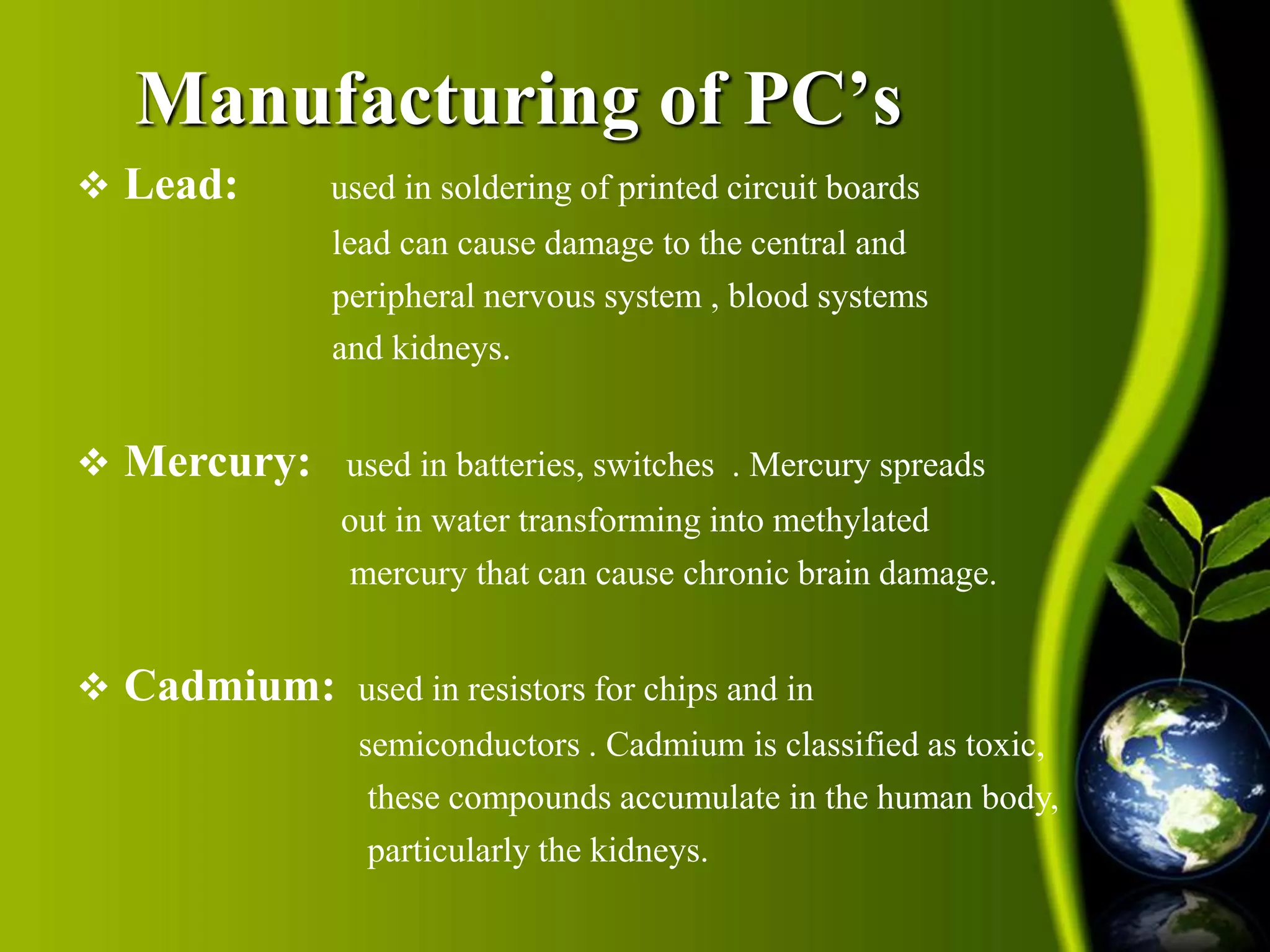
This document discusses green computing and how to reduce the environmental impact of computing. It describes how green computing aims to efficiently use computing resources and design, manufacture, and dispose of computers with minimal environmental impact by reducing hazardous materials and maximizing energy efficiency. Specific green approaches discussed include using more sustainable materials like bamboo in manufacturing, implementing power management features to reduce energy usage, and properly disposing of e-waste to avoid toxic chemicals polluting the land. The overall goal of green computing is to lessen computing's carbon footprint and make the industry more environmentally friendly.