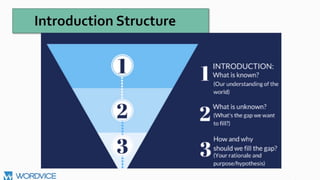
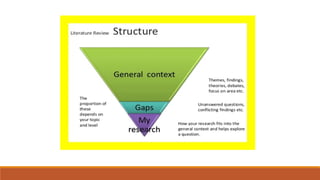
The document provides guidance on writing a research proposal. It explains that a research proposal justifies conducting research on a particular topic by presenting the benefits and outcomes of the proposed study. It recommends including a title, abstract, introduction, literature review, research methodology, potential results, discussion, and references. The introduction should provide background context on the research problem, state the aims and research question, and introduce any hypotheses. The literature review critically evaluates previous work and relates it to the research question.