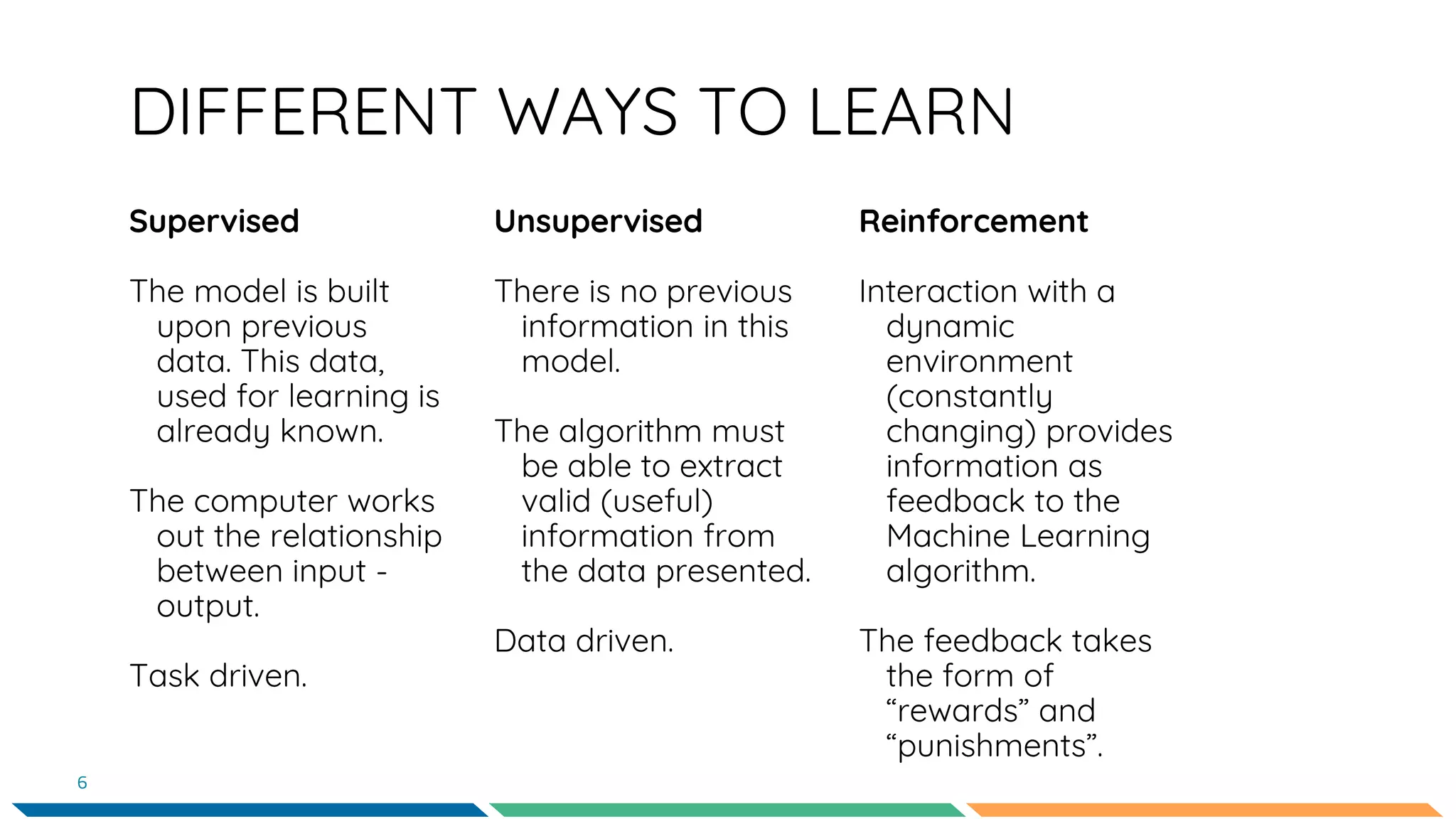
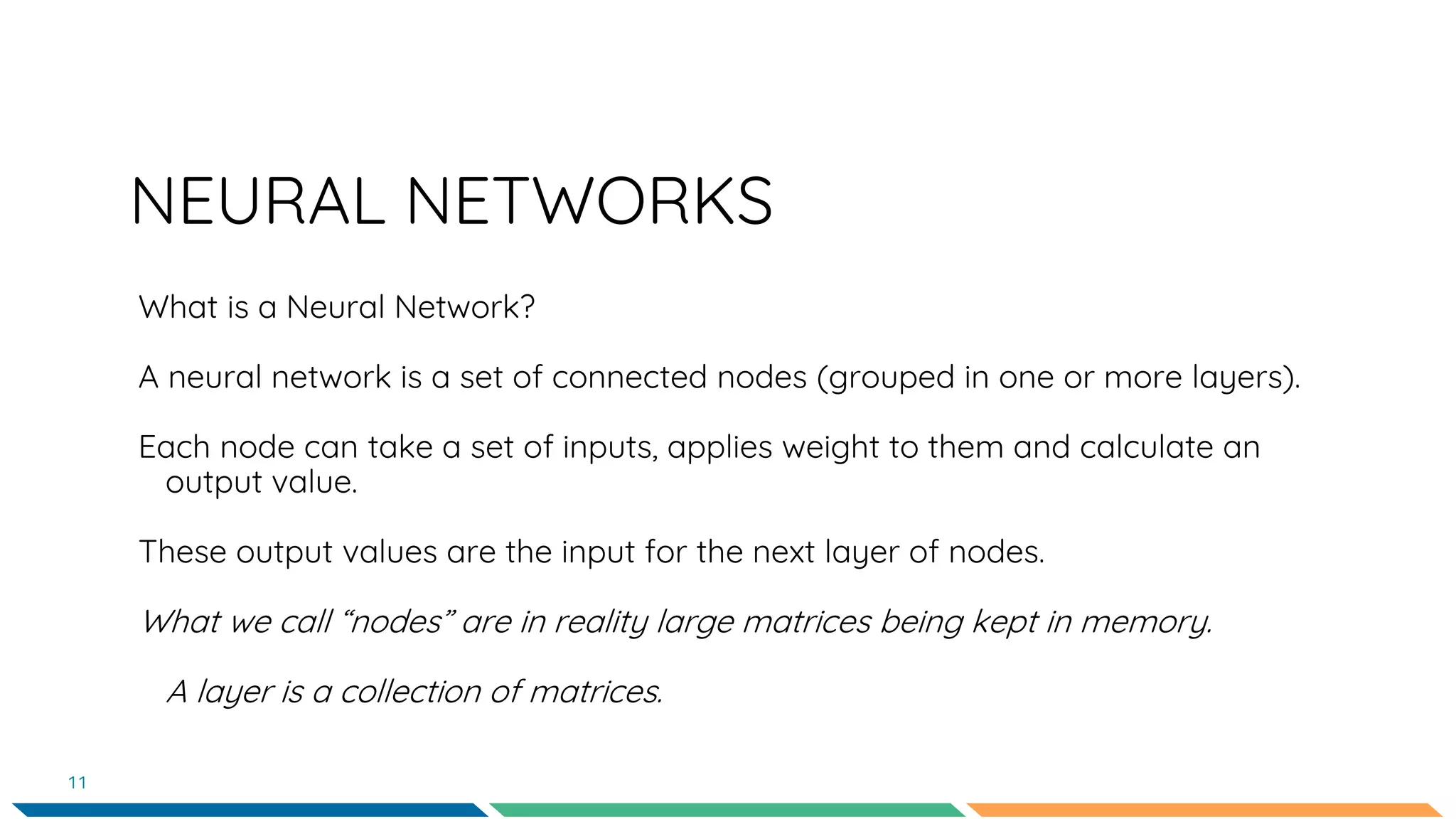
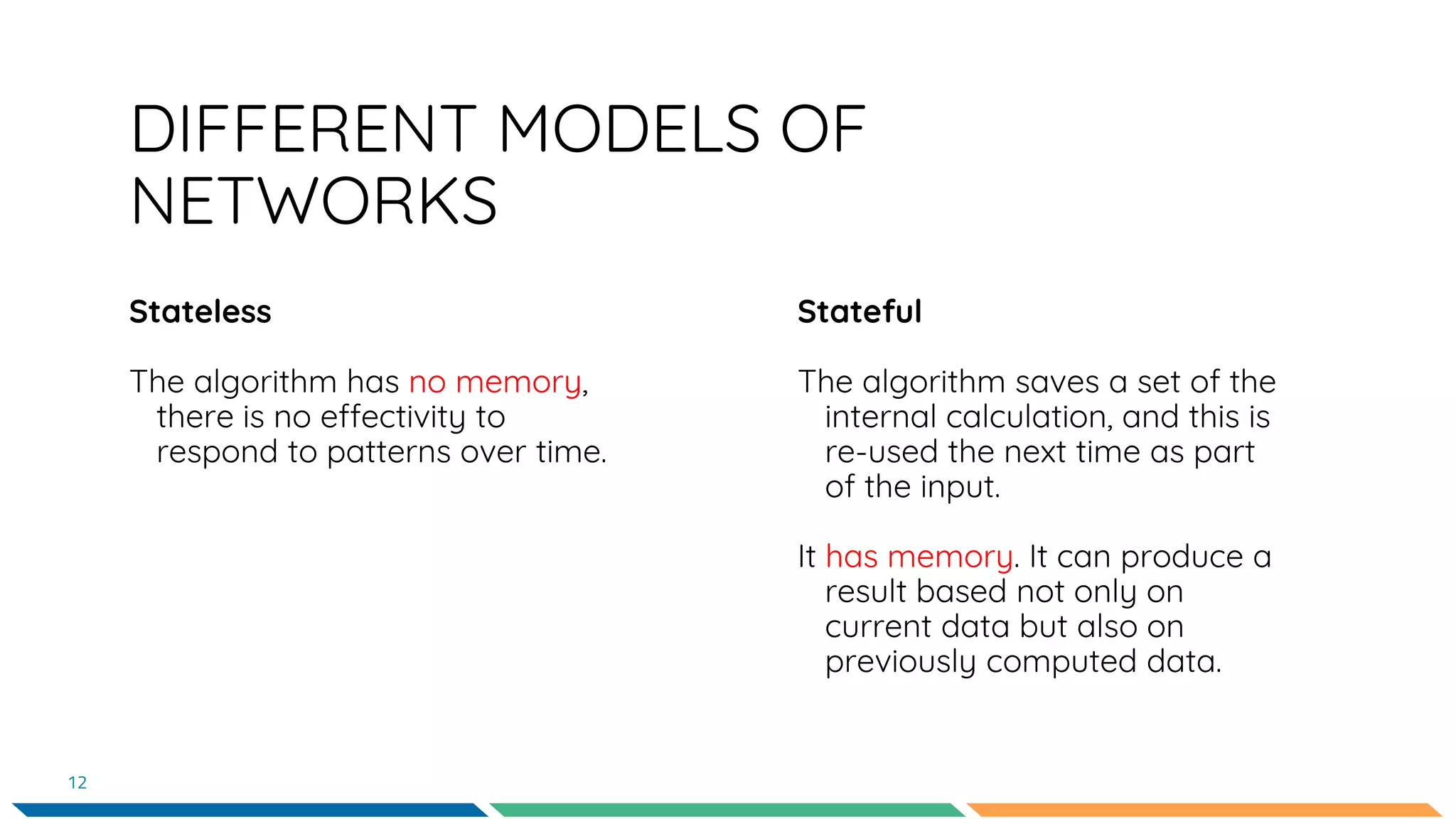
