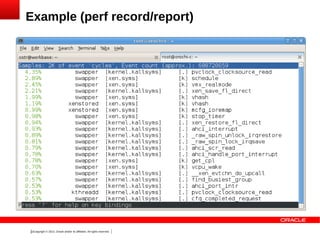
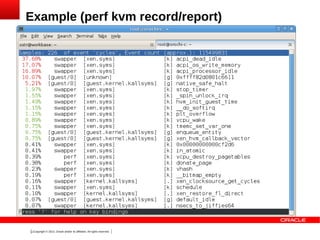
The document outlines the agenda and discussions from the Oracle Xen Developer Summit held on October 24-25, 2013, focusing on profiling methods, existing tools, and the performance (perf) framework within the Xen hypervisor. It details desired properties, high-level design features, current limitations, and future enhancements for profiling in Xen. The presentation emphasizes managing performance monitoring unit (PMU) contexts and the need for ongoing development and coordination with Linux patches.