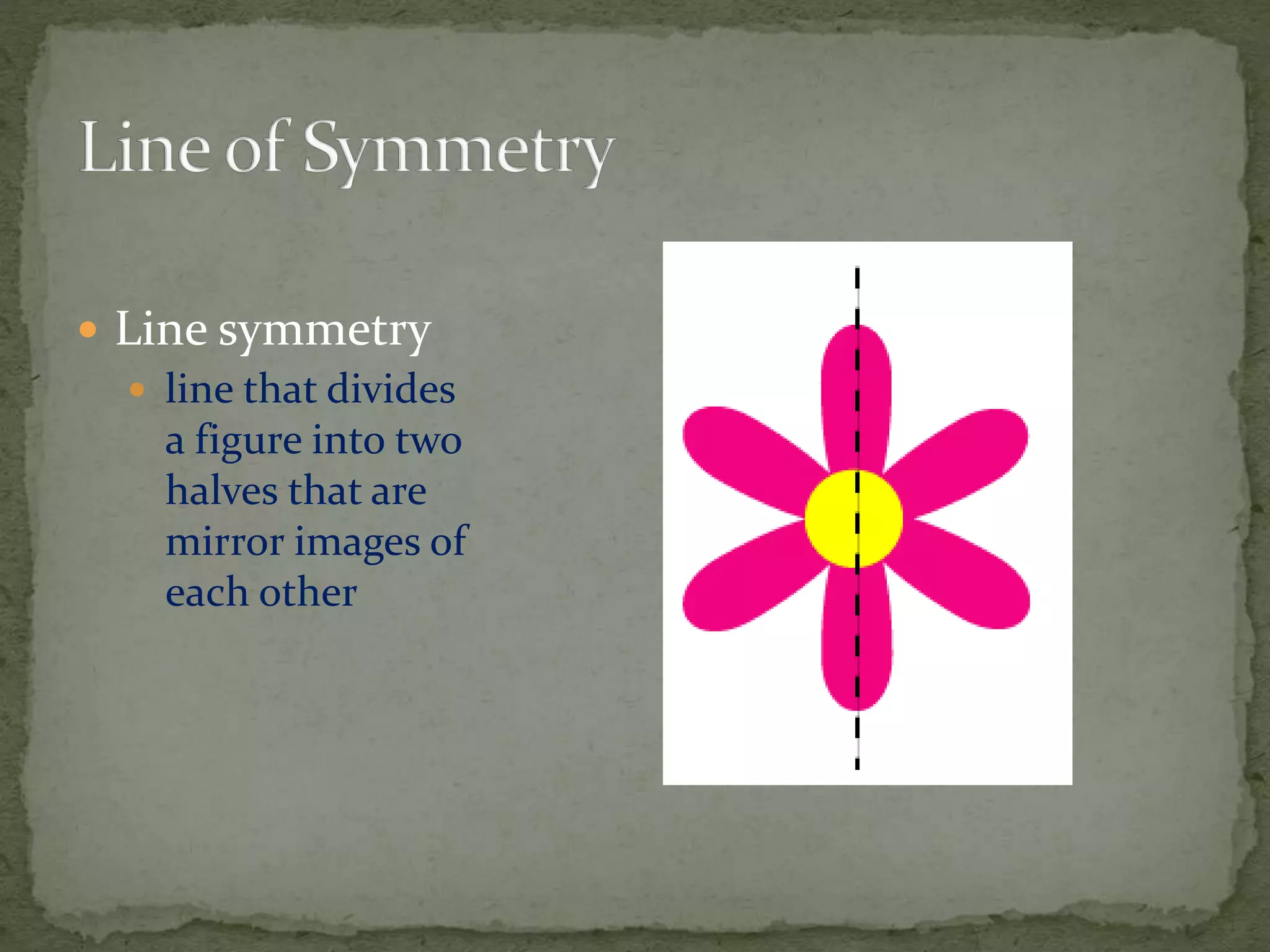
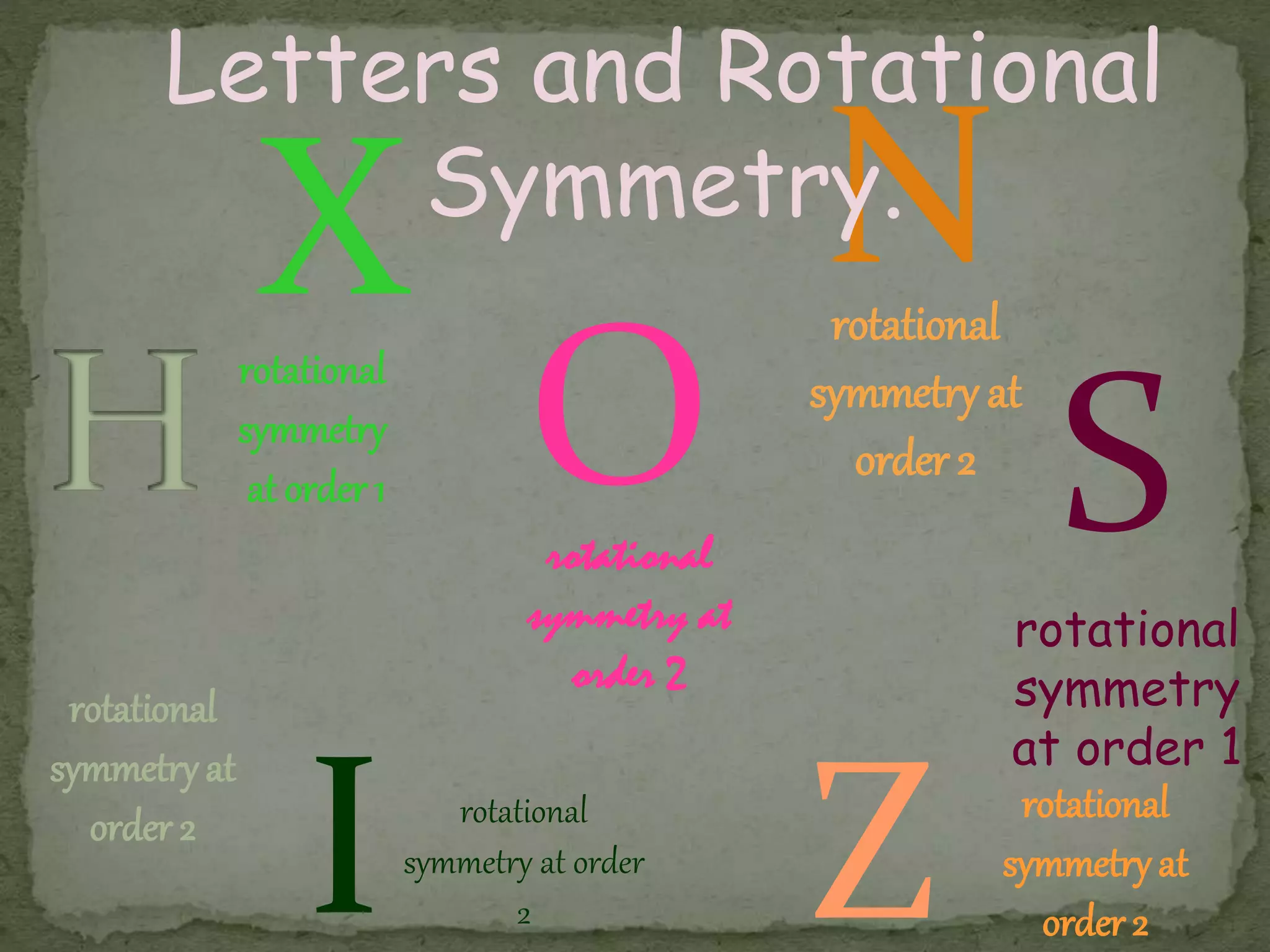
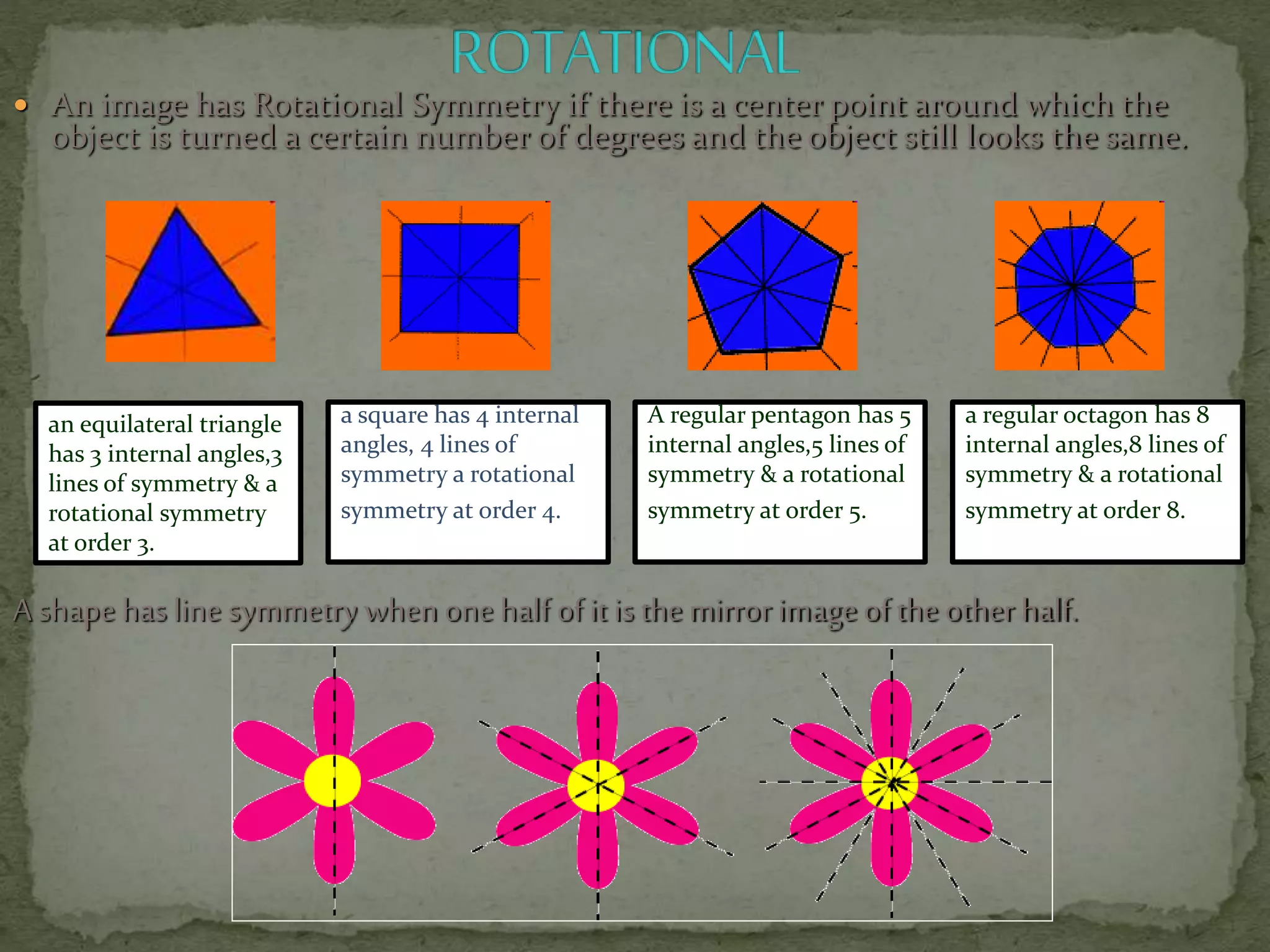
