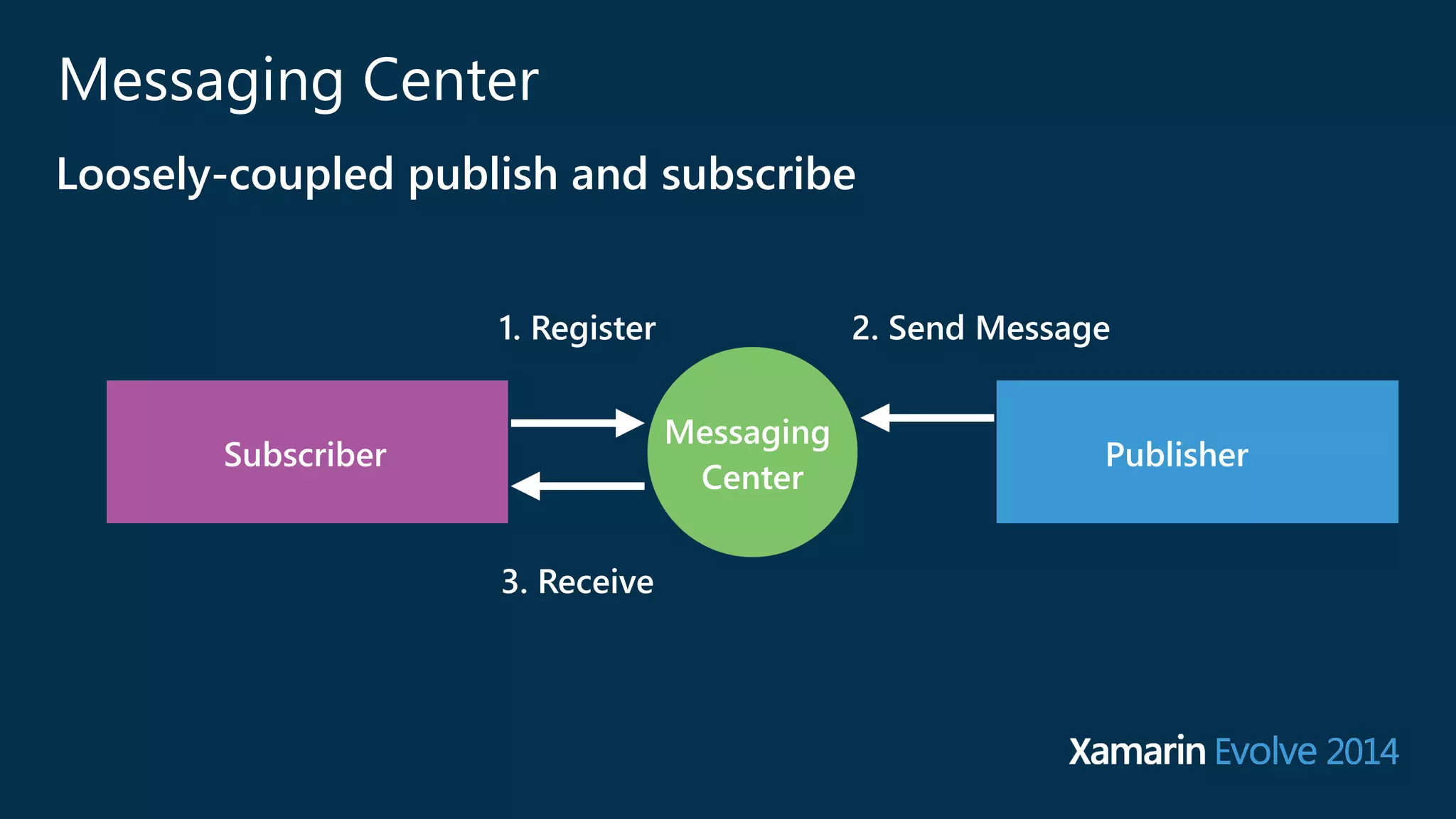
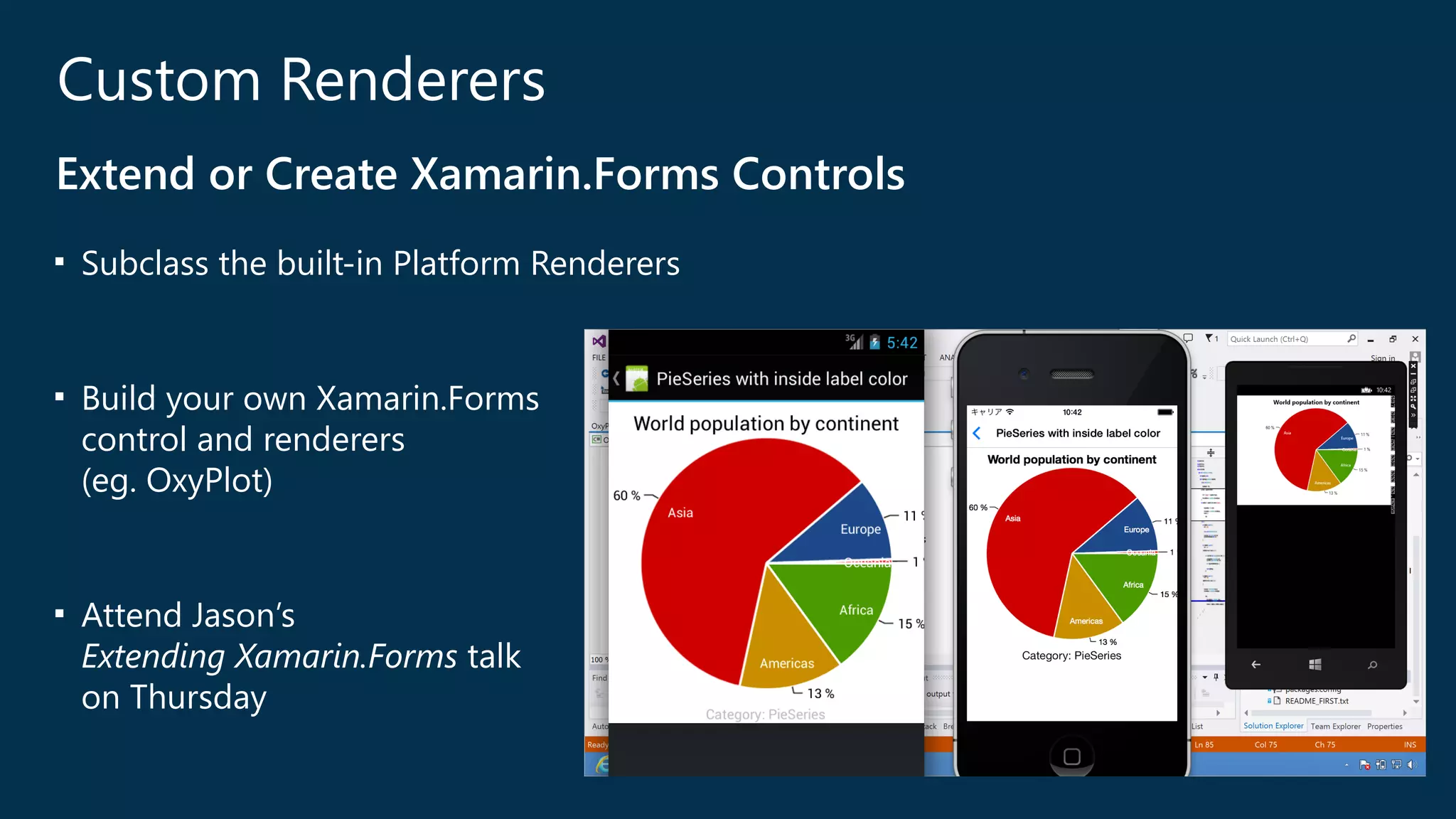
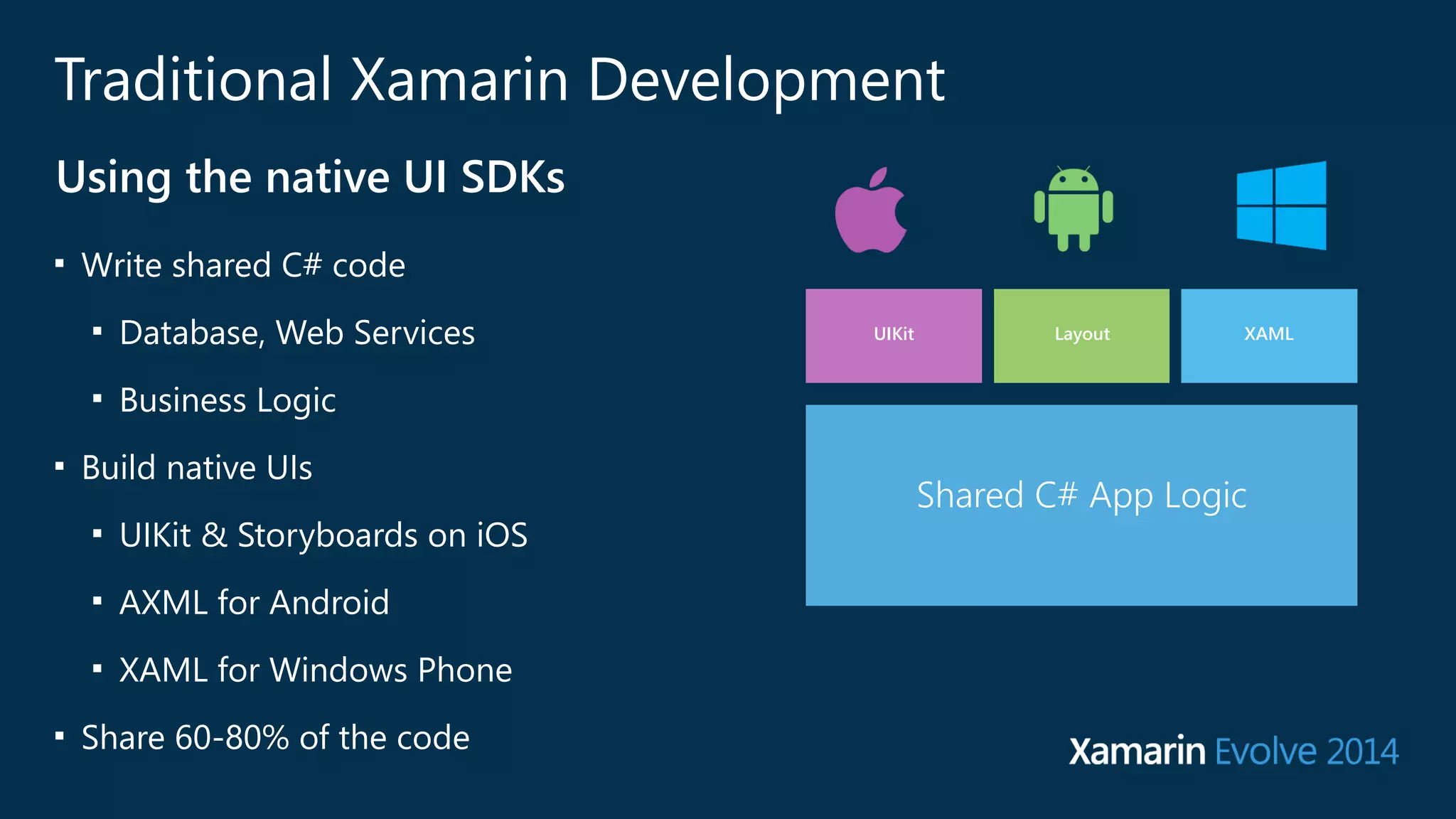
