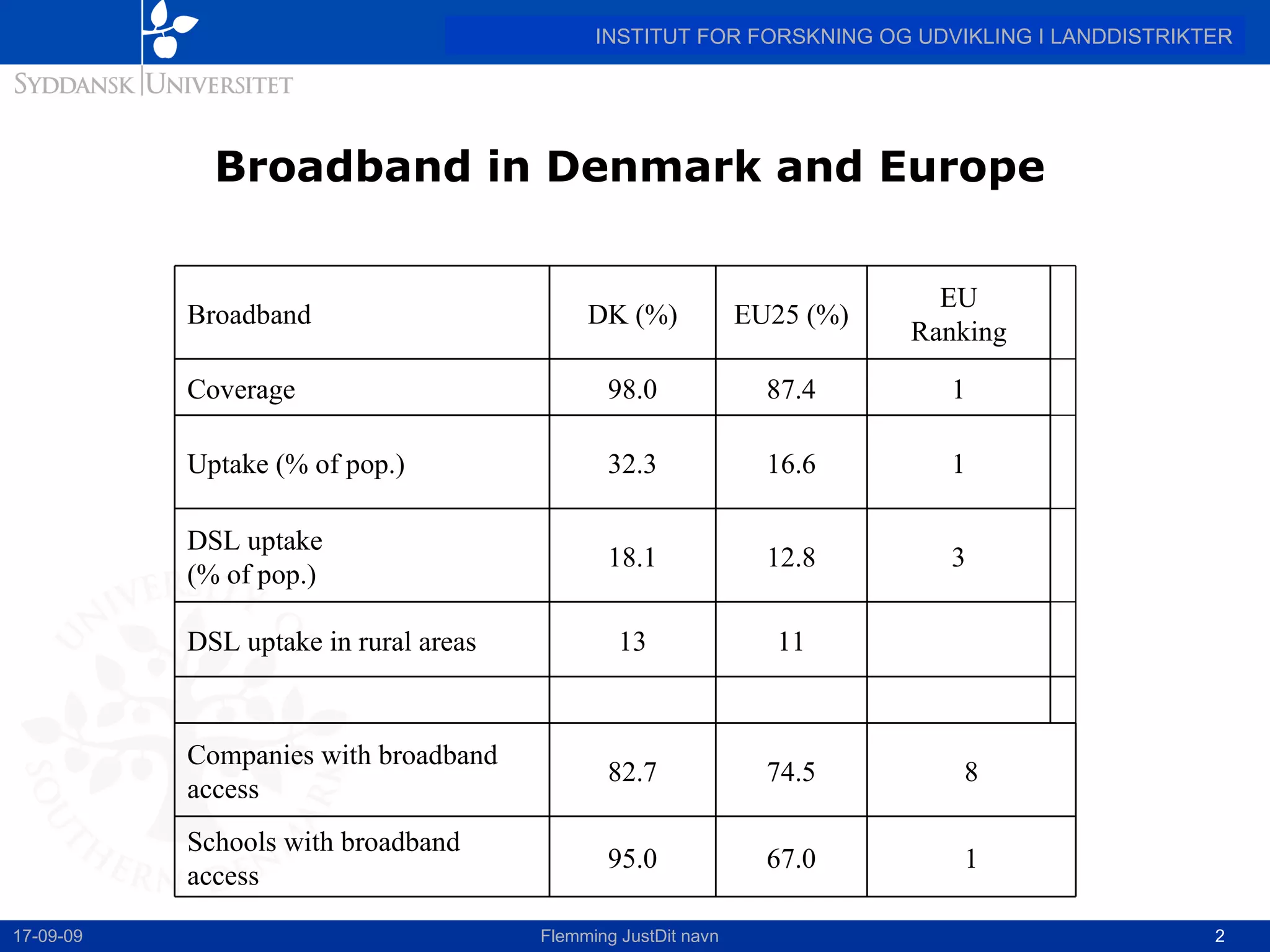
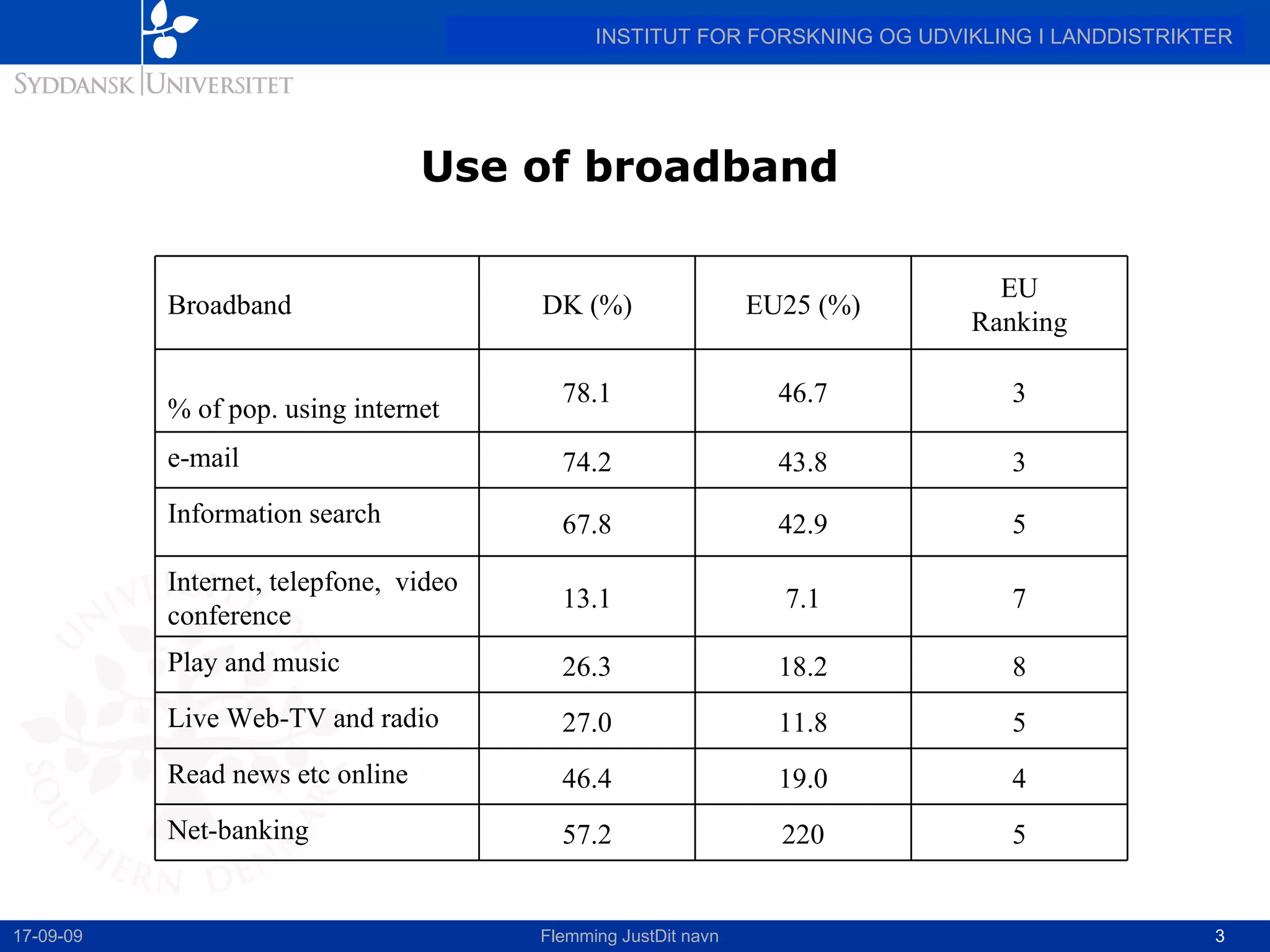
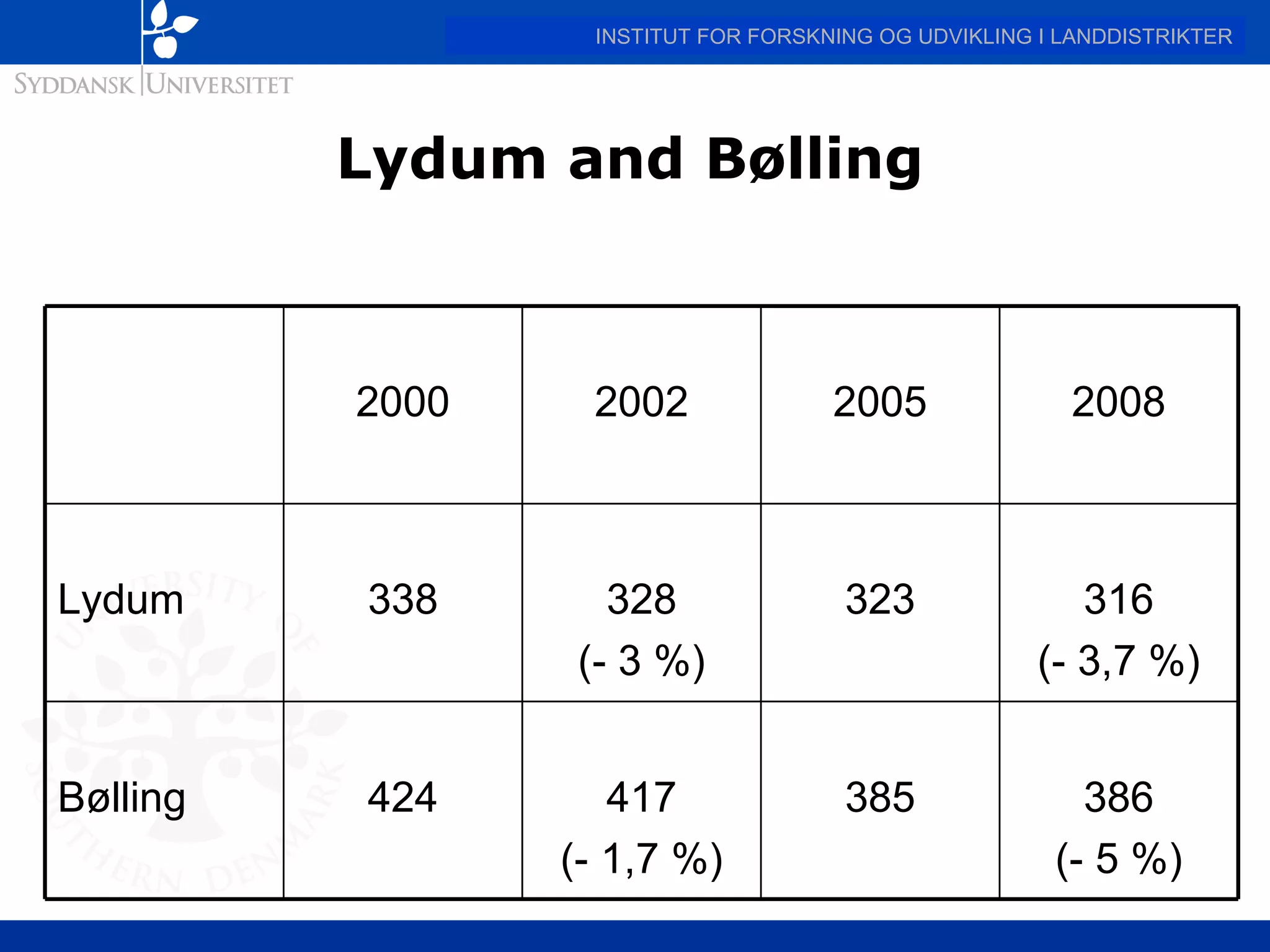
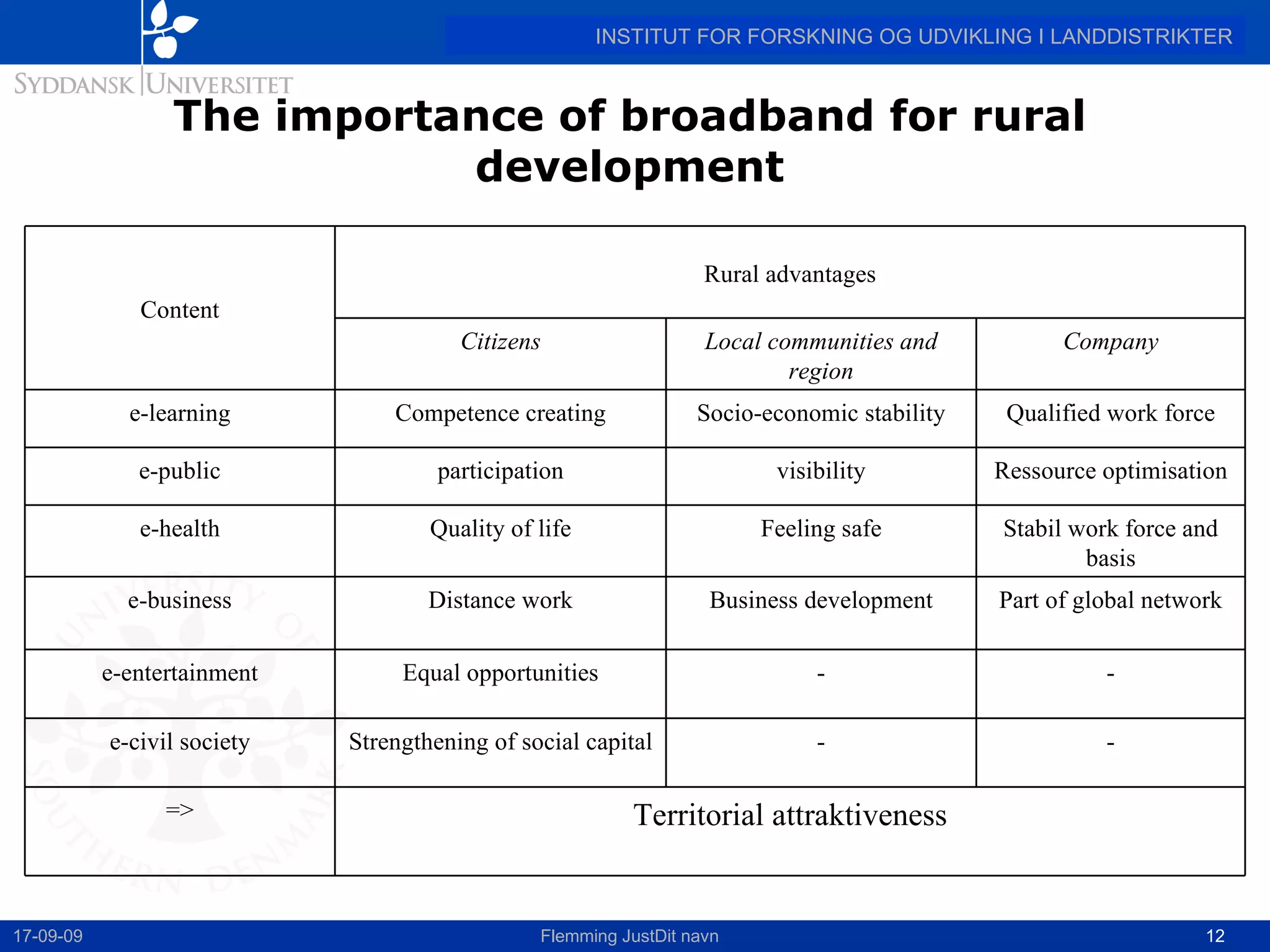
This document discusses the state of broadband in Denmark, highlighting its significant coverage and usage compared to the EU average. It emphasizes the disparities in broadband access and uptake between urban and rural areas, pointing to the slower growth and lower speeds in less developed regions. The report concludes by advocating for broadband as a crucial tool for rural development, urging for political leadership to address the existing broadband gap.