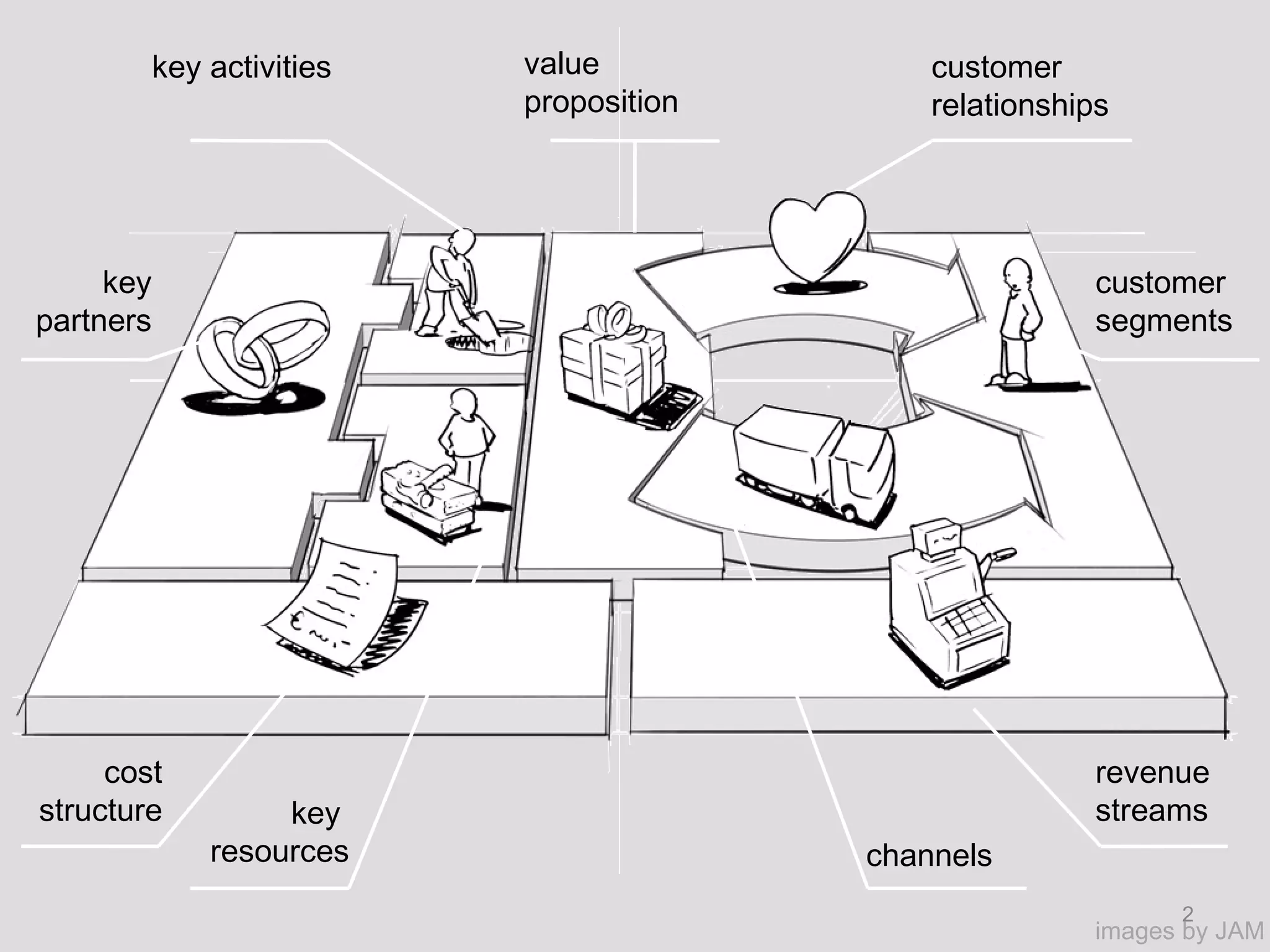
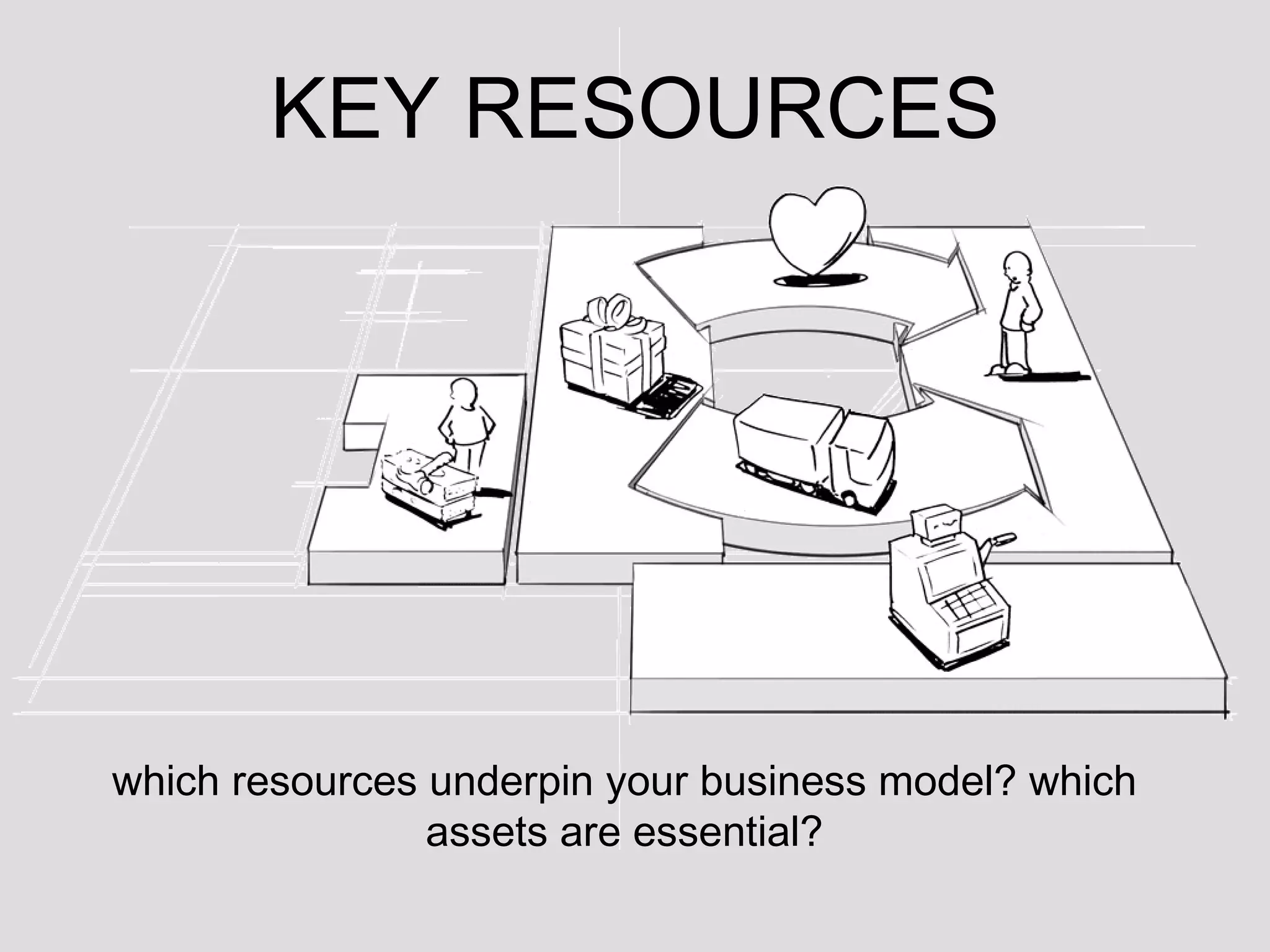
