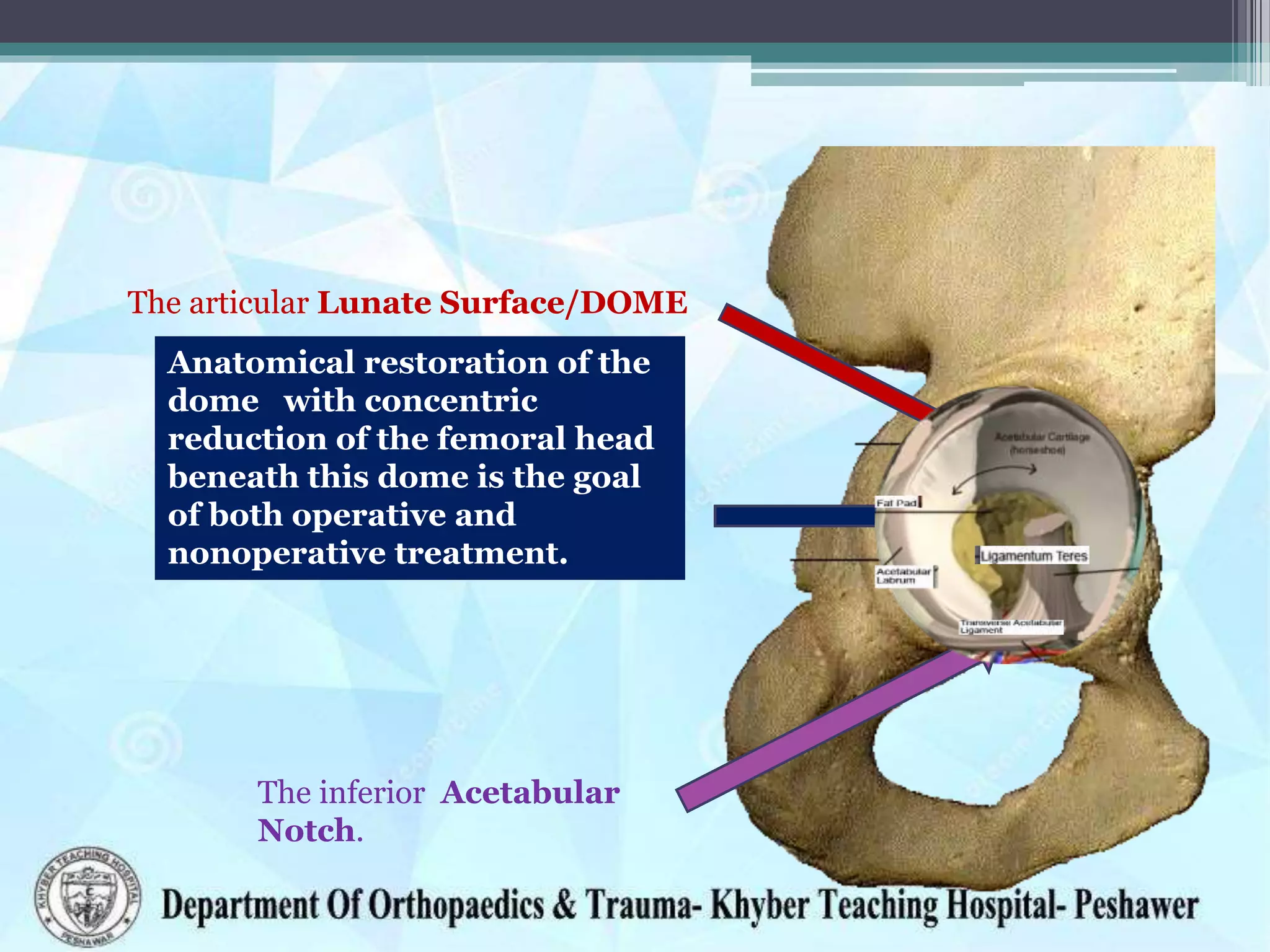
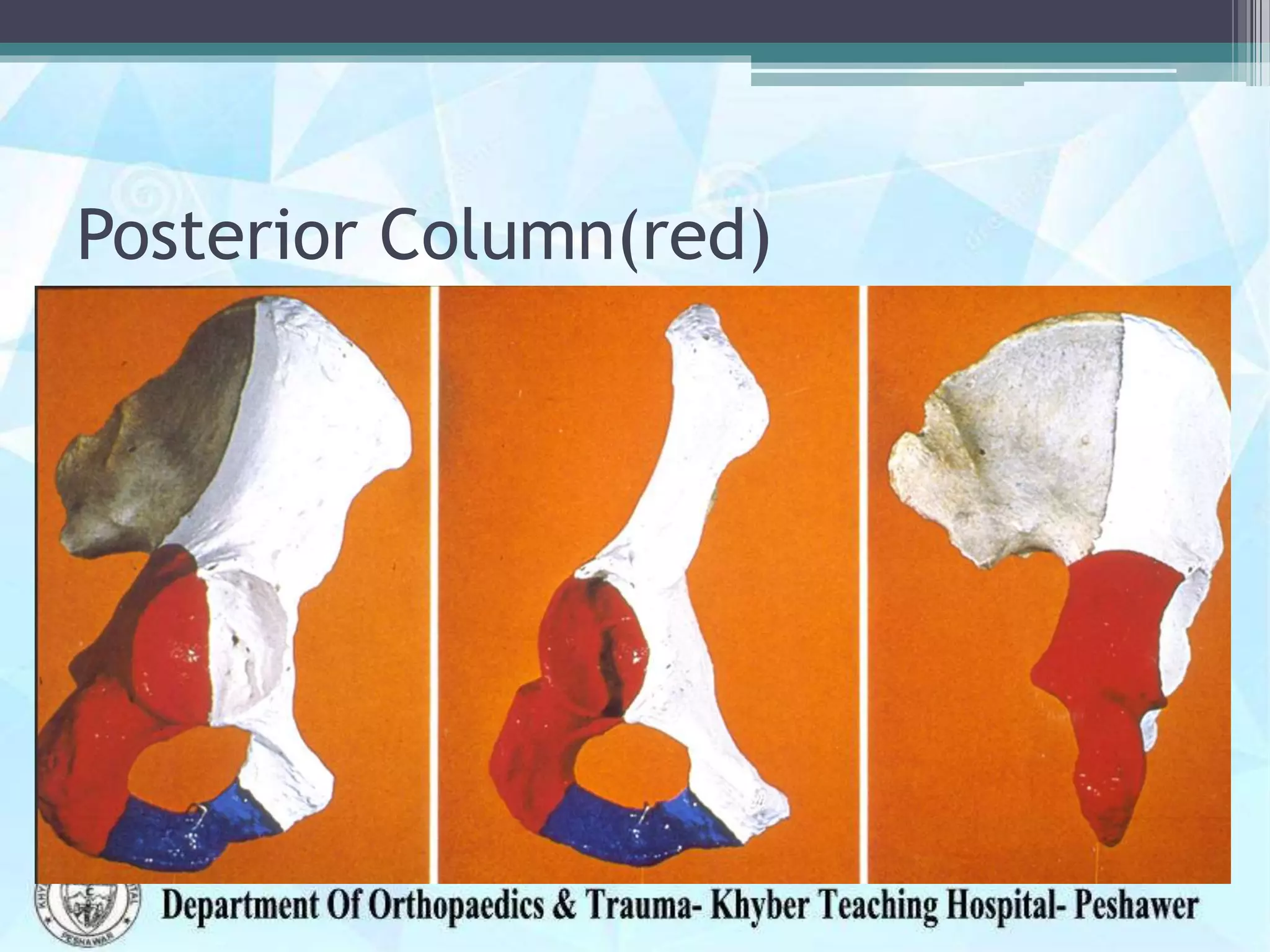
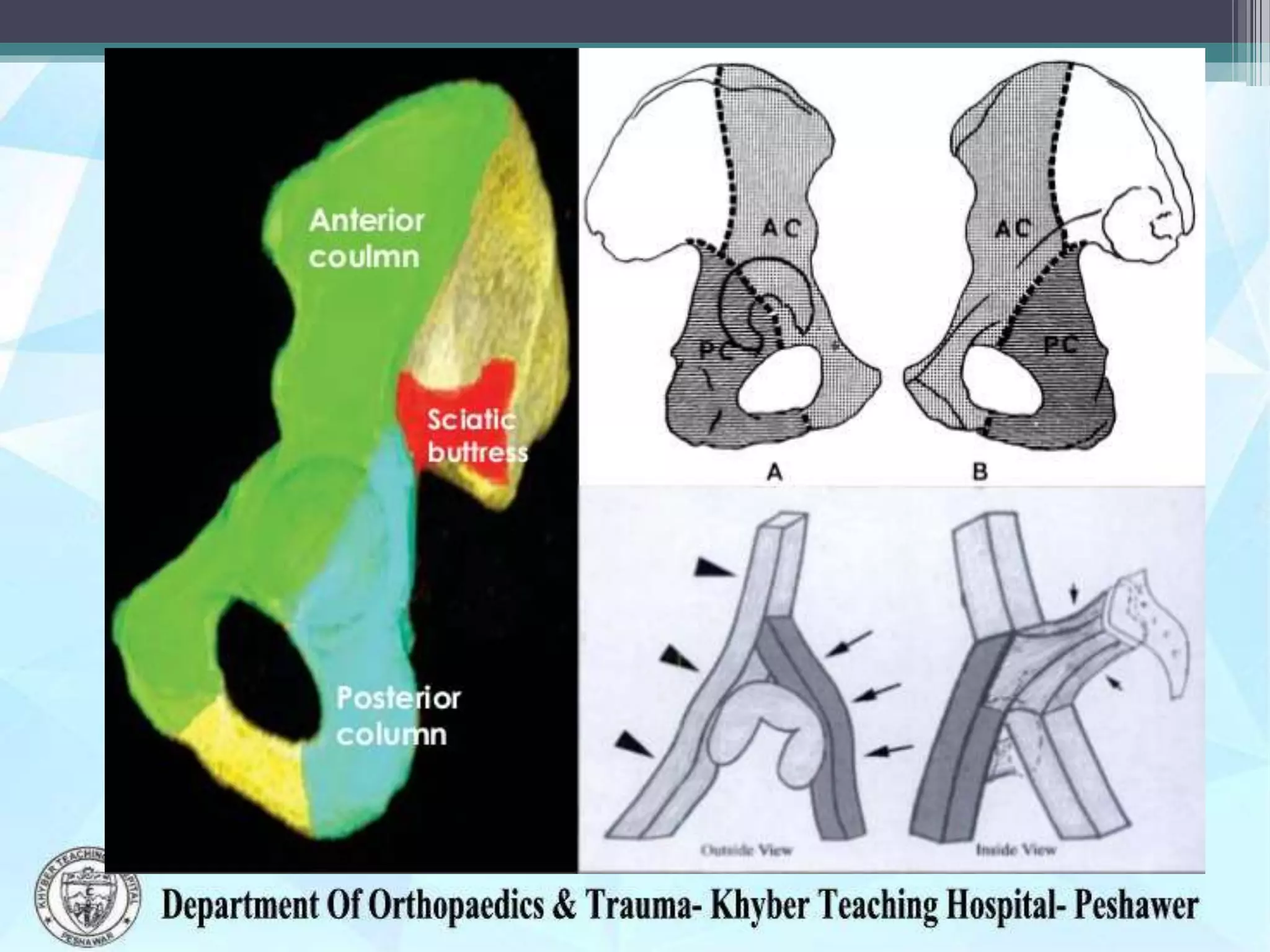
