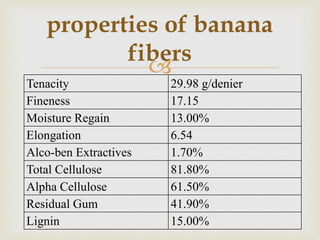
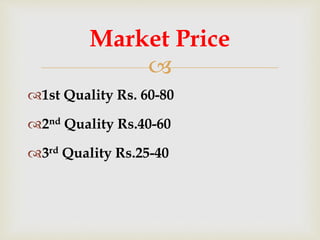
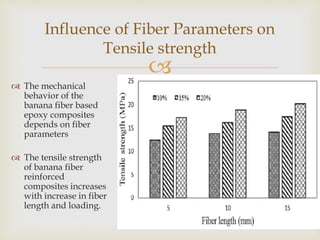
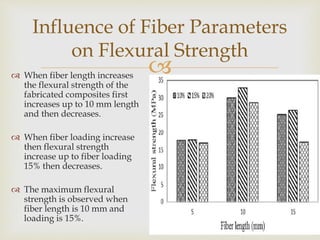
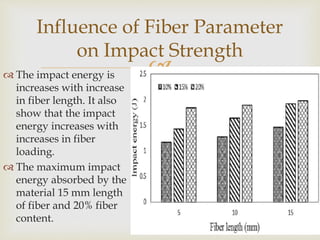
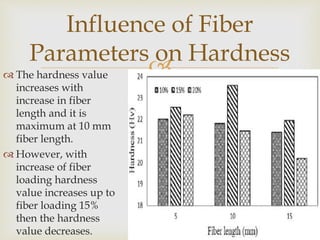
Banana fiber is a natural fiber obtained from banana plants. It has good mechanical properties and is lightweight, strong, and absorbent. Banana fiber can be spun into yarn and woven into textiles. It is also used to reinforce composites, providing strength while being renewable and biodegradable. Research shows banana fiber composites have increasing strength with longer fibers and higher fiber loading up to a point, making it suitable for various applications.