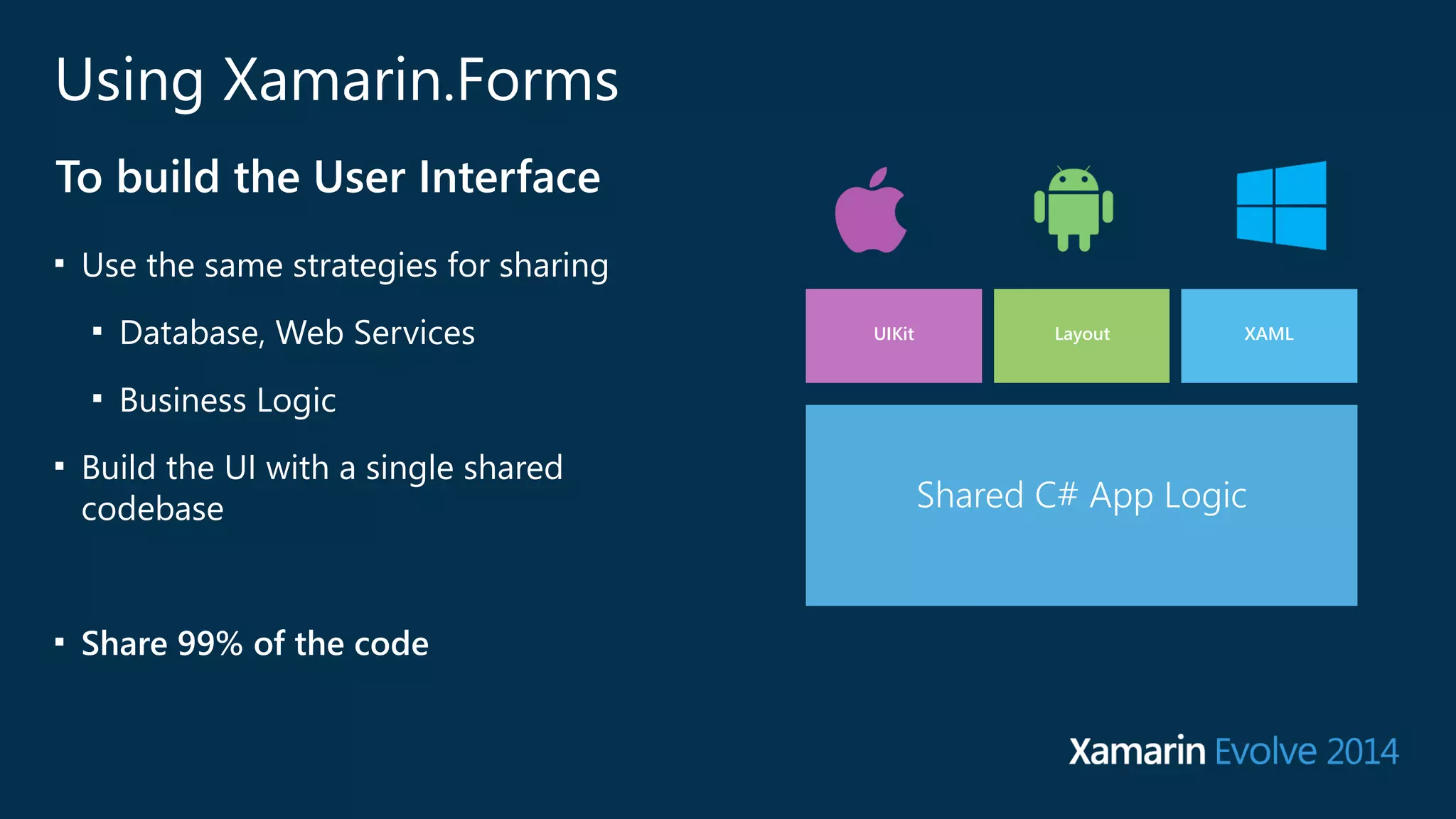
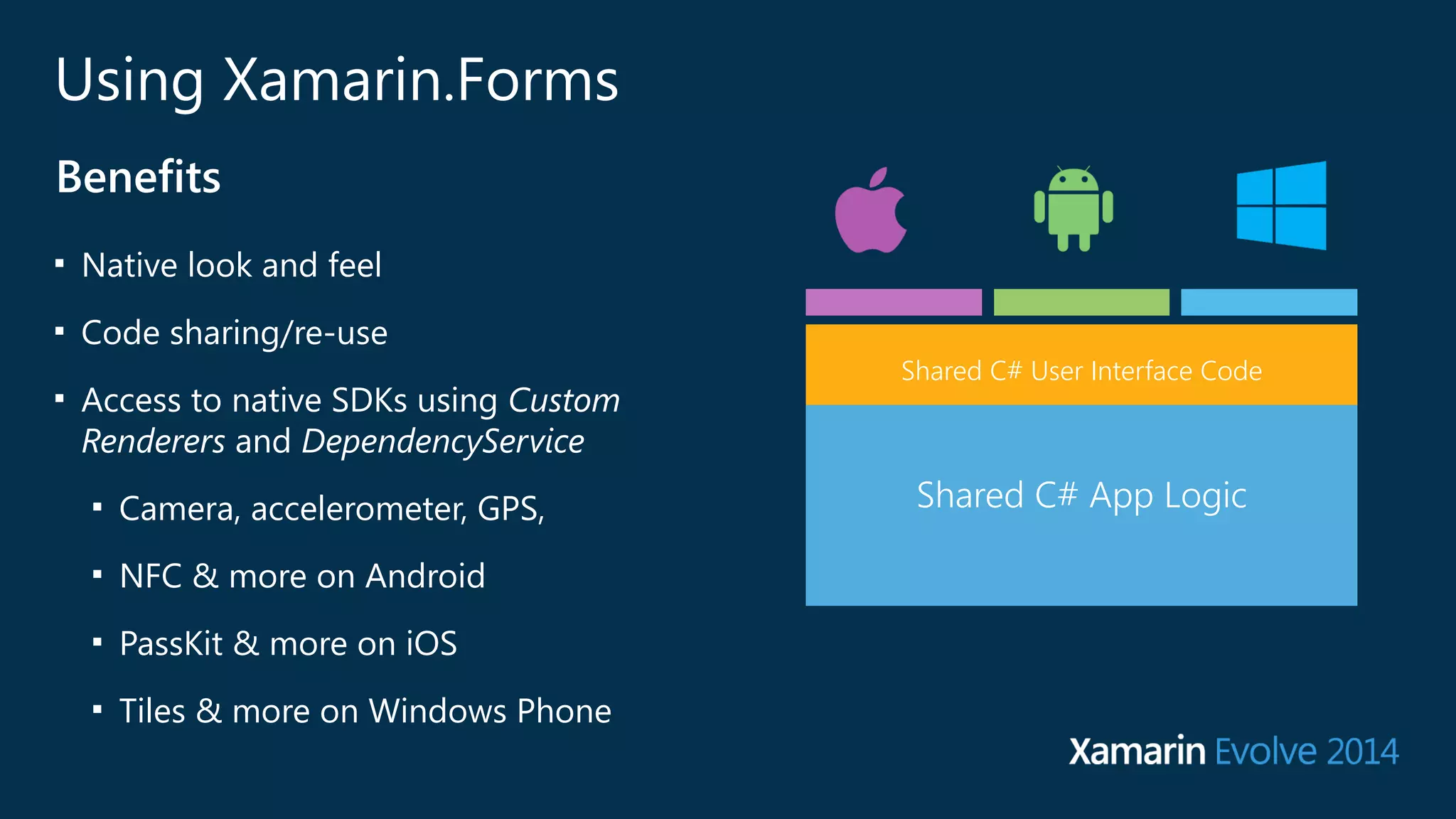
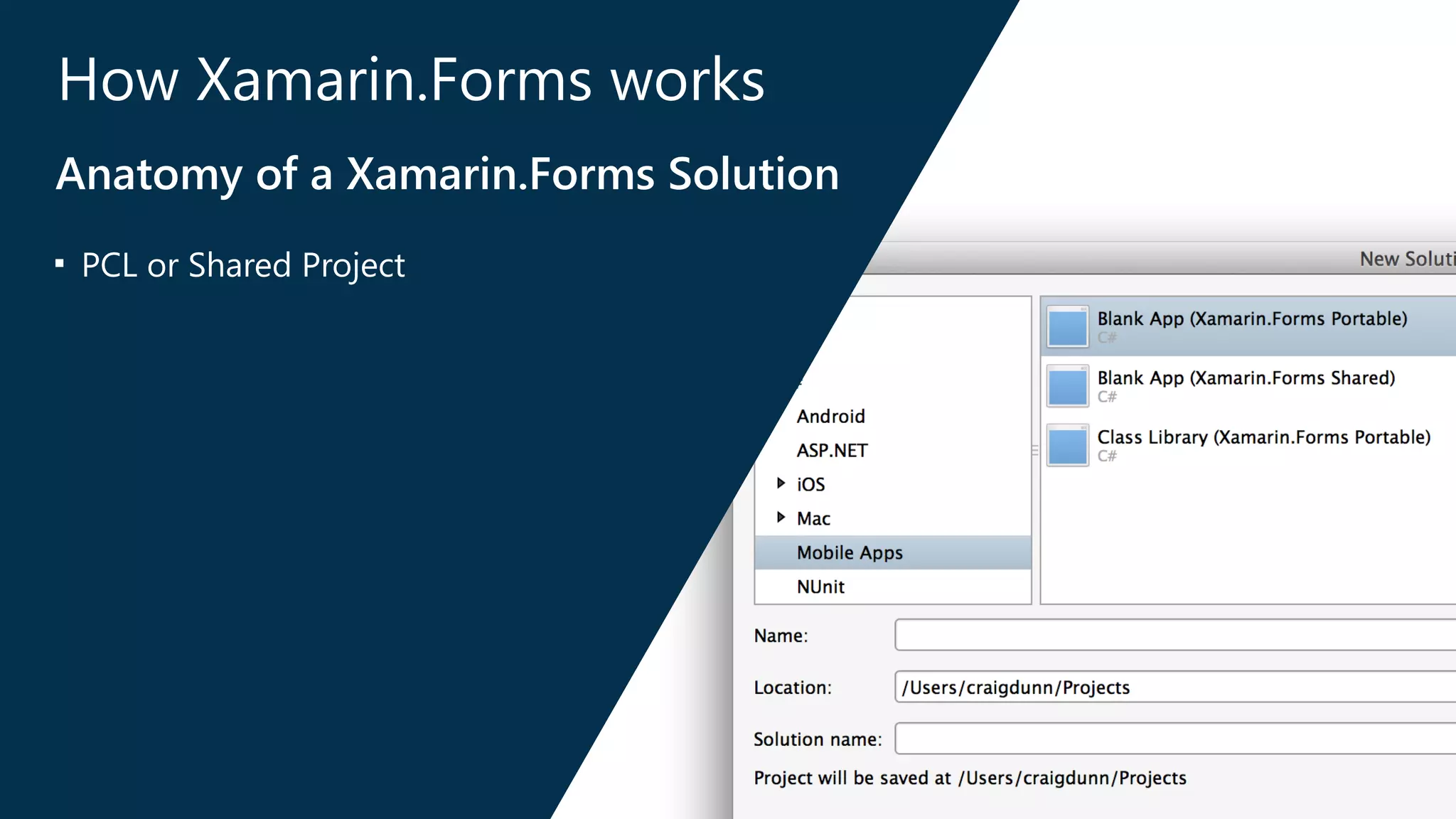
