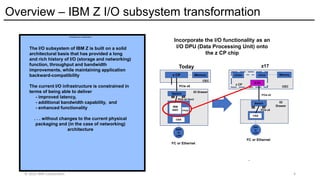
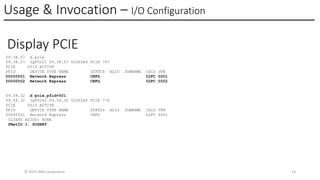
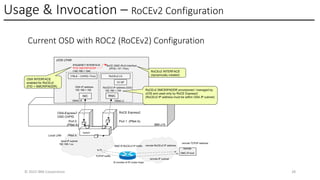
The IBM z17 has undergone a transformation with an entirely new System I/O hardware and architecture model for both storage and networking. The z17 offers I/O capability that is integrated directly within the Z processor complex. The new system design moves I/O operations closer to the system processor and memory. This new design approach transforms I/O operations allowing Z workloads to grow and scale to meet the growing needs of current and future IBM Hybrid Cloud Enterprise workloads. This presentation will focus on the networking I/O transformation by introducing you to the new IBM z17 Network Express feature.
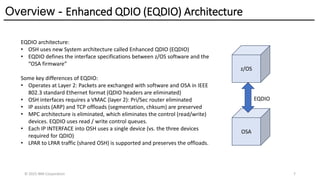
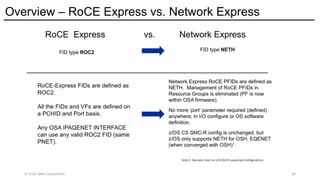
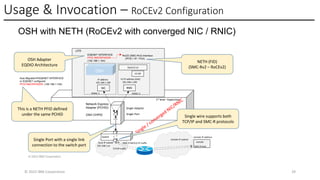
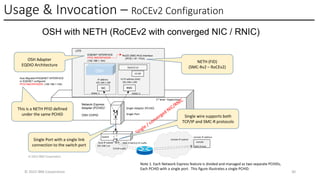
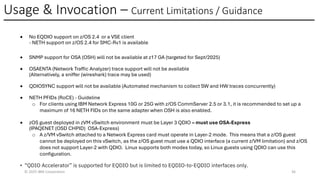
The Network Express feature introduces new system architecture called Enhanced QDIO (EQDIO). EQDIO allows the updated z/OS Communications Server software to interact with the Network Express hardware using new optimized I/O operations. The new design and optimizations are required to meet the demand of the continuously growing I/O rates. Network Express and EQDIO build the foundation for the introduction of advanced Ethernet and networking capabilities for the future of IBM Z Hybrid Cloud Enterprise users.
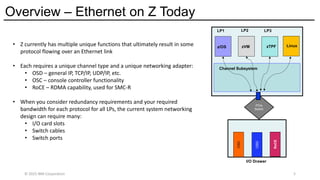
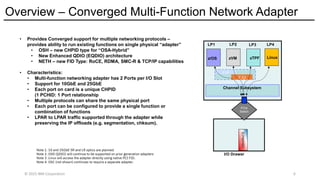
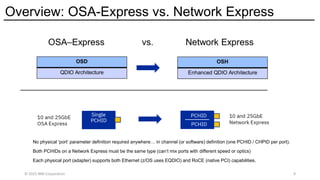
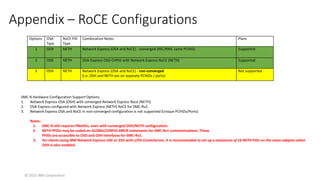
The Network Express feature also combines the functionality of both the OSA-Express and RoCE Express features into a single feature or adapter. A single Network Express port supports both IP protocols and RDMA protocols. This allows each Network Express port to function as both a standard NIC for Ethernet and as an RDMA capable NIC (RNIC) for RoCE protocols. Converging both protocols to a single adapter reduces Z customers’ cost for physical networking resources. With this change, IBM Z customers can now exploit Shared Memory Communications (SMC) leveraging RDMA (SMC-R) technology without incurring additional hardware costs.