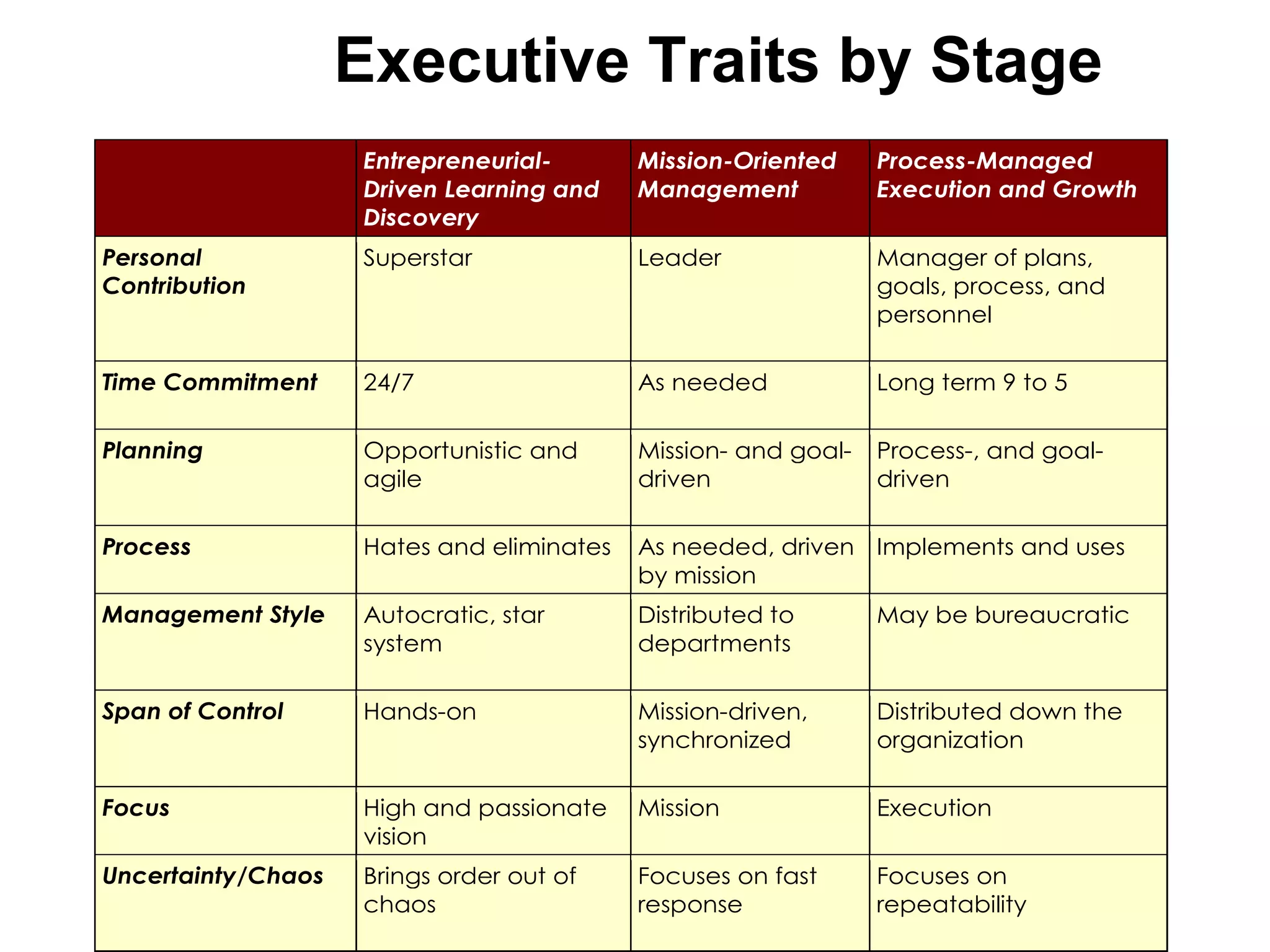
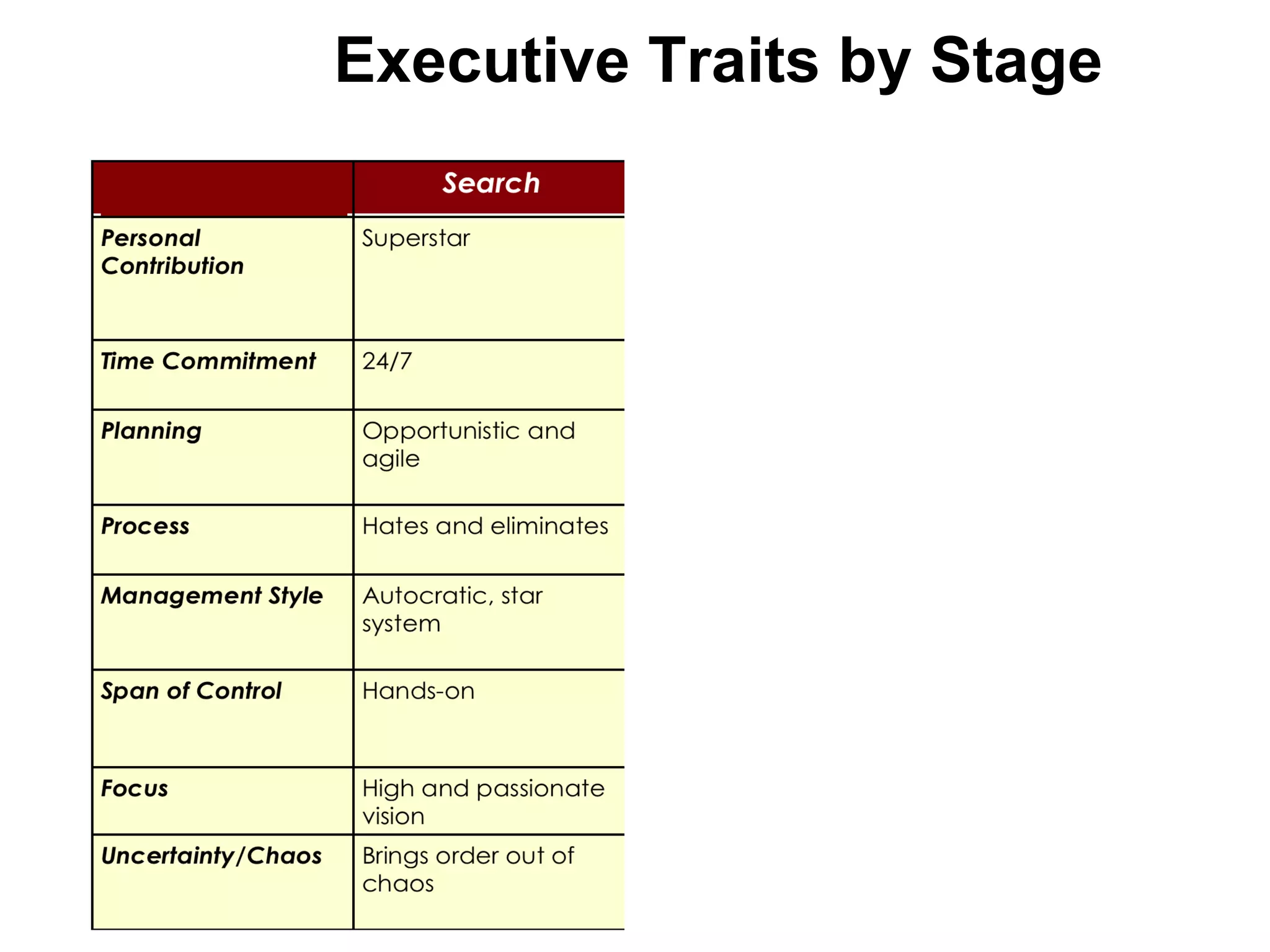
