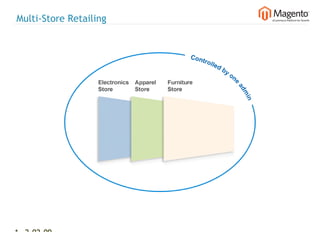
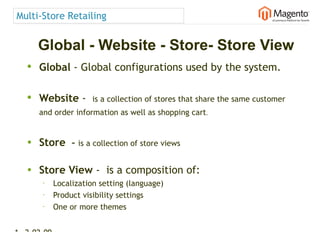
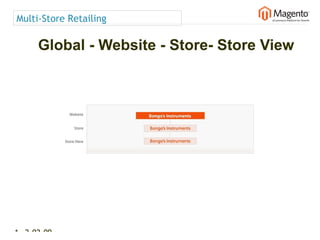
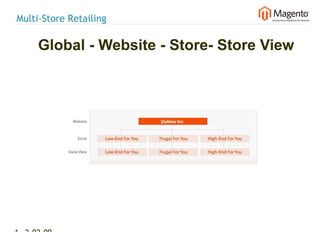
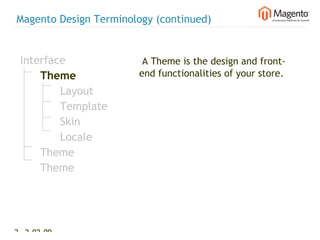
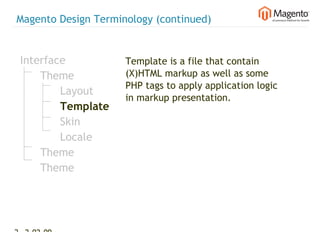
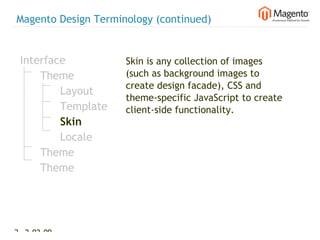
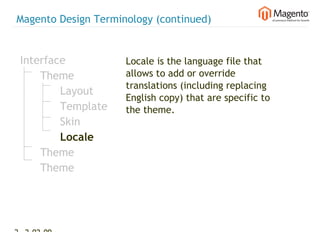
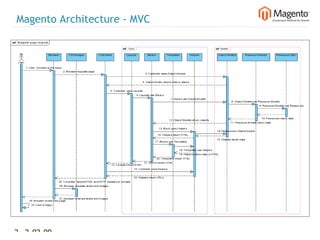
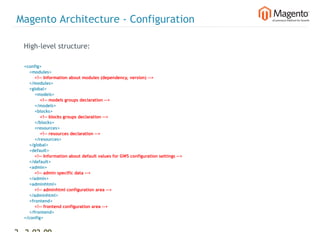
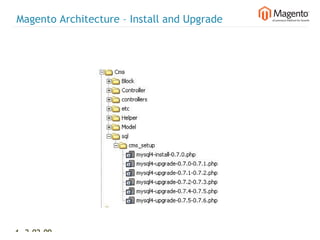
The document summarizes Magento's architecture and configuration. It describes how Magento uses an MVC pattern and object-oriented design principles. It also explains how Magento relies heavily on XML configuration files to define models, blocks, system settings and more. These configuration files can come from core modules, custom modules, and the database for store-specific settings.














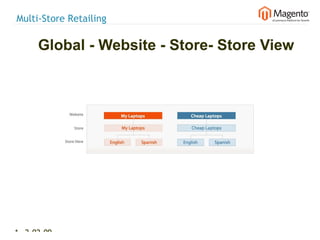



















![Magento Architecture – Cluster Organization
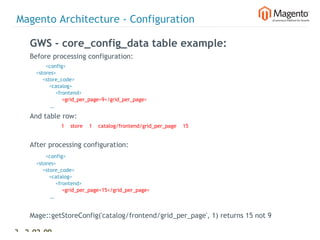
Setting up read write connections
app/etc/local.xml
<config>
<global>
<resources>
<default_setup>
<connection>
<host><![CDATA[localhost]]></host>
<username><![CDATA[root]]></username>
<password><![CDATA[]]></password>
<dbname><![CDATA[magento_sample_data]]></dbname>
<active>1</active>
</connection>
</default_setup>
<default_read>
<connection>
<use/>
<host><![CDATA[localhost]]></host>
<username><![CDATA[root]]></username>
<password><![CDATA[]]></password>
<dbname><![CDATA[magento_sample_data_read]]></dbname>
<active>1</active>
</connection>
</default_read>
47 2-02-09 |](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/yoavkutner-dutchento-090707152942-phpapp02/85/Yoav-Kutner-Dutchento-47-320.jpg)



