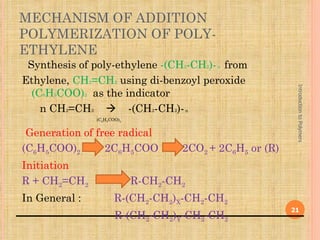
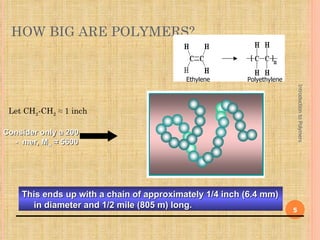
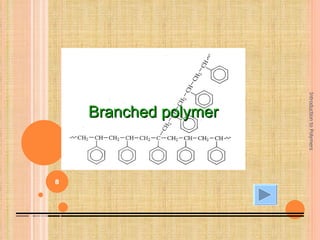
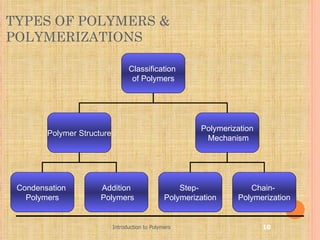
Polymers are macromolecules formed by linking together small repeating units called monomers. There are two main types of polymerization: addition and condensation. Addition polymers are formed without the elimination of small molecules when monomers containing carbon-carbon double bonds polymerize via a chain reaction mechanism involving three steps: initiation, propagation, and termination. Condensation polymers are formed with the elimination of small molecules like water or ammonia when bifunctional monomers react. Common examples of addition polymerization include polyethylene formed from ethylene monomers using a free radical initiator like benzoyl peroxide.









![ADDITION POLMERIZATION
Self addition of several bifunctional monomers to
each ohter takes place by chain reaction without
the elimination of any simple molecules.
Introduction to Polymers
GENERAL REACTION:
n [CH2=CH] [-CH2-CH-]n
| |
Y Y
Where Y=H,Ethylene,CH3,Propylene,Cl, Vinyl 15
Chloride, C6H5, Sterene, CN , Acrylonitrile](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/polymers-120412110202-phpapp01/85/Polymers-15-320.jpg)

![CONDENSATION
POLYMERIZATION
• Self addition of several bifunctional monomer to
each other takes place accompanying elimination
of simple molecues like H2O,NH3 & HCL
Introduction to Polymers
• General reaction:
n[HOOC-X-COOH] + n[HO-Y-OH]
HO-[….OC-X-COO-Y-O]n-H + (2n-1)H20
17](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/polymers-120412110202-phpapp01/85/Polymers-17-320.jpg)
![E.g..
Terylene is obtained by condensing terpthalic
Introduction to Polymers
acid [HOOC-C6H4-COOH] with ethylene glycol
[HO-C2H4-OH]
Nylon is made by the condensation of adipic acid
[HOOC-(CH2)4-COOH] with hexamethylene
diamine [NH2-(CH2)6-NH2]
18](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/polymers-120412110202-phpapp01/85/Polymers-18-320.jpg)
![MECHANISM OF ADDITION POLYMERIZATION
{FREE RADICLE REACTION MECHANISM}
Free Radical Mechanism of chain reaction
involves 3 stages namely
Introduction to Polymers
II. Initiation
III.Propagation
IV.Termination
SCHEMATIC REPRESENTATION
[ R* - Free radical
M* - Unsaturated Monomer]
19](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/polymers-120412110202-phpapp01/85/Polymers-19-320.jpg)