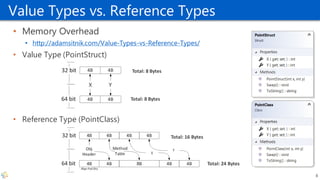
The document provides a comprehensive overview of high-performance C# 7 programming, targeting those unfamiliar with C# or facing performance issues. It covers essential techniques for optimizing algorithms, memory usage, and networking, along with highlights of new features introduced in C# 7.x. Various tools and concepts related to performance measurement and garbage collection are also discussed.