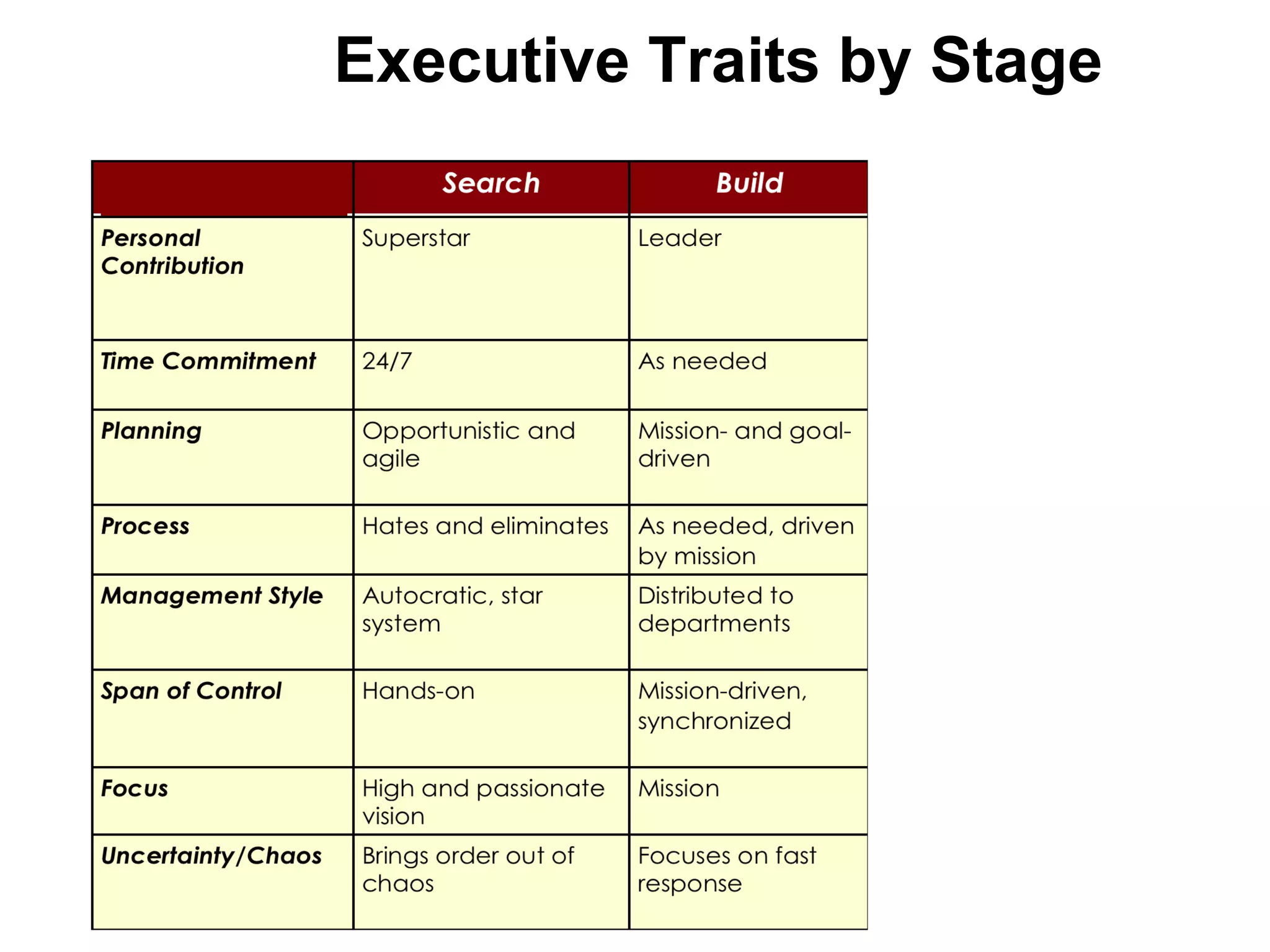
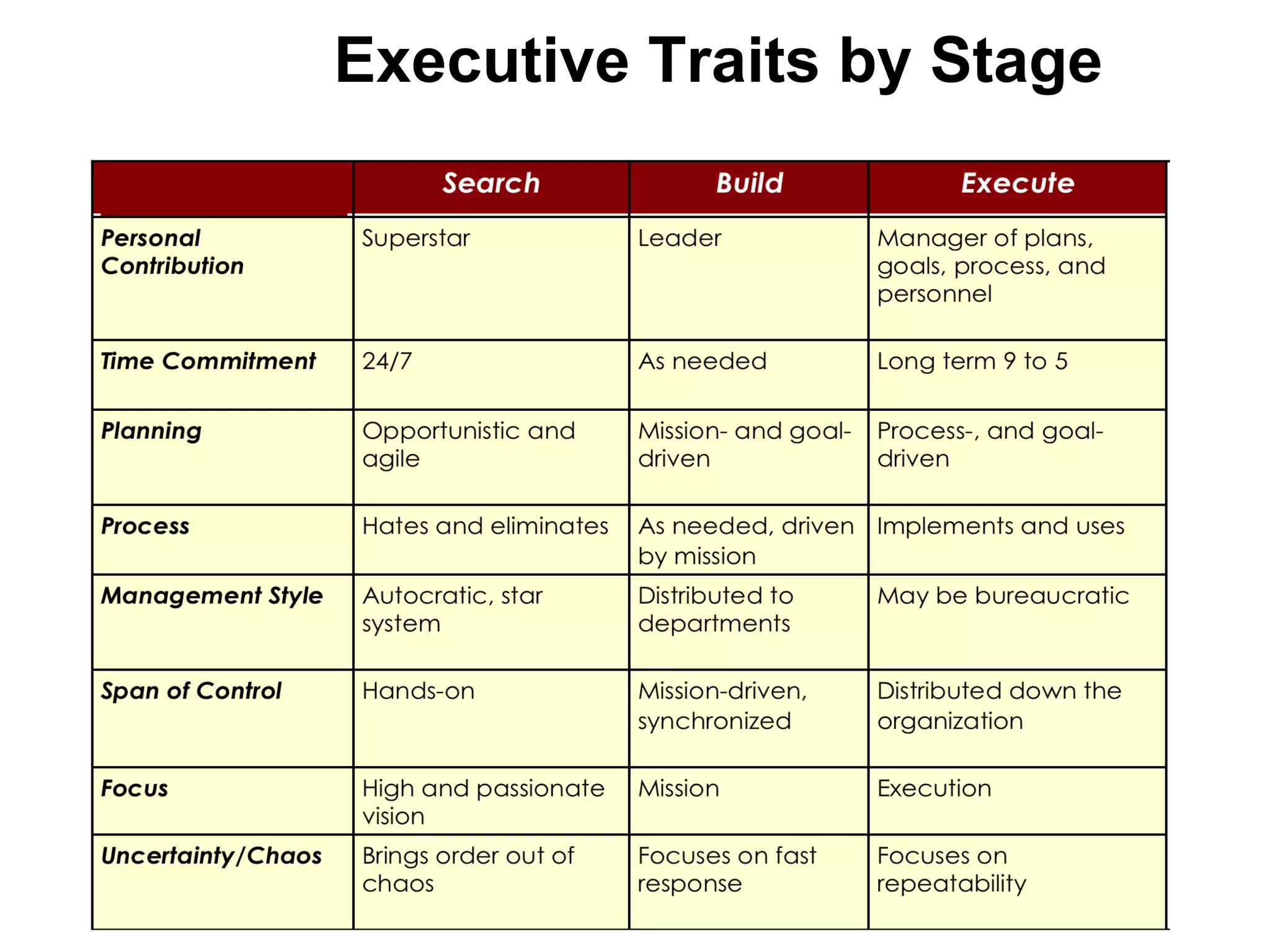
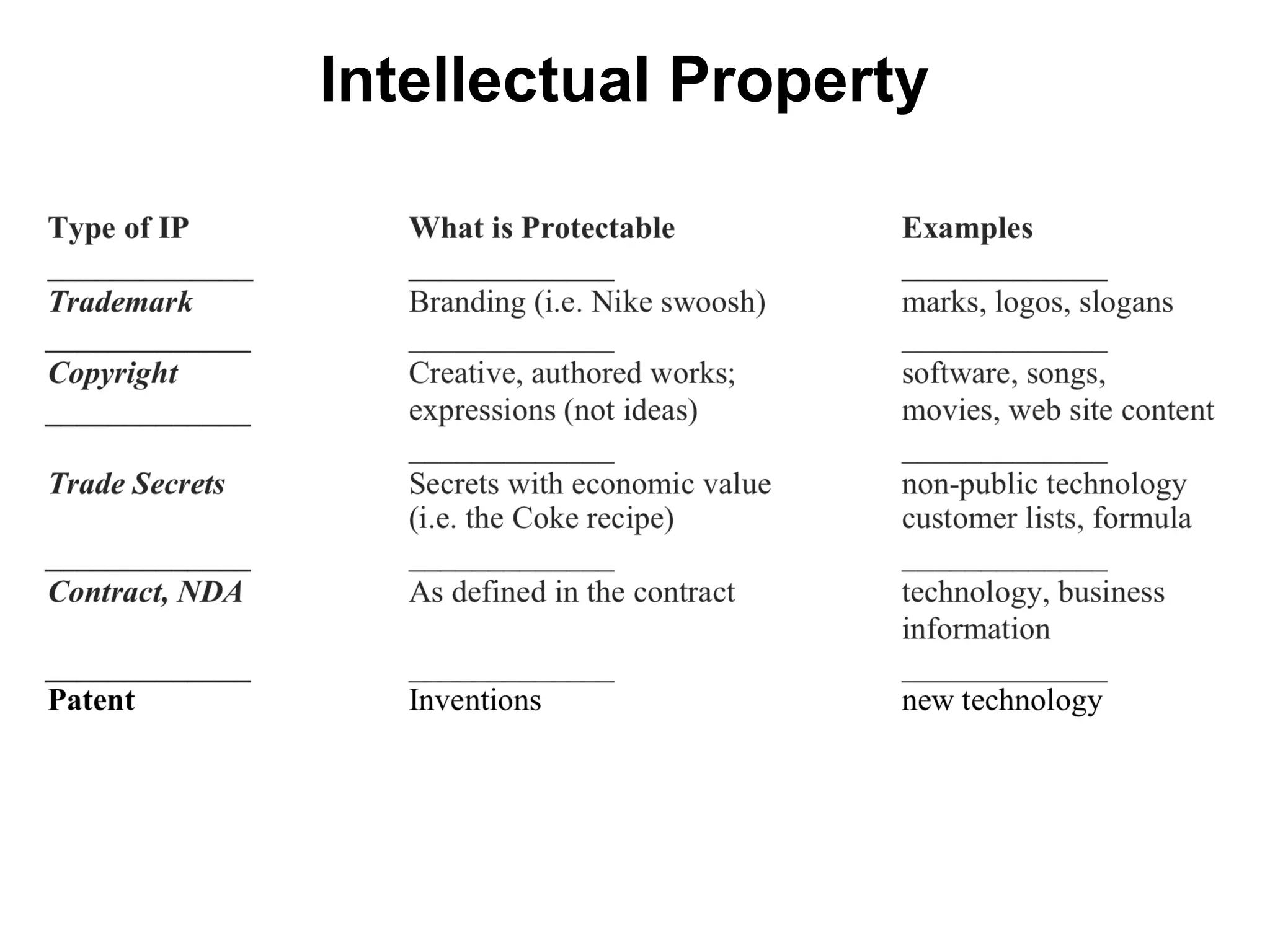
