HR-PPT.pptx
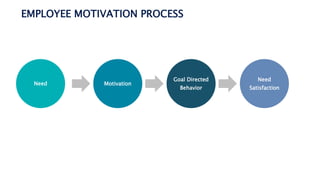
- 1. EMPLOYEE MOTIVATION PROCESS Need Motivation Goal Directed Behavior Need Satisfaction
- 3. EXPECTANCY THEORY (VROOM’S) Yes Yes Motivated No Not Motivated No Not Motivated
- 4. ULRICH’S STAGES OF EMPLOYEE CONNECTION Competence Commitment Connection Productivity x x =
- 5. TUCKMAN TEAM DEVELOPMENT MODEL Time Effectiveness Forming Team is dependent on the leader Storming Leaders mediates and focuses Norming Leader facilities Performing Leader delegates and overseas The leaders goal is to make the team self reliant and then move on. Teams go through four stages. Teams can regress when membership changes. A mature team may need no leadership
- 6. THE FOUR CONTRIBUTION STAGES Explain how careers develop in distinct stages – each different from another. STAGE 1 STAGE 2 STAGE 3 STAGE 4 Dependently Independently Through Others Strategically • Willingly accepts supervision • Demonstrates competence on a portion of a larger project • Performs effectively on detailed and routine tasks • Shows directed creativity and initiative • Performs well under time and budget pressure • Learns how “we” do things • Assumes significant responsibility • Relies on less supervision, works independently and produces results • Builds expertise • Develops credibility and a reputation • Builds a strong collegial network • Develops broader business perspective, help others understand in the broader business context and needs. • Contributes to the performance of others as a manager, mentor, or idea leader. • Represents the work group on important issues. • Builds a strong internal and external network. • Provides strategic direction • Builds organizational capability through work system and process improvement. • Exercise power for the benefit of the organization. • Sponsors and prepares future leaders. • Represents the organization to key external groups on critical strategic issues.
- 8. FORMS OF INCENTIVE COMPENSATION Profit Sharing Gain Sharing Pay for Knowledge Lump-Sum Bonus Bonus based on company profits. Bonus based on productivity gains, cost savings, or quality improvements. Salary increase based on learning new job tasks One time cash-payments or option to buy shares of company stock based on performance.
- 9. MASLOW’S HIERARCHY OF NEEDS THEORY Self- Actualization Esteem Love / Belonging Safety Physiological People have five levels of needs that seek to satisfy Breathing, food, water, sex, sleep, homeostasis, excretion. Security of: body, employment, resources, morality, family, health, property. Friendship, partnership, family, sexual intimacy. Self-esteem, confidence and achievement, respect of others. Morality, idealism, creativity, spontaneity, problem solving.
- 10. HUMAN RESOURCE RESPONSIBILITIES Core Responsibilities of HRM Employee compensation and benefits Employee training and performance evaluation Employee compensation and benefits Planning for staffing needs Employee recruitment and selection
- 11. HRM – DEVELOPMENTAL STAGES FOR SMALL GROUPS Tuckman’s model Forming Storming Norming Performing Team members meet each other Team members learn about the task All team members learn what their roles will be Team members learn how to work together Team members learn about the other members Leader focuses the team Team starts to work and act together Roles evolve into helping the team succeed Team members are more likely to express opinions Team members work hard toward goal Members are flexible and help each other Leader’s role is blurred – everyone is focused
- 12. ULRICH’S HR COMPETENCY MODEL Credible Activist Capability Builder HR Innovator & Integrator HR Innovator & Integrator Change Champion Strategic Positioner
- 13. THE LEADERSHIP CODE – 5 RULES FOR LEADERSHIP Personal Proficiency Human Capital Developer Build the next generation Strategist Shape the future Executor Make things happen Talent Manager Engage today’s talent Individual Organization Near-Term Operational Long-Term Strategic
- 14. OPERATIVE FUNCTIONS OF HRM Compensation Procurement Development Maintenance /Motivation Integration • Job analysis and design • Human resource planning • Recruitment • Selection • Placement • Orientation • Socialization • Industrial relations • Discipline • Grievance redressed • Dispute settlement • Collective bargaining • Employee well-being • Social security • Worker’s participation • Motivation • Job rotation • HR Records, research and audit • HR information system • Job evaluation • Performance evaluation • Wages administration • Incentives and benefits • Career planning and development • Worker’s training • Executive development • Organizational development
