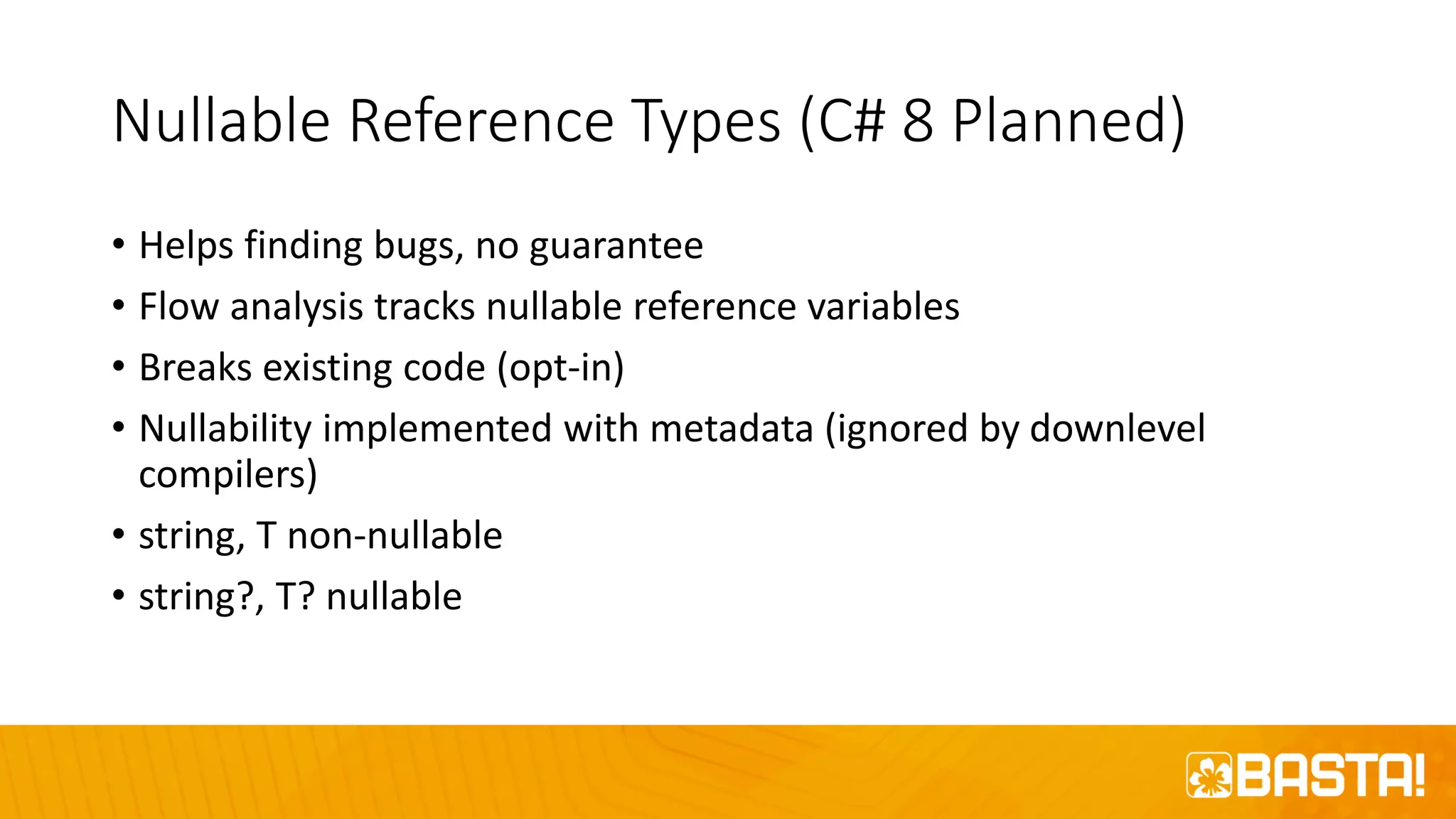