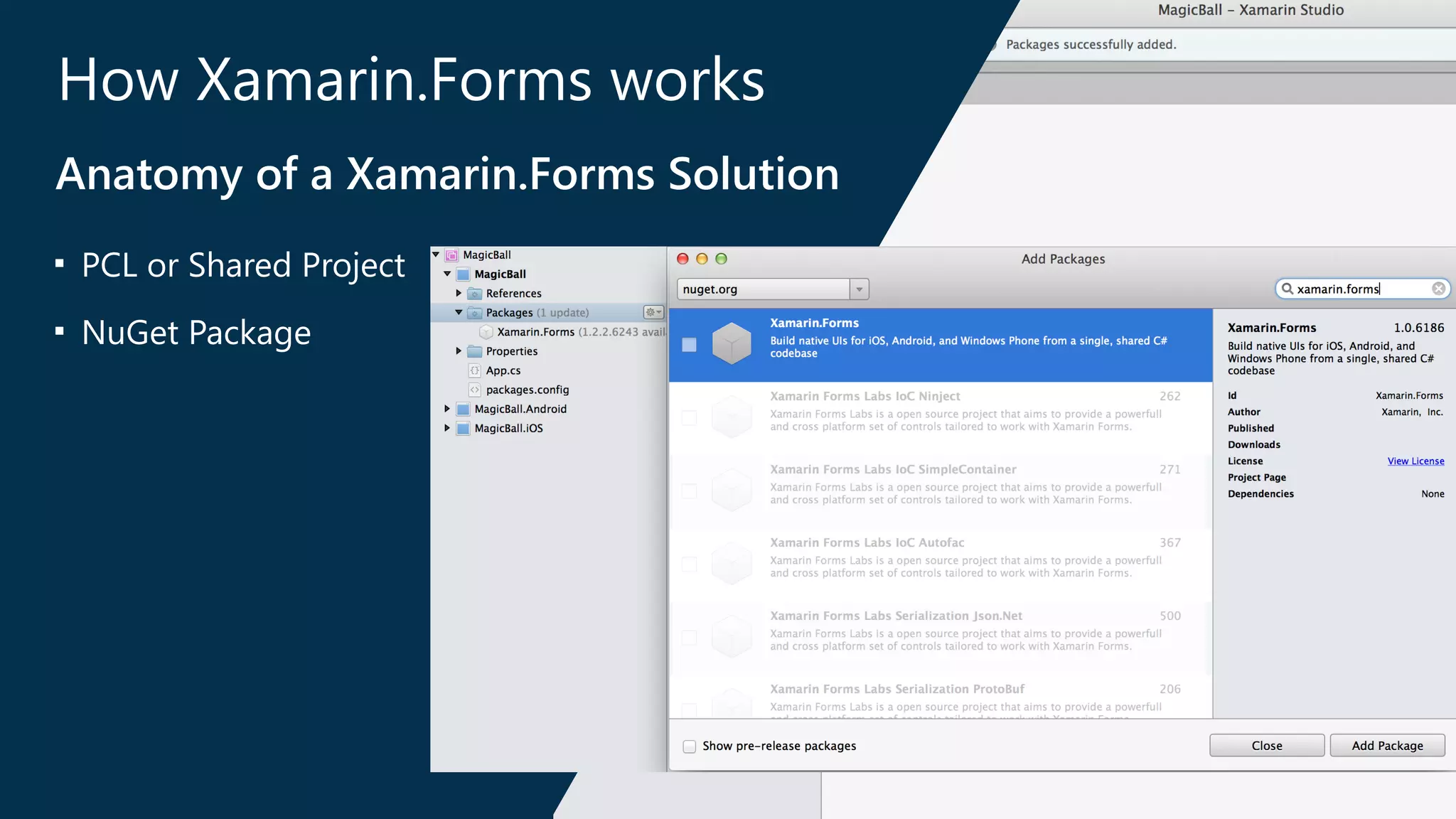
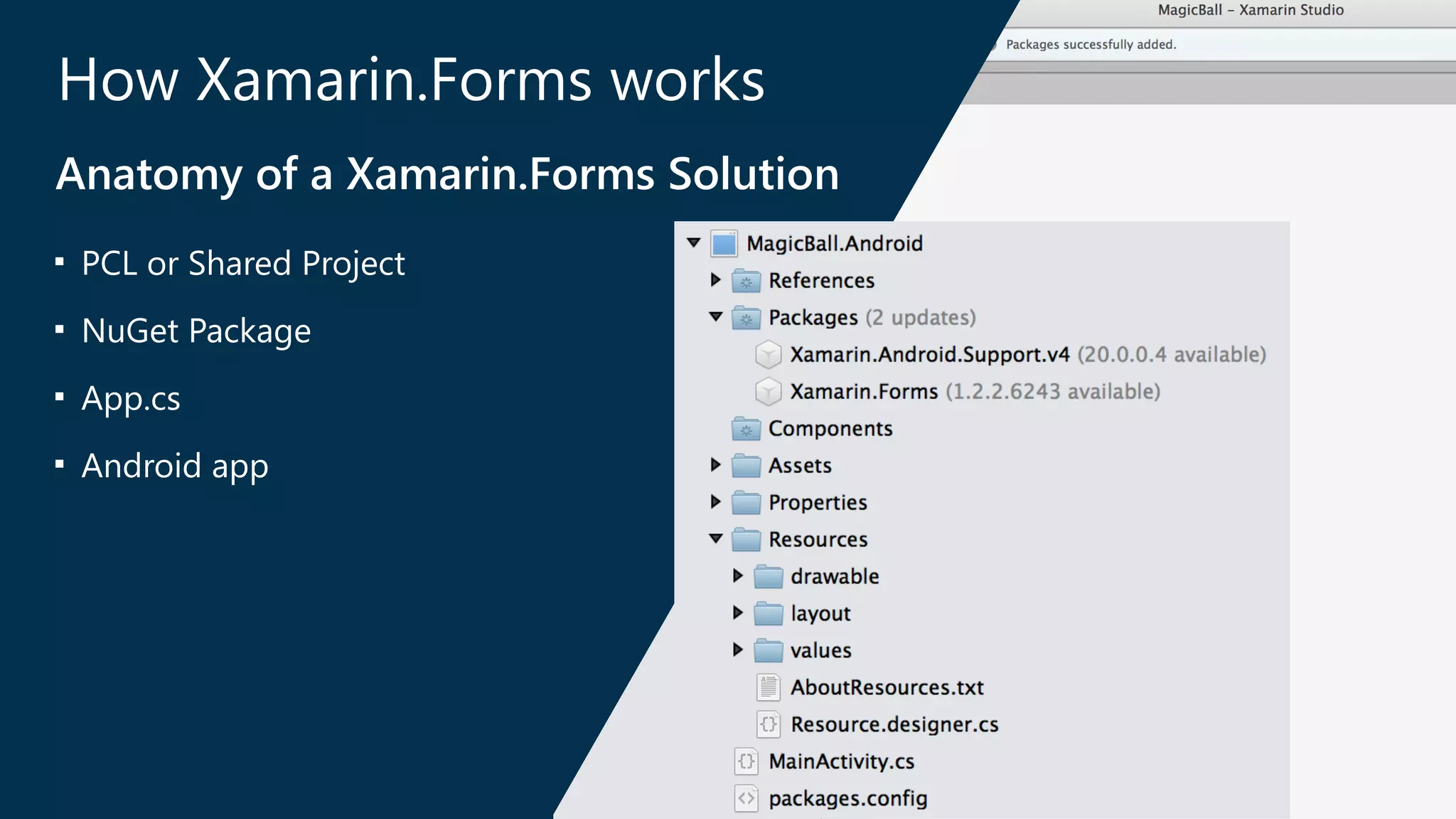
The document introduces Xamarin.Forms, a framework for building native user interfaces for iOS, Android, and Windows Phone using a shared C# codebase. It covers the structure of a Xamarin.Forms app, various components like buttons and labels, and the benefits of using Xamarin.Forms, such as code sharing and access to native SDKs. Additionally, it discusses advanced features like dependency services, data binding, and custom renderers to enhance application functionality.