- 15. FOUR STAGES OF CONTRIBUTION MODEL Key Transitions (Novation’s) Impact Contribute Strategically Contribute Through Others Contribute Independently Contribute Dependently
- 16. PEOPLE CAPABILITY MATURITY MODEL Level 5 Optimizing Level 4 Managed Level 3 Defined Level 2 Repeatable Level 1 Initial People Management Competence Management Team Management Capability Management Managed practices Tailored practices Measured and aligned practices Continuously improving practices
- 17. HERZBERG’S THEORY OF MOTIVATION Hygiene Factors Motivational Factors • Interpersonal relationships, supervisors, peers and subordinates • Technical supervision • Company policy administration • Job security • Working conditions • Salary / personal life • Work itself • Achievement • Possibility of growth • Responsibility • Advancement / Recognition • Status
- 18. GUEST MODEL OF HRM Human Resource Outcomes • Strategic planning/ implementation • Commitment • Flexibility/ adaptability • Quality Policies • Organizational job design • Policy formulation and implementation/management of change • Recruitment, selection and socialization • Appraisal, training and development • Manpower flows, through, up and out of the organization • Rewards systems • Communications system Organizational Outcomes • High job performance • High problem-solving • Successful change • Low turnover • Low absence • Low grievance level • High cost-effectiveness
- 19. HR COMPETENCY MODEL – SHRM Communication Relationship Management Ethical Practice HR Expertise Leadership and Navigation Consultation Diversity and Inclusion Business Critical Evaluation
- 20. HR ANALYTICS MATURITY MODEL Stage 4: Predictive Analysis Development of predictive models, scenario planning, risk analysis and mitigation, integration with strategic planning Stage 3: Strategic Analysis Segmentation, statistical analysis, development of people models, analysis of dimensions to understand cause and delivery of actionable solutions. Stage 2: Advanced Reporting Operational reporting for benchmarking and decision making, multi- dimensional analysis and dashboards. Stage 1: Operational Reporting Operational reporting for measurement of efficiency and compliancy, data exploration and integration, development of data dictionary
- 21. Level 4: Organizational Capability Source of: Business performance capability & learning agility, executive drive, cultural & systematic focus Level 3: Talent & performance improvement Source of: talent development and performance consulting, integrated with HR/TM improving alignment, process & tech focus. Level 2: Training and developing excellence Source of: designed instruction, evolving governance & operations, improving L&D core processes, program focused. Level 1: Incidental Training Source of: ad-hoc job support, mentoring and apprenticeship, emerging need for professional training, SME focused. HIGH IMPACT LEARNING ORGANIZATION MATURITY MODEL
- 22. HRM GOALS Motivation • TQM and productivity • Rewards • Compensation Development • Employee training • Employee development Maintenance • Benefit administration • Safety and health • Communication • programs Inception • Strategic human • Resource planning • Recruiting • Employee presentation HRM Goals
- 23. MODEL OF STRATEGIC HRM Corporate Objective HR Objective Individual Objectives Developing and Retaining Letting Go Recognizing Assessing Staffing Planning
- 24. NEW HR COMPETENCY MODEL Strategic Contribution Culture Management Fast Change Strategic Decision-Making Market-driven Connectivity • Achieving results • Effective relationships • Personal Communication • Staffing • Development • Organizational structure • Performance Management
- 25. THE WARWICK MODEL OF HRM Outer Context Socioeconomic, Technological, Political-legal, Competitive Inner Context Culture, structure, politics/leadership, task technology, business outputs HRM Content HR flows, work systems, reward systems, employee relations HRM Context Role, definition, organization, HR outputs Business Strategy Content Objectives, product market, strategy and tactics
- 27. Mental Models Personal Mastery Systems Thinking Building Shared Vision Team Learning 5 COMPONENTS OF A LEARNING ORGANIZATION Focusing on group solving using systems thinking
- 28. INTEGRATING HRM WITH BUSINESS OUTCOMES Shared Understanding Shaping The Working Environment Human Resourcing Continuous Learning Performance Accountability
- 29. HR MANAGEMENT ACTIVITIES Environmental • Strategic human • Resource planning • Recruiting Talent Management • Strategic human • Resource planning • Recruiting Total Rewards • Strategic human • Resource planning • Recruiting Risk management and worker protection • Strategic human • Resource planning • Recruiting Staffing • Strategic human • Resource planning • Recruiting Employee & Labor Relations • Strategic human • Resource planning • Recruiting Legal Framework & Practice • Strategic human • Resource planning • Recruiting Legal Political Technological