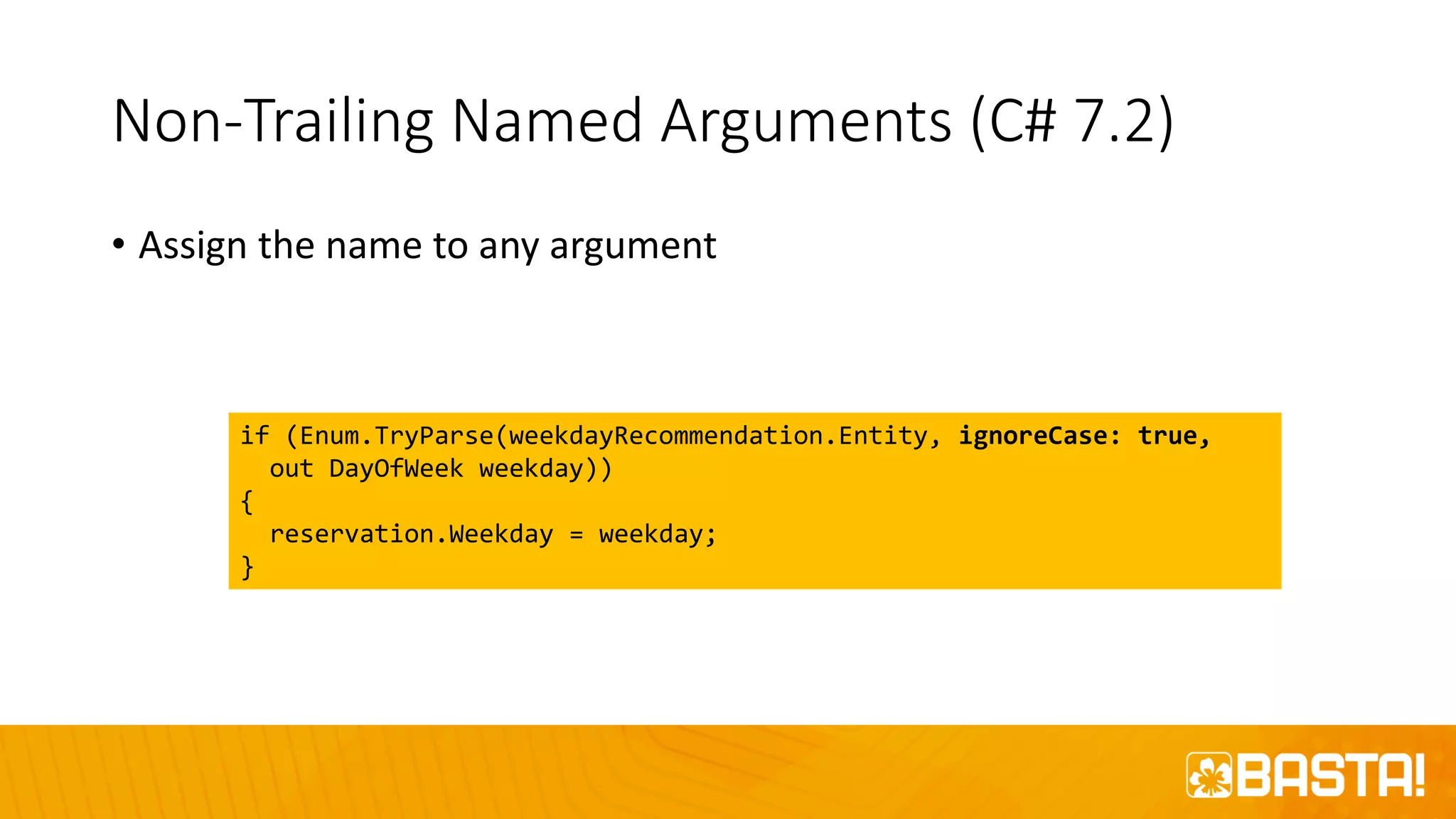
