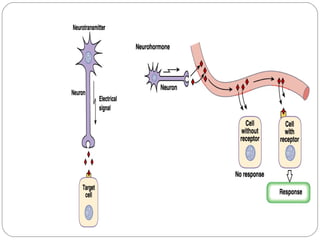
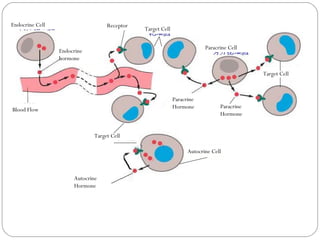
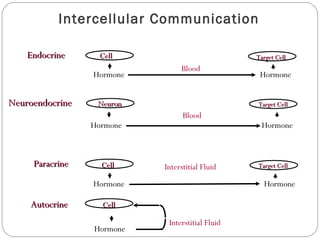
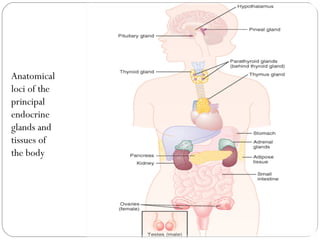
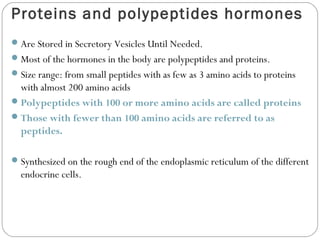
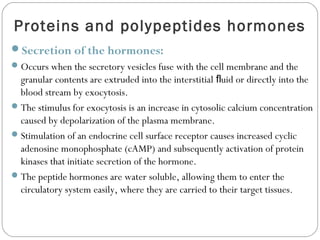
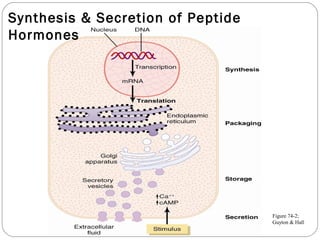
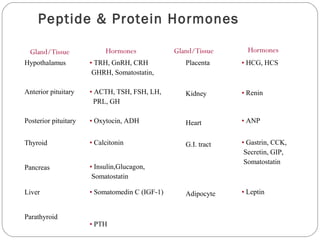
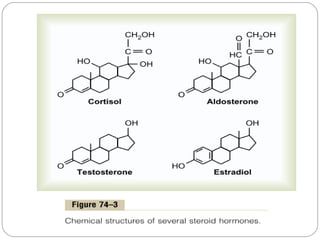
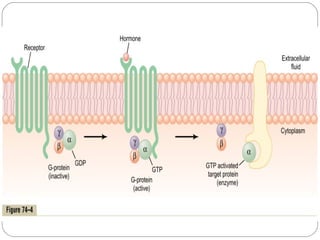
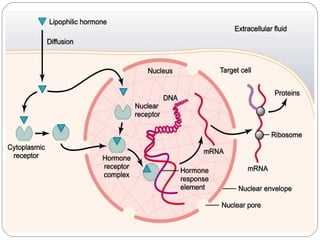
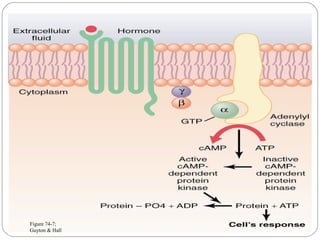
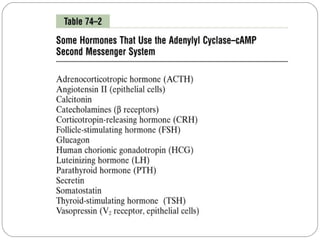
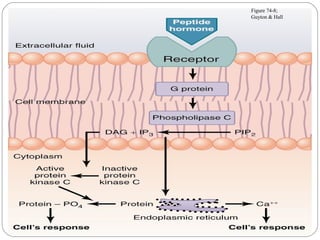
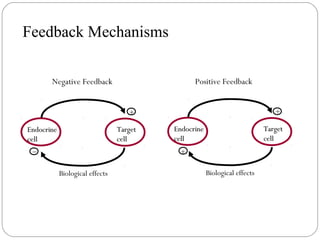
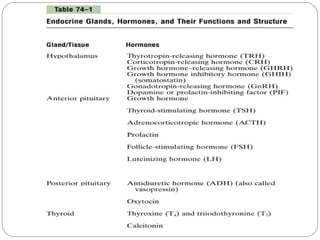
Chemical messengers known as hormones coordinate body functions through various modes of communication between cells. Endocrine hormones are secreted into the bloodstream and target distant cells. Neuroendocrine hormones also target distant cells through the blood. Paracrine hormones act on neighboring cells, while autocrine hormones act on the same cells that secrete them. Hormones can be proteins, peptides, steroids, derivatives of the amino acid tyrosine, or cytokines. They bind to receptors that trigger intracellular signaling cascades to produce physiological responses in target cells.