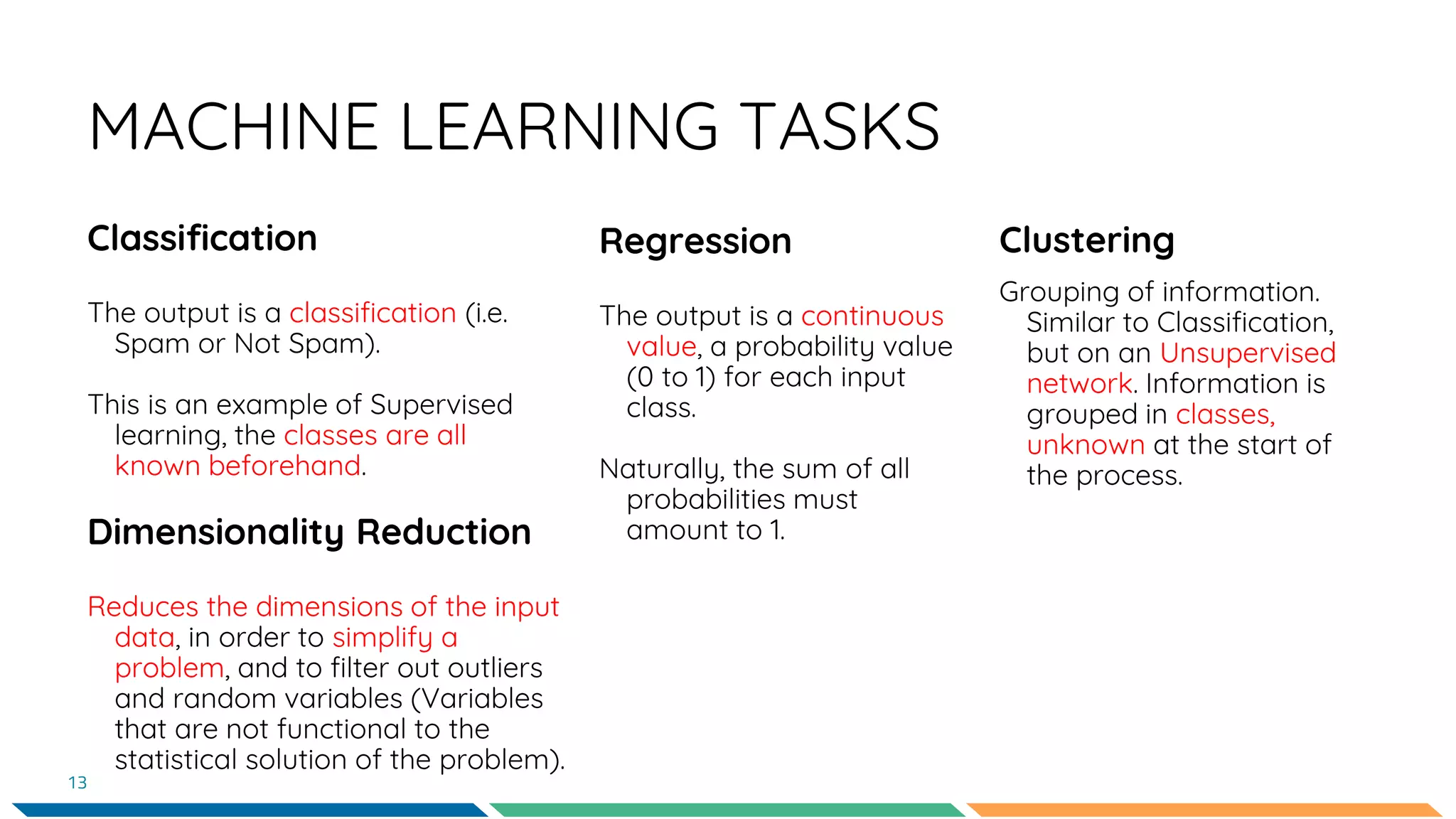
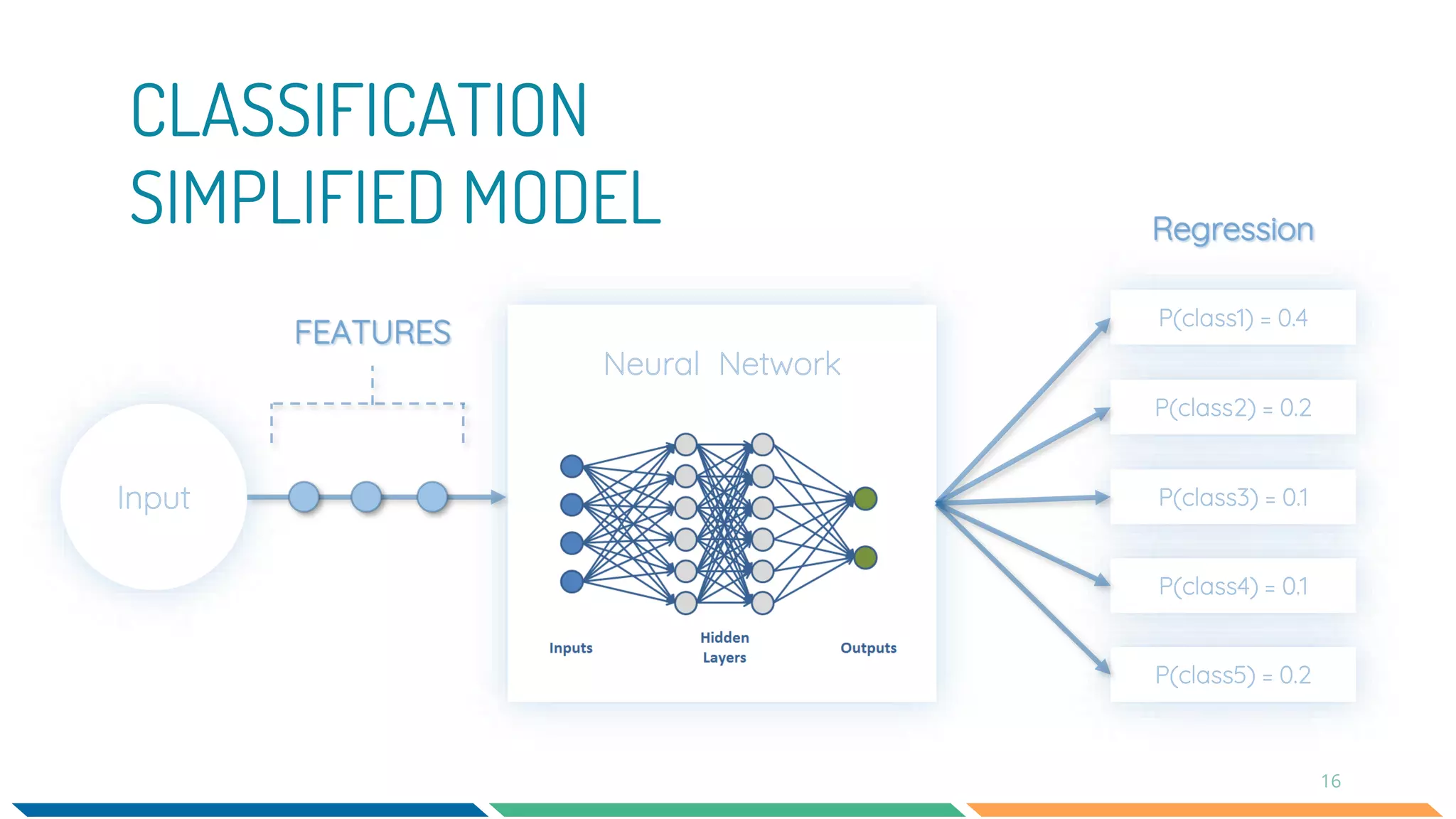
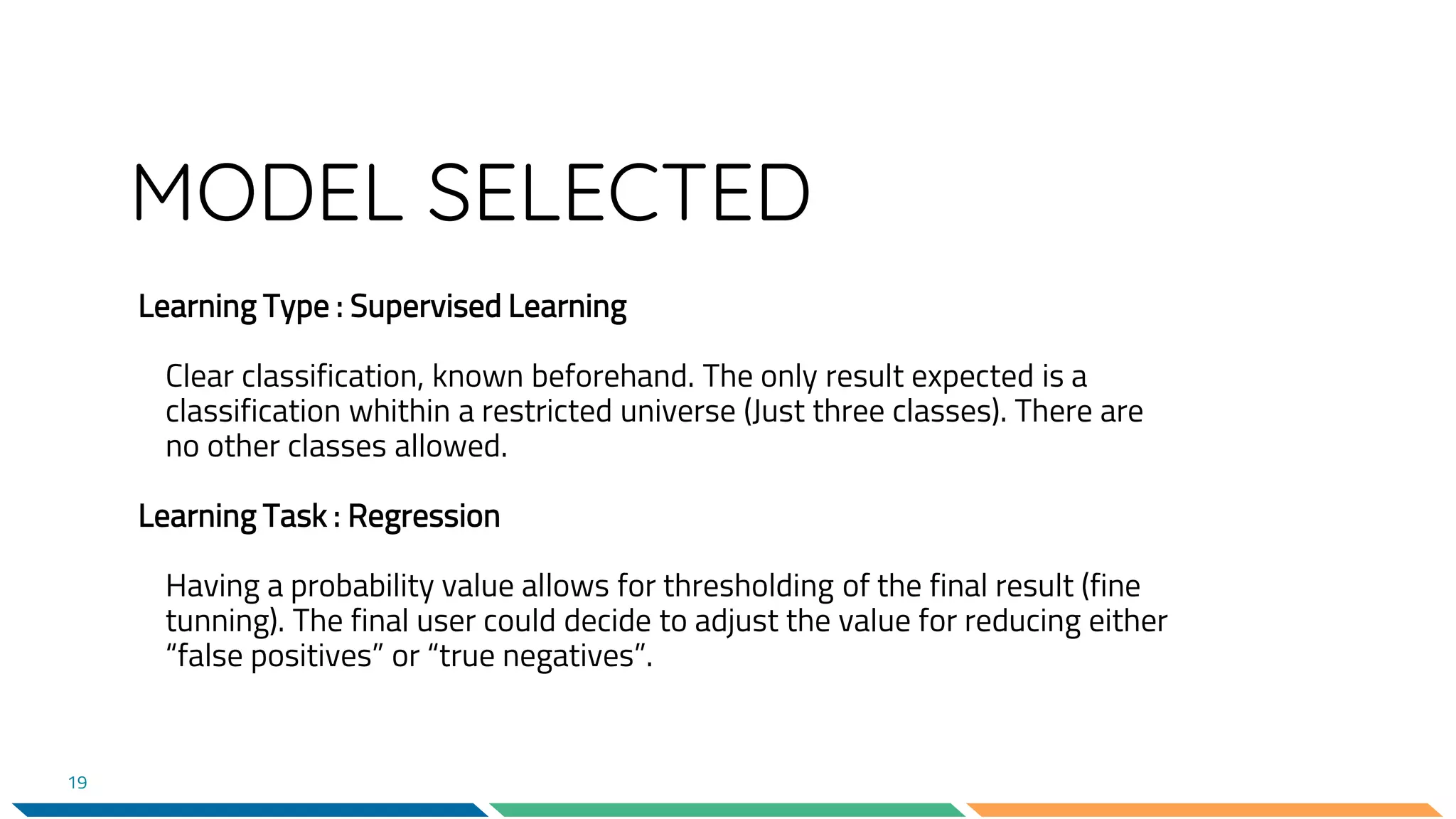