- 30. HR COMPETENCY MODEL International Personnel Management Association (IPMA) Model Leader HR Expert Business Partner Change Agent
- 31. HUMAN RESOURCE DEVELOPMENT Training Development Performance Appraisal Performance Management Career Planning Career Development Organization Development Designed to provide learners with knowledge and skills Designed to provide learners with knowledge and skills Designed to provide learners with knowledge and skills Designed to provide learners with knowledge and skills Designed to provide learners with knowledge and skills Designed to provide learners with knowledge and skills Designed to provide learners with knowledge and skills
- 32. THE HARVARD MODEL OF HRM Stakeholder Interests Stakeholders Management Employee groups Government Community / Unions Situational Factors Stakeholders Management Employee groups Government Community / Unions HRM Policy Choices Stakeholders Management Employee groups Government HR Outcomes Stakeholders Management Employee groups Government Long-Term Consequences Stakeholders Management Employee groups
- 33. FOUR STAGES OF CONTRIBUTION MODEL Performance Expectation Primary Role Major Stage Transition Issue Minor Stage Transition Issue Dependently Independently Through Others Strategically Designed to provide learners with knowledge and skills Designed to provide learners with knowledge and skills Designed to provide learners with knowledge and skills Designed to provide learners with knowledge and skills Designed to provide learners with knowledge and skills Designed to provide learners with knowledge and skills Designed to provide learners with knowledge and skills Designed to provide learners with knowledge and skills Designed to provide learners with knowledge and skills Designed to provide learners with knowledge and skills Designed to provide learners with knowledge and skills Designed to provide learners with knowledge and skills Designed to provide learners with knowledge and skills Designed to provide learners with knowledge and skills Designed to provide learners with knowledge and skills Designed to provide learners with knowledge and skills STAGE 1 STAGE 2 STAGE 3 STAGE 4
- 34. ULRICH’S MODEL OF HRM
- 35. Change Management Performance Improvement Instructional Design Knowledge Management Coaching Training Delivery Learning Technologies Integrated Talent Management Managing Learning Programs Evaluate Learning Impact Competencies for the Training & Development Profession Areas of Expertise Foundation Competencies Business Skills Global Mindset Industry Knowledge Interpersonal Skills Personal Skills Technology Liberace ASTD COMPETENCY MODEL (2013)
- 36. THE EMOTIONAL COMPETENCY FRAMEWORK Self Others Awareness Actions Self Awareness Social Awareness Social Skills Self Management Positive impact on others An HR department is an essential, if not critical, component of any business regardless of the organization's size. An HR department is an essential, if not critical, component of any business regardless of the organization's size. An HR department is an essential, if not critical, component of any business regardless of the organization's size. An HR department is an essential, if not critical, component of any business regardless of the organization's size.
- 37. ULRICH’S MATRIX ON THE 4 ROLES OF HR Day to day / Operational Focus People Process Future / Strategic Focus HR Strategic Partner An HR department is an essential, if not critical, component of any business regardless of the organization's size. Change Agent An HR department is an essential, if not critical, component of any business regardless of the organization's size. Administrative Expert An HR department is an essential, if not critical, component of any business regardless of the organization's size. Employee Champion An HR department is an essential, if not critical, component of any business regardless of the organization's size.
- 38. MCLAGAN’S HUMAN RESOURCE WHEEL Training & Development Organization Development HR Research & Info Systems Union / Labor Relations Career Development Organizational/ Job Design Employee Assistance Compensation & Benefits Human Resource Planning Performance Management System Selection & Staffing Human Resource Result An HR department is an essential, if not critical, component of any business regardless of the organization's size. Primary HRM Functions Obtaining, Maintaining and developing employees. Primary HRD Functions Improving individual, group, and organizational effectiveness.