![Dependency Service
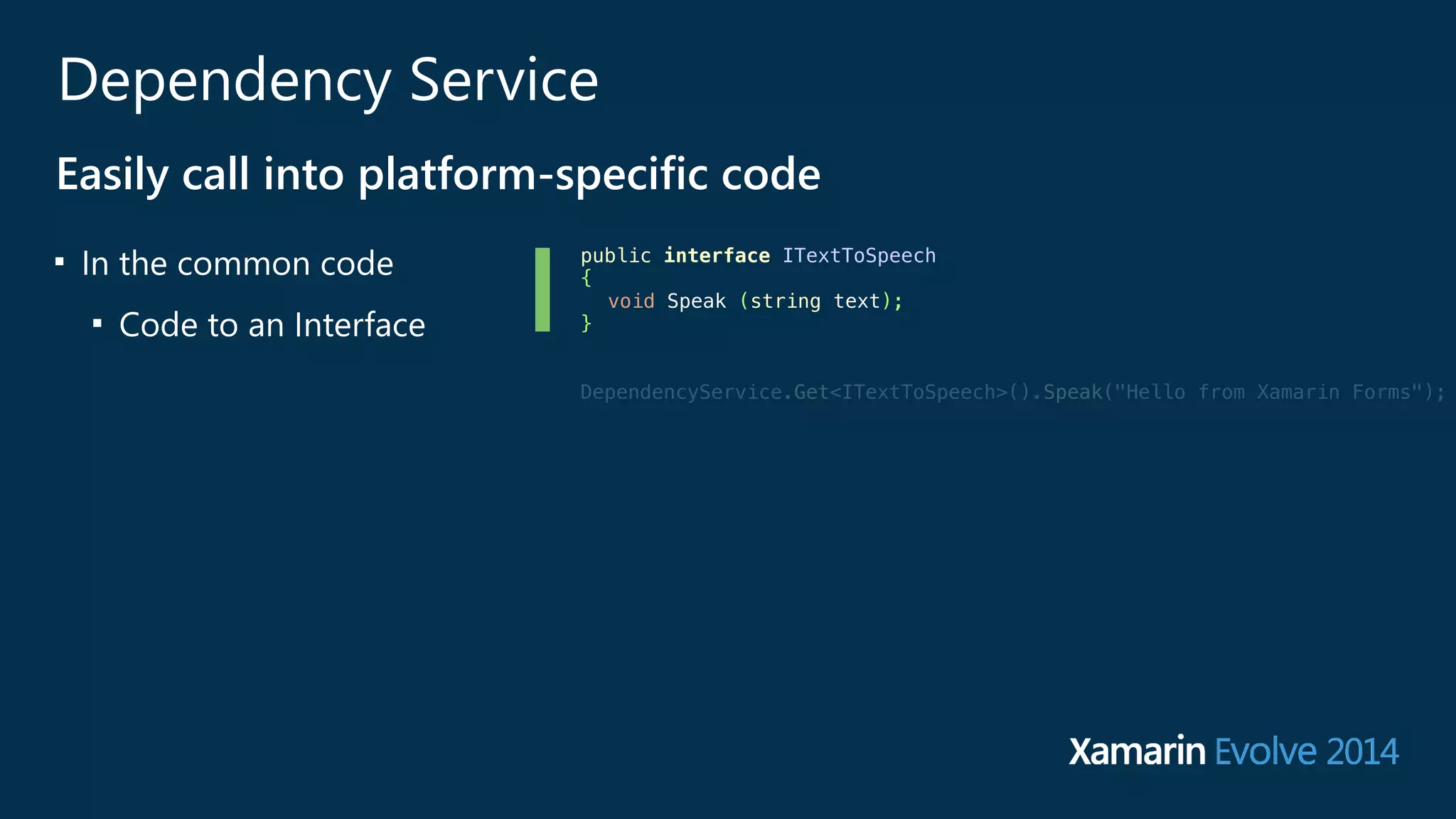
Easily call into platform-‐specific code
■ In the common code
■ Code to an Interface
■ Use DependencyService
■ For each platform
■ implement the Interface
[assembly: Xamarin.Forms.Dependency (typeof (Speech))]
public class Speech : ITextToSpeech
{
public Speech () { }
public void Speak (string text)
{
var speechSynthesizer = new AVSpeechSynthesizer ();
var speechUtterance = new AVSpeechUtterance (text) {
Rate = AVSpeechUtterance.MaximumSpeechRate/4,
Voice = AVSpeechSynthesisVoice.FromLanguage ("en-US"),
Volume = 0.5f,
PitchMultiplier = 1.0f
} ;
speechSynthesizer.SpeakUtterance (speechUtterance);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/firstxamarinformsapp-141008133228-conversion-gate01/75/Your-First-Xamarin-Forms-App-29-2048.jpg)
![Dependency Service
Easily call into platform-‐specific code
■ In the common code
■ Code to an Interface
■ Use DependencyService
■ For each platform
■ implement the Interface
■ use Dependency
attribute on the
assembly
[assembly: Xamarin.Forms.Dependency (typeof (Speech))]
public class Speech : ITextToSpeech
{
public Speech () { }
public void Speak (string text)
{
var speechSynthesizer = new AVSpeechSynthesizer ();
var speechUtterance = new AVSpeechUtterance (text) {
Rate = AVSpeechUtterance.MaximumSpeechRate/4,
Voice = AVSpeechSynthesisVoice.FromLanguage ("en-US"),
Volume = 0.5f,
PitchMultiplier = 1.0f
} ;
speechSynthesizer.SpeakUtterance (speechUtterance);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/firstxamarinformsapp-141008133228-conversion-gate01/75/Your-First-Xamarin-Forms-App-30-2048.jpg)