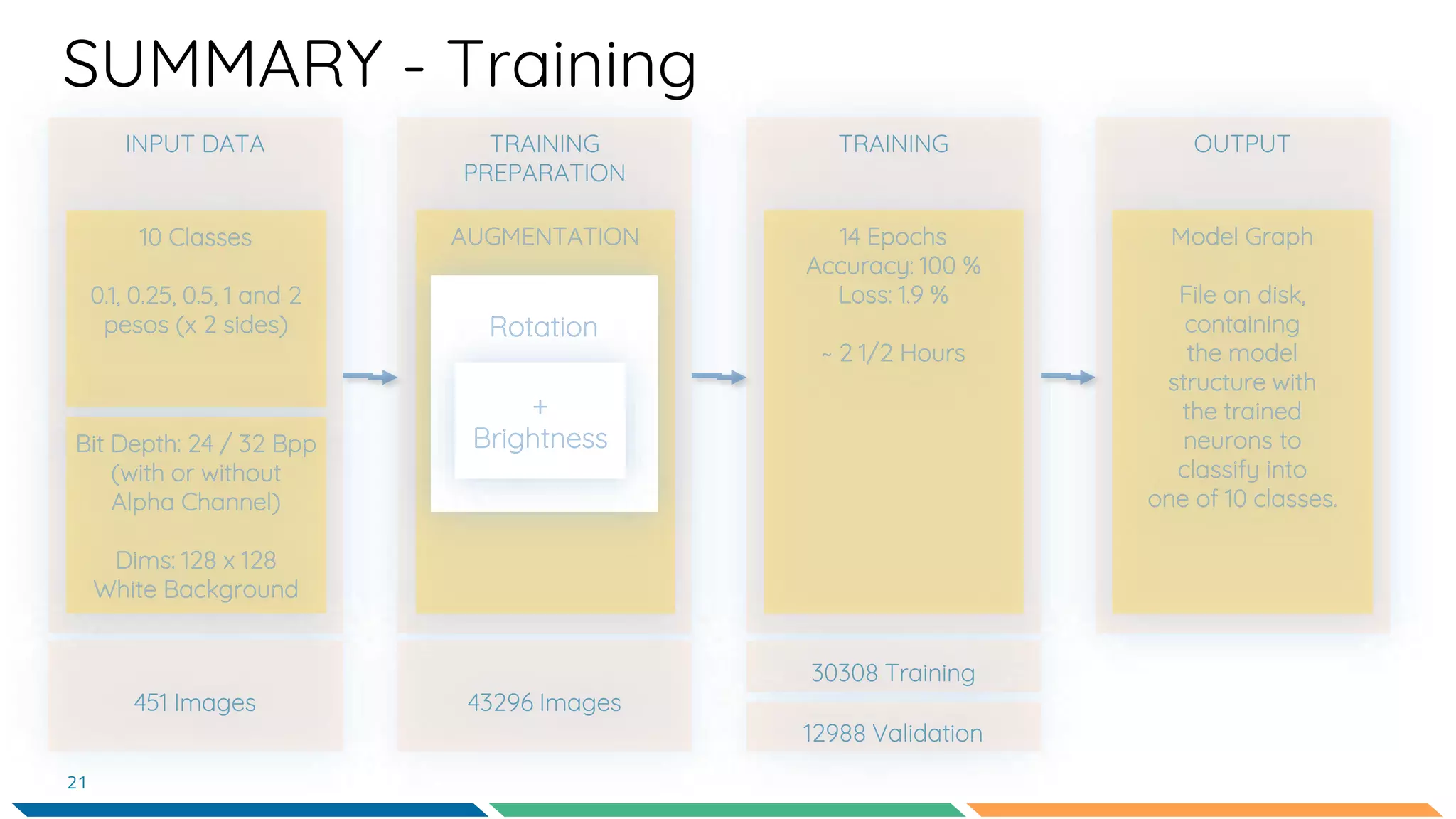
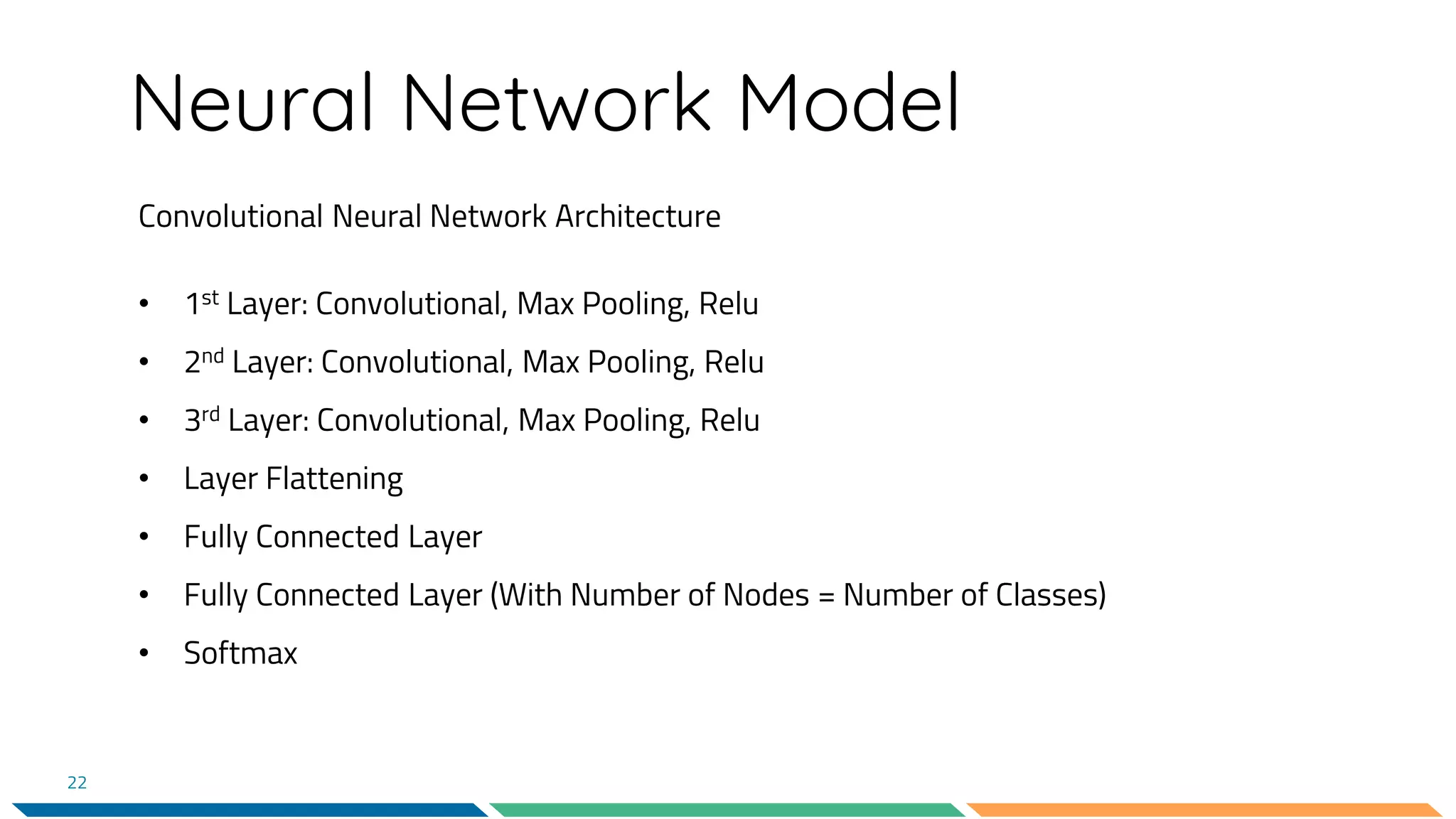
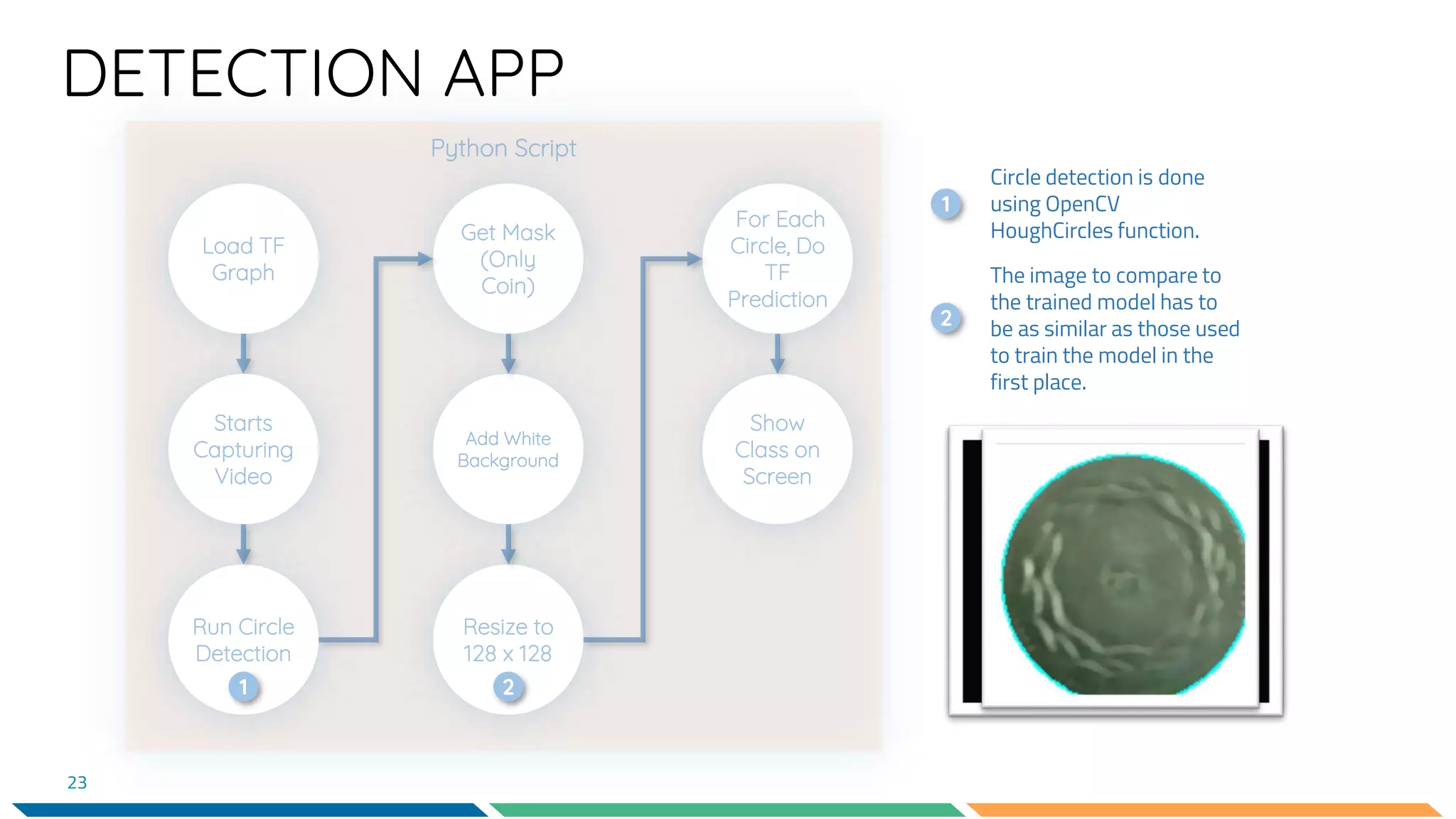
This document provides an overview of machine learning and neural networks. It discusses different types of machine learning including supervised, unsupervised, and reinforcement learning. It also describes common machine learning tasks like classification, regression, and clustering. The document then focuses on neural networks, describing their basic structure and components. It provides examples of classification and coin identification. The remainder of the document discusses tools used for machine learning like TensorFlow and Python. It outlines the model, data preparation, and neural network architecture selected for a coin classification task.