- 39. THE HR PROFESSION MAP BY CIPD Organization design Service delivery and information Learning and talent development Performance and reward Resourcing and talent planning Employee engagement Organization development Employee relations Strategy insights and solutions Leading and managing the human resource function
- 40. BRIDGES TRANSITION MODEL Time Importance Ending, Losing, Letting Go The New Beginning
- 41. ULRICH’S MATRIX ON THE 4 ROLES OF HR Day to day / Operational Focus People Oriented Process Oriented Future / Strategic Focus HR Strategic Partner Management of strategic human resources Change Agent Management of transformation and change Administrative Expert Management of firm infrastructure Employee Champion Management of employee contribution
- 42. HR STRATEGY MAP Enhance ROI of HR Strategic Initiatives Enhance employee productivity Create positive work environment Enhance “Internal Customer” satisfaction Apply excellent recruitment process Develop strategic employee competencies Implement best talent management practices Optimize performance management system Develop Internal HR Capabilities Deploy HRIS System Financial Internal Customers HR Internal Process Learning
- 43. HIGH IMPACT TALENT MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK Leadership Management Succession Management Career Management Performance Management Capability & Competency Management Workforce Planning TALENT INFRASTRUCTURE Talent Strategy & Business Alignment Learning & Capability Development Talent Acquisition Total Rewards Business Metrics & Scorecards Governance
- 44. EVOLUTION OF HR MANAGER ROLES Leader • Ethical • Takes risks • Decisive • Develops staff • Creates trusts Employee advocate Values diversity Resolves conflict Communicates well Respects other Functional expert Knows HR Principles Customer oriented Applies business Manages resources HC developer Individual focus Manages change Future Orientation CoachTeam Relationships Strategic partners Mission oriented Strategic planner System Innovator Understands team behavior
- 45. CHANGING VALUES – CHANGING WORK STYLES -1945 Traditionalist • Avoid • System conformant • Little willingness to change -1962 Boomer • Tetchy towards criticism • Impartial • Egocentric • Focused more on processes than results -1980 Generation X • Impatient • Sceptic • Lazy • Low level of assertiveness • Cynical 1981+ Generation Y • Needs guidance • Requires (company) structures • Lacks << personal drive • Disloyal
- 46. HR MANAGEMENT – TASKS Main areas plus overall tasks Staff Recruiting • Personnel planning • Recruiting • Personnel marketing • Selection of personnel • Education and training Employ Staff • Staff allocation • Staff transfer and relocation • Staff care • Staff training and development • Staff detainment • Performance appraisal • Payroll • HR administration Staff Lay-off • Redundancies • Staff reduction Overall Responsibilities • HR company policy • HR organization • Personnel management • HR communication • HR controlling • Works council • Labor laws and social welfare
- 47. HR MANAGEMENT – TARGET GROUPS Target groups for HR work (internal, external) Internal Groups External Groups Company management Senior office Works council Employee Apprentice Trainee Student trainee Other employees General government Trade association Chamber of trade/Chamber of commerce Employment agency Surroundings Temporary employment agencies Executive consultants Other companies
- 48. DEVELOPMENT STAGES OF HRM How HRM has turned into a strategic competitive advantage HR Administration HR Structuring HR Development HR Strategy HR cross-link to other departments Integration of personnel competencies Payroll. Rights of co-determination HRM institutionalization and personnel planning Recognition of workforce assets and career planning Value-add through HR work HRM as competitive advantage Professionalization of HR, development of HR vision By 1950 By 1960 By 1970 By 1980 By 1990 By 2000 Development Stages Key Examples
- 49. THE EFFECTS OF DYNEXITY Dynexity causes changes in HR management Number of Employees Constant change of employee numbers e.g. due to company growth or downsizing. Number of Employees Constant change of responsibilities and subjects. Structures & Processes Constant change of structures and processes. Dynamic Business Environment
- 50. OVERVIEW OF COMPETENCIES HR Key competencies Operational Expertise Method Skills Personal Skills Social Competencies • Labor law expertise • Expertise in business administration • Expertise in teaching psychology • Expertise in organizational psychology • Analytical skills • Didactical skills • Computer skills • Expertise in evaluation and organization • Presentation skills • Project management skills • Organization-oriented acting and thinking • Assertiveness • Empathy • Communication skills • Conflict management skills • Problem solving skills • Sociable • Ability to motivate others • Persuasive power • Team player • Resilience • Flexibility • Credibility • Integrity • Creativity • Ability to learn • Self-critical, self-analytical • Self-consistent • Goal achiever
- 51. HR JOB TITLES – CAREER PROGRESSION VP of HR of CHARO HR Director HR Manager HR Generalist HR Assistant/Intern Recruiting Manager Recruiter Senior Recruiter Subject Matter Expert (Consultant) HR Specialist Advanced Specialist (Role benefits, training, etc.)
Editor's Notes
- Sadgasdgfasdgfasdfasdfº
- sdfasdfasdf