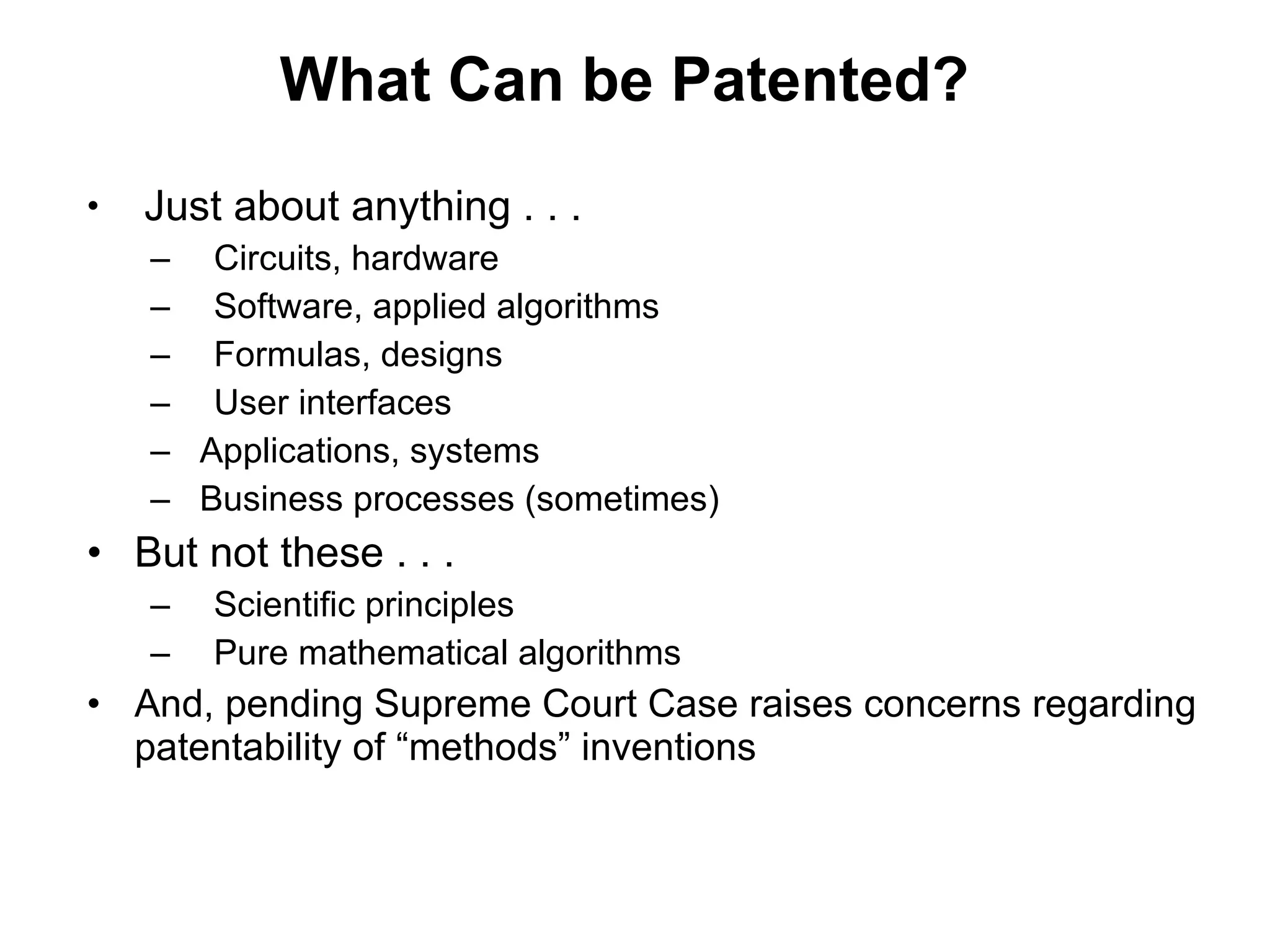
The document discusses key resources and activities for business models. It describes four critical resources: physical, financial, human, and intellectual resources. It provides examples for each type of resource. It also discusses key activities that are important to perform well for a business model, such as manufacturing, supply chain management, product development, and regulatory approval processes.