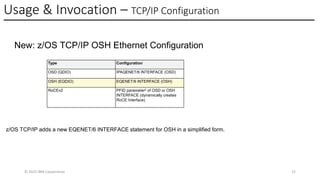
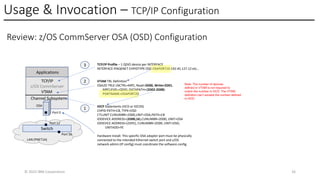
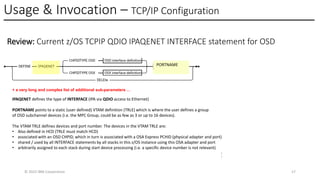
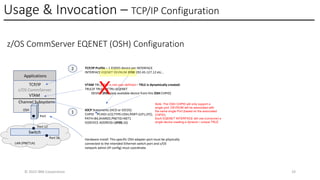
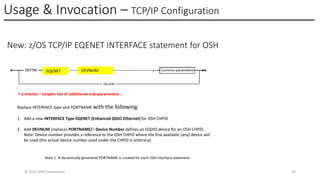
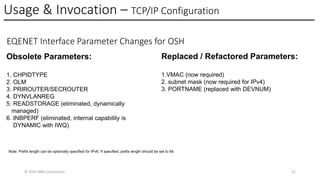
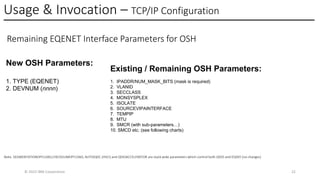
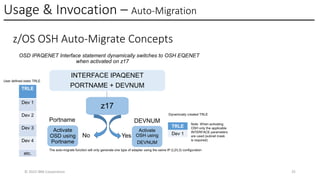
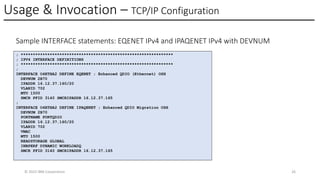
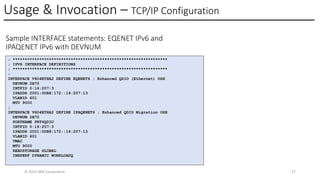
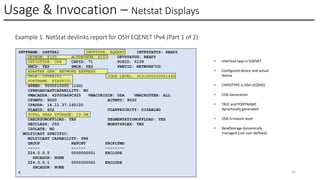
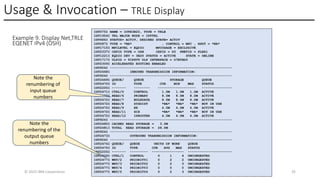
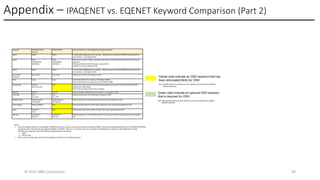
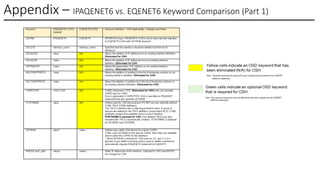
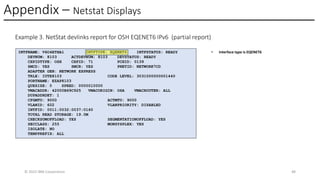
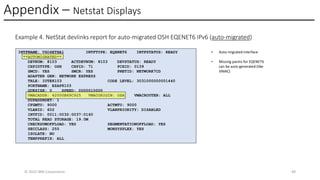
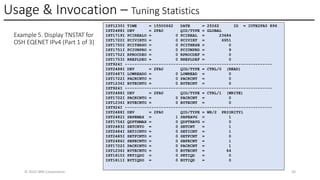
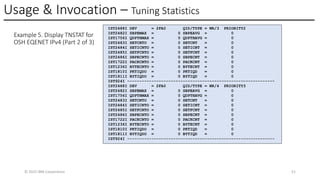
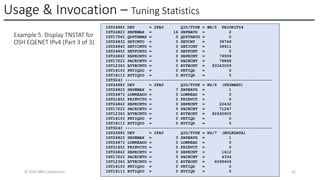
In this session, the speakers will focus on how z/OS Communications Server has been updated to support the Network Express feature. An introduction to the new Enhanced QDIO Ethernet (EQENET) interface statement used to configure the new OSA is provided. EQDIO provides a variety of simplifications, such as no longer requiring VTAM user defined TRLEs, uses smarter defaults and removes outdated parameters. The speakers will also cover migration considerations for Network Express. In addition, the operational aspects of managing and monitoring the new OSA and RoCE interfaces will be covered. The speakers will also take you through the enhancements made to optimize both inbound and outbound network traffic. Come join us, step aboard and learn how z/OS Communications Server is bringing you the future in network communications with the IBM z17 Network Express feature.