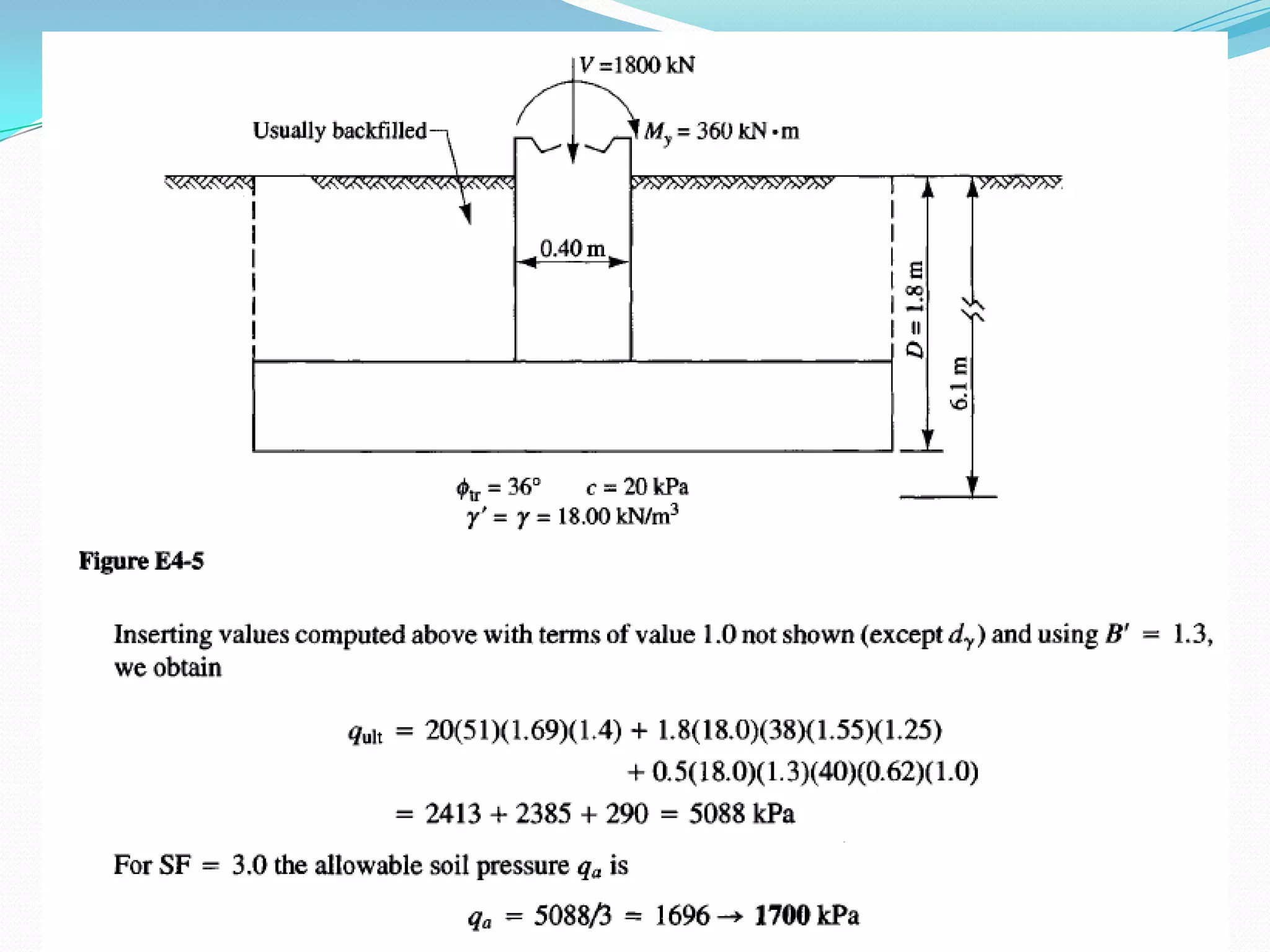
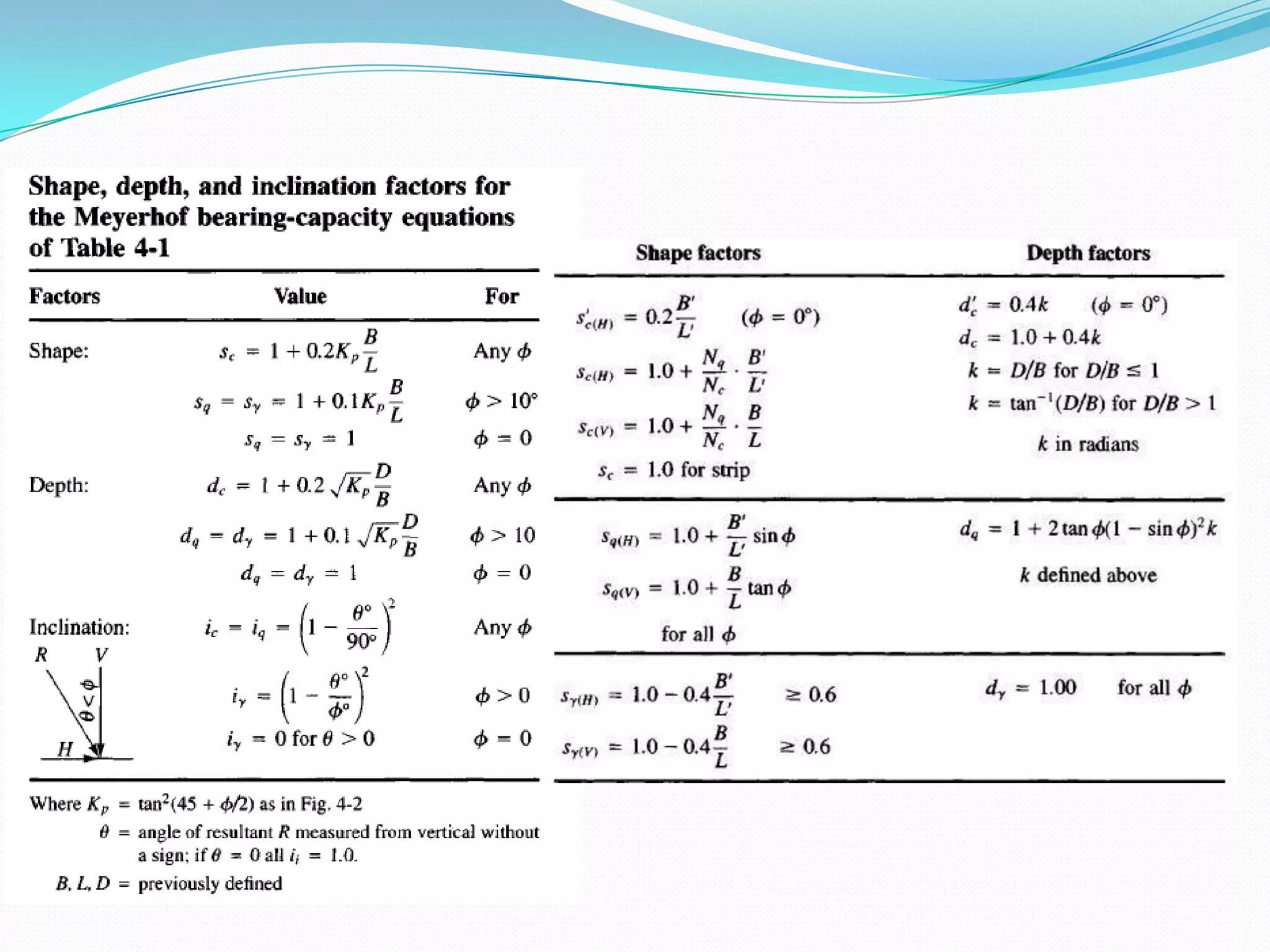
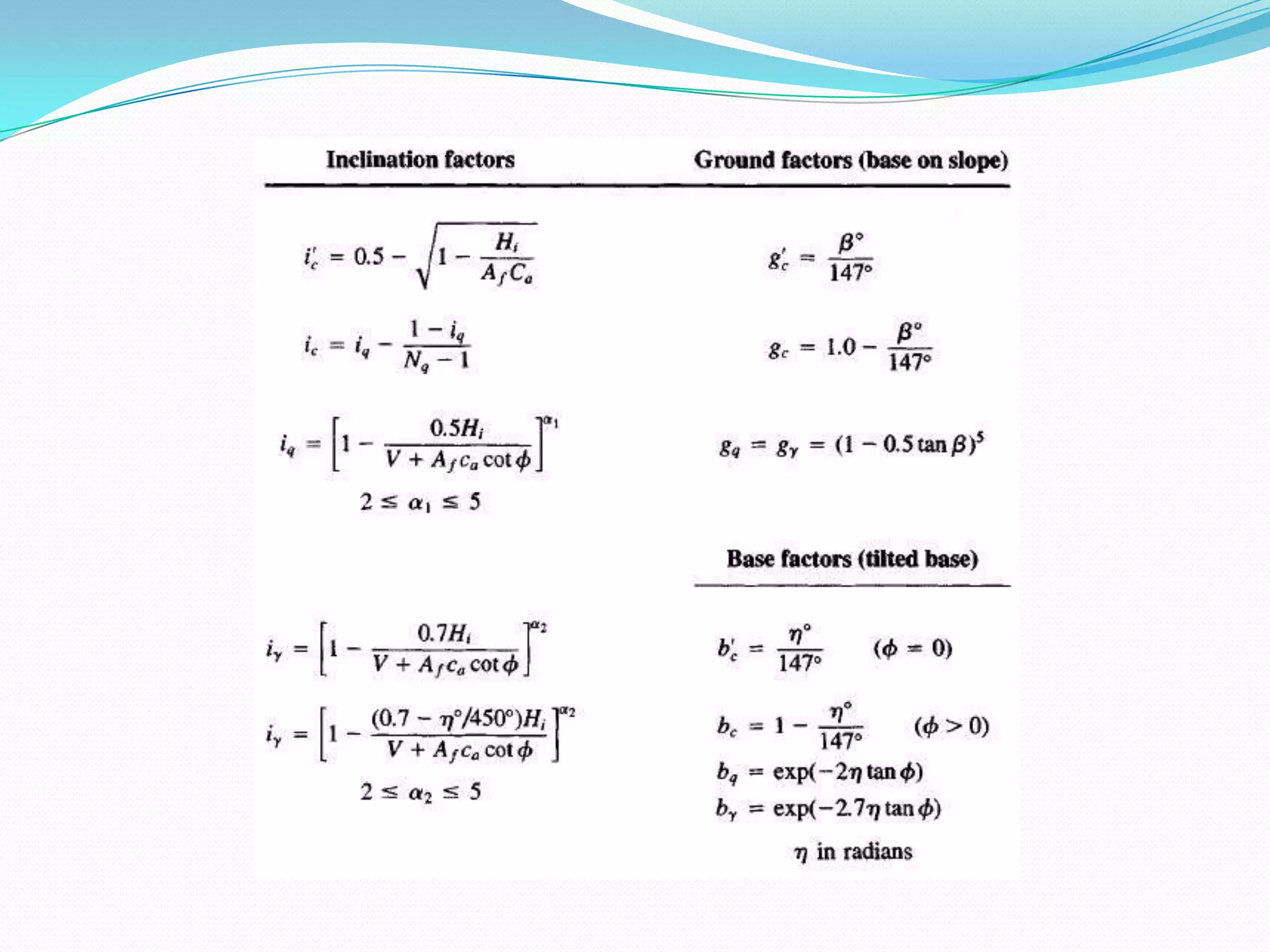
This document discusses how to account for the effects of eccentric loads on the design of rectangular footings. It provides equations to calculate the modified width and length of a footing based on the load eccentricities. It also provides the minimum footing dimensions required for a central column and describes how to calculate the ultimate bearing capacity of an eccentric footing using either the Hansen/Vesic or Meyerhof methods.