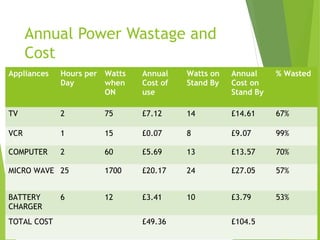
The document discusses green computing, defined as designing and using computers in an environmentally friendly manner, covering its benefits, hazards of non-green computing, and manufacturing impacts, particularly from toxic materials. It highlights the importance of proper disposal of electronic waste and offers strategies for reducing energy consumption through various practices like reusing and recycling components. Additionally, it mentions the Energy Star program as an initiative to label energy-efficient products, promoting reduced environmental impact.