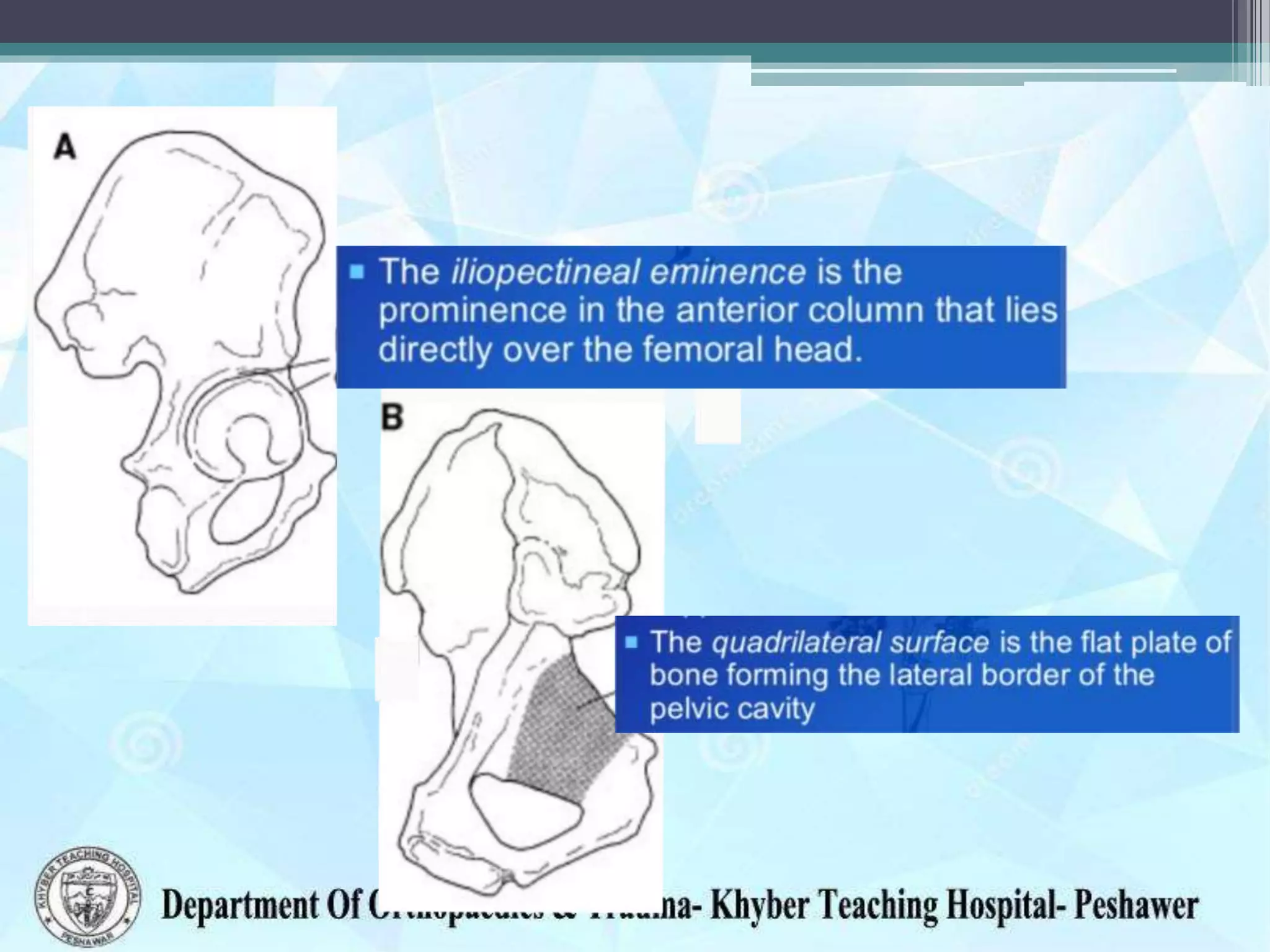
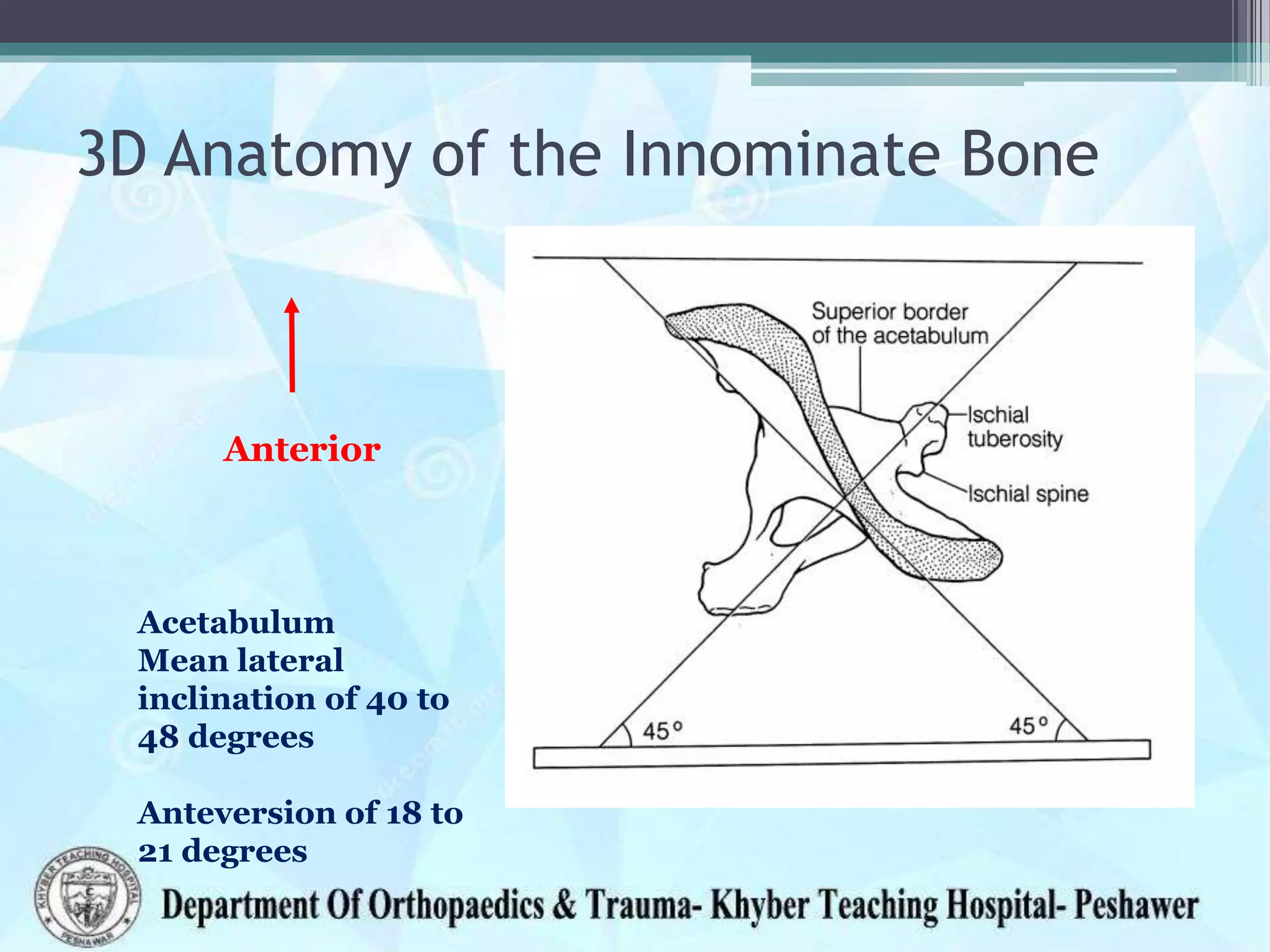