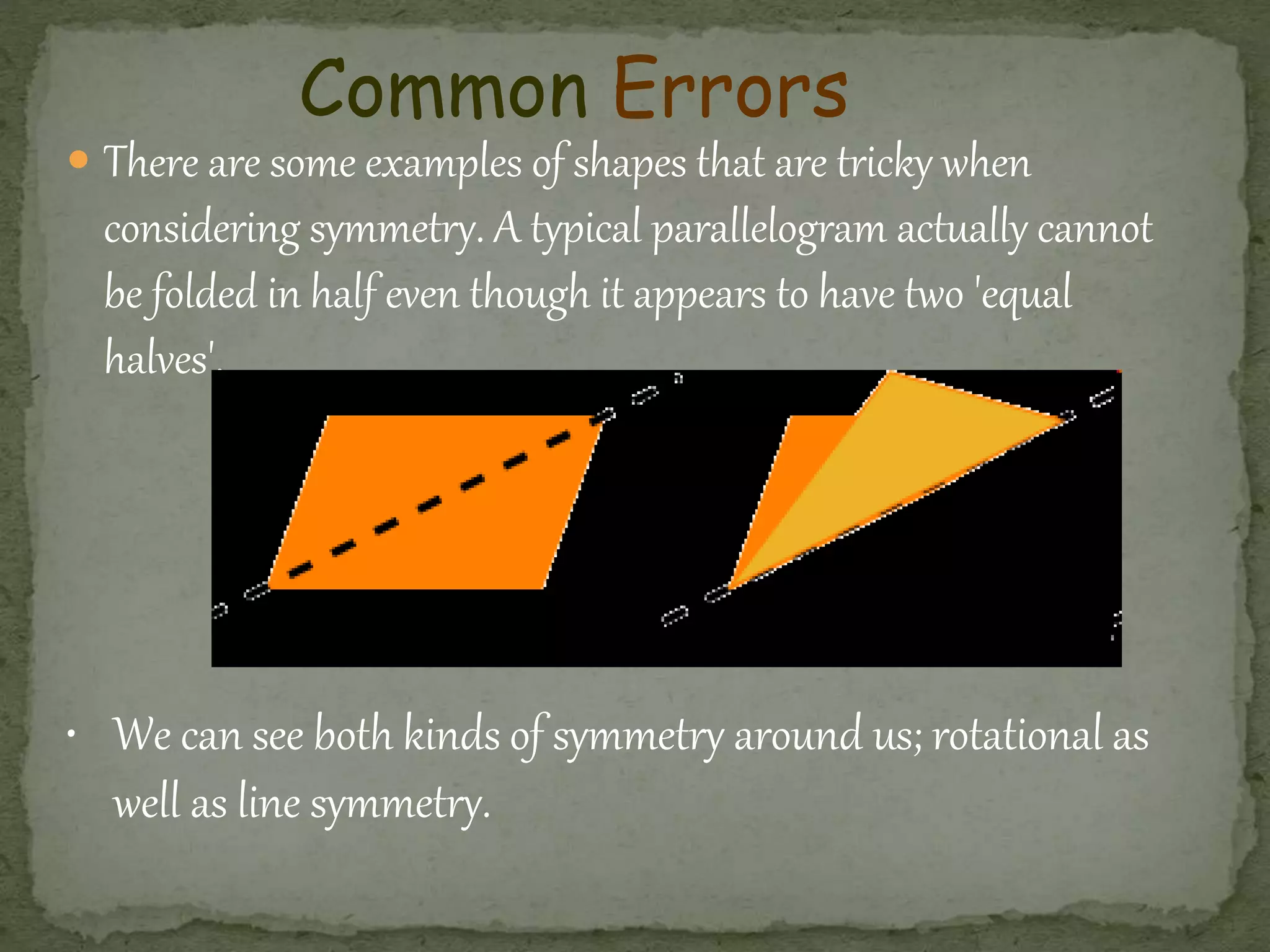
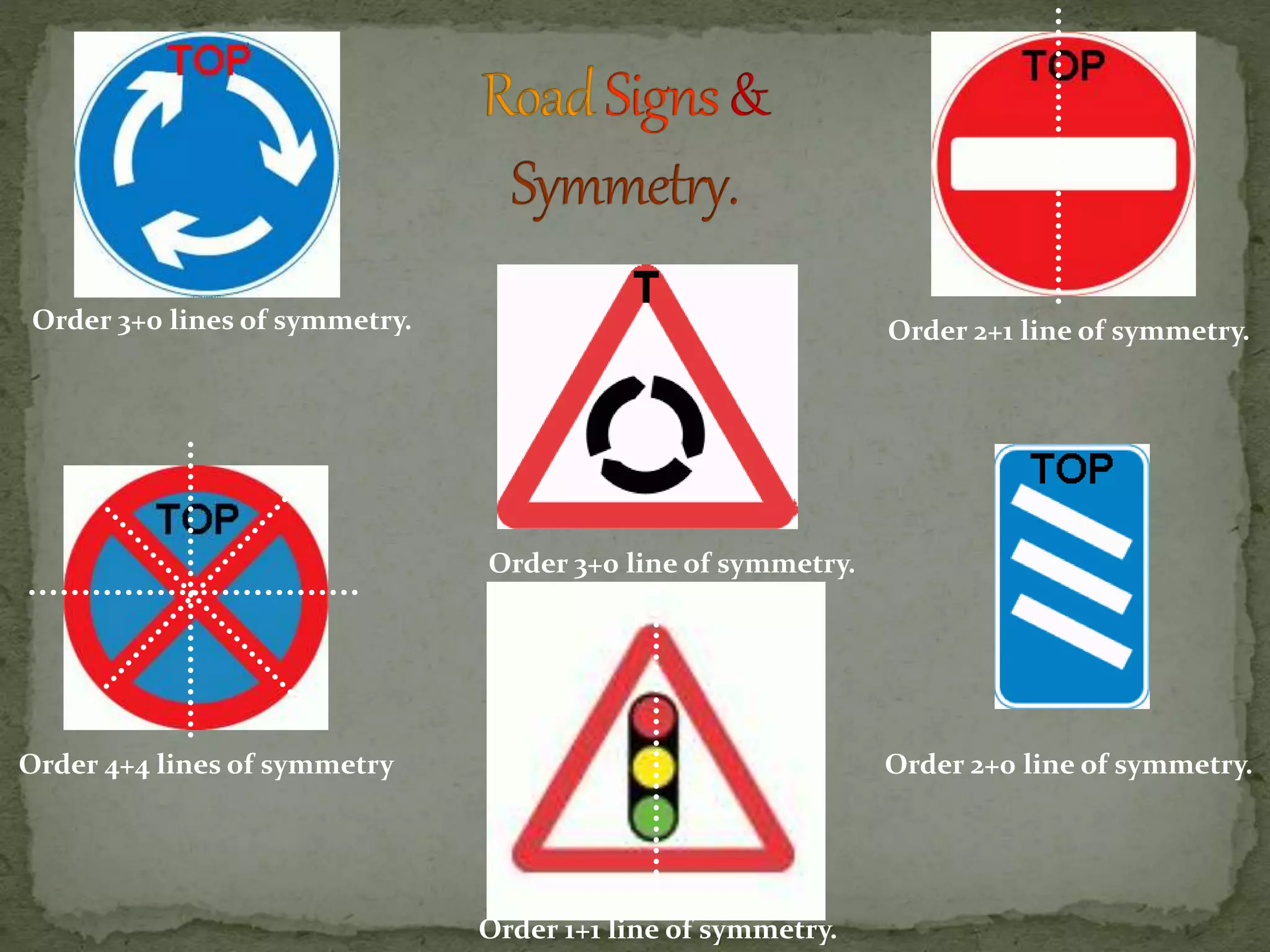
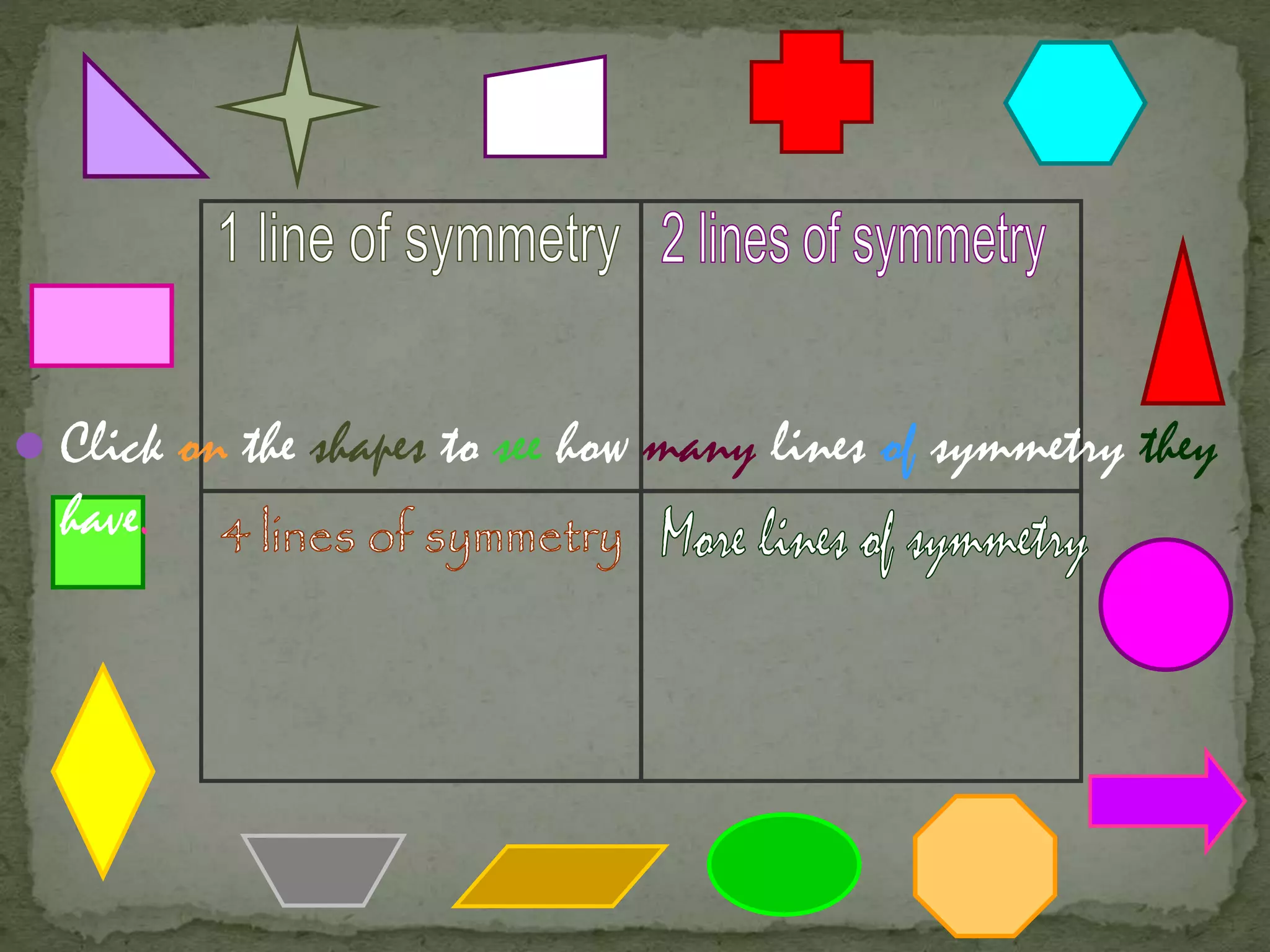
This document discusses different types of symmetry, including line symmetry and rotational symmetry. It provides examples of line symmetry in letters of the alphabet and examples of rotational symmetry in shapes like triangles, squares, and pentagons. It also discusses symmetry in architecture, flags, and natural phenomena. Symmetry is a fundamental organizing principle in nature and art that involves preserving certain properties when an object is transformed in some way.