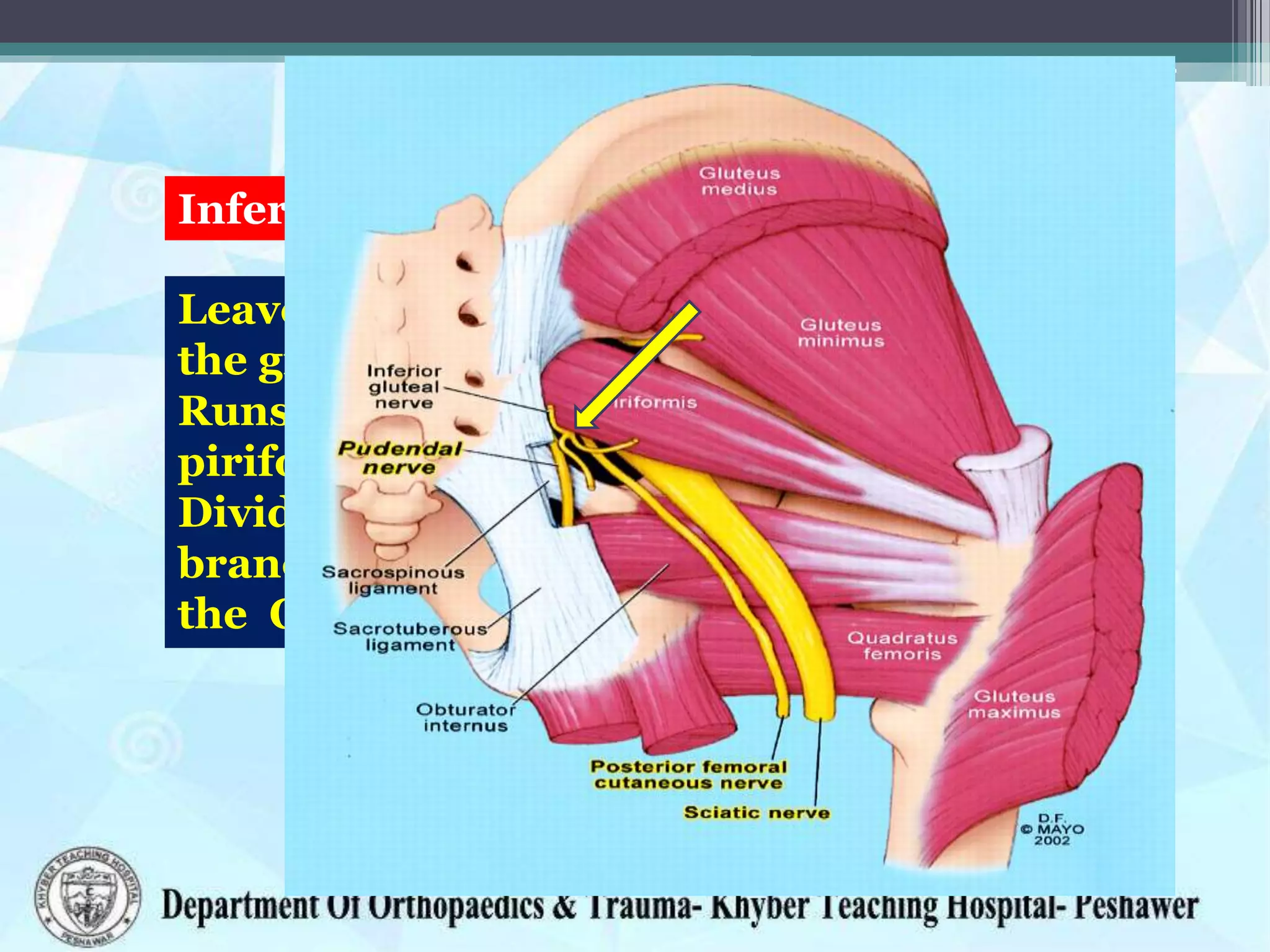
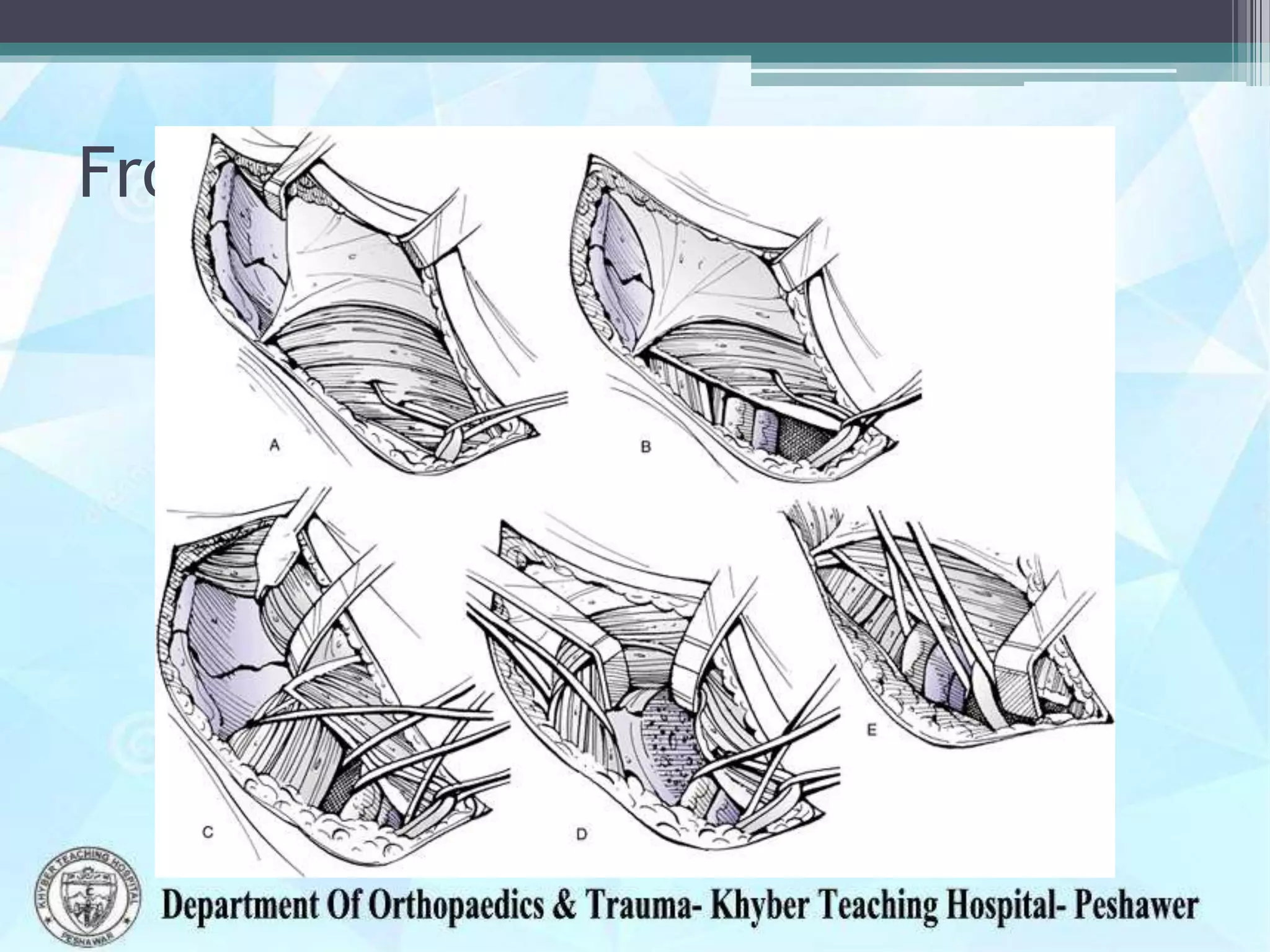
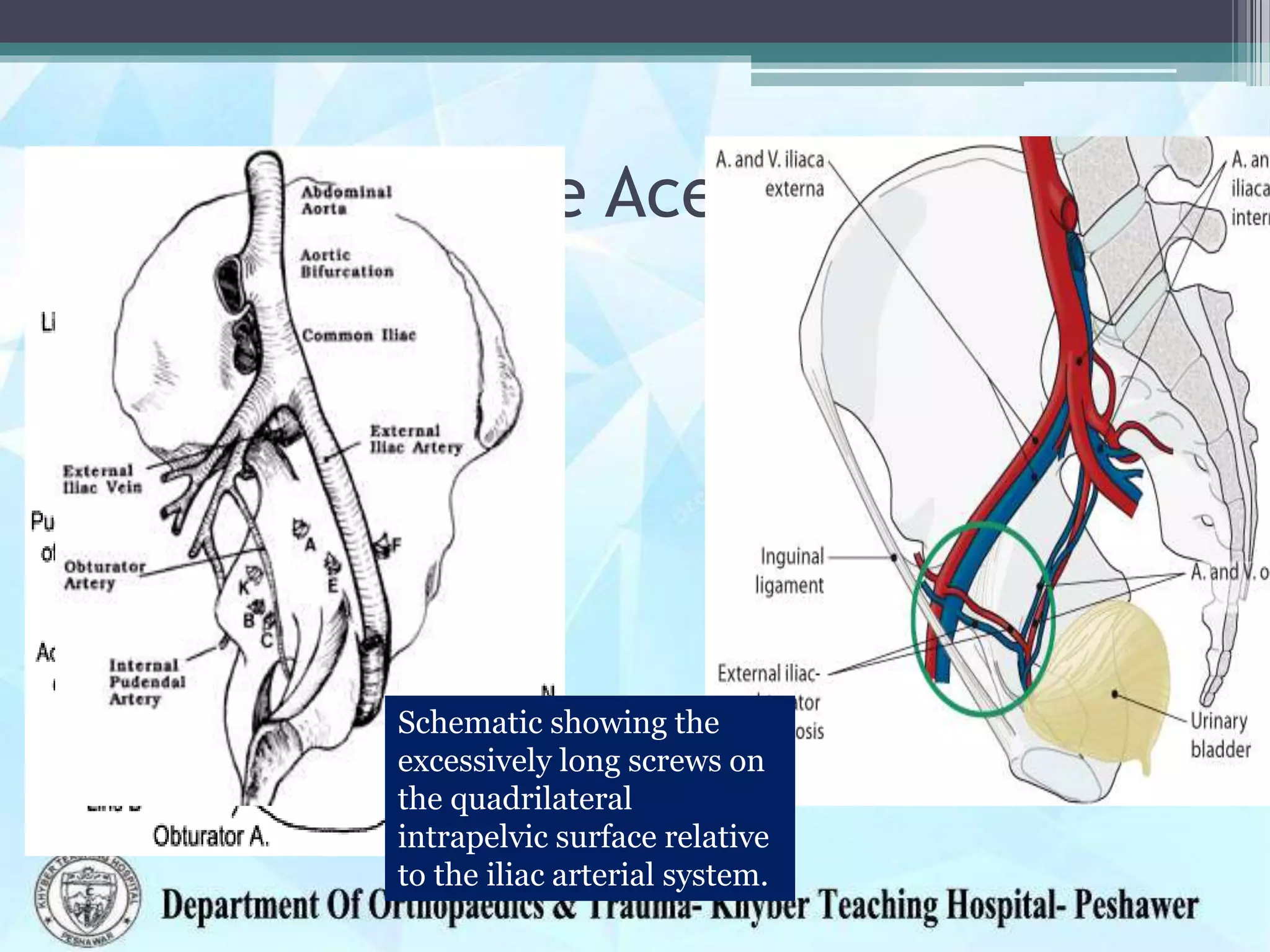
The document provides information on the anatomy of the acetabulum. It discusses:
1) The components that make up the acetabulum where the three bones of the pelvis meet, including the articular surface and acetabular fossa.
2) The embryological development of the hip joint from 4-11 weeks of gestation and continued growth after birth.
3) Structures around the acetabulum including nerves, vessels, muscles and bony landmarks.
4) Forces across the hip joint during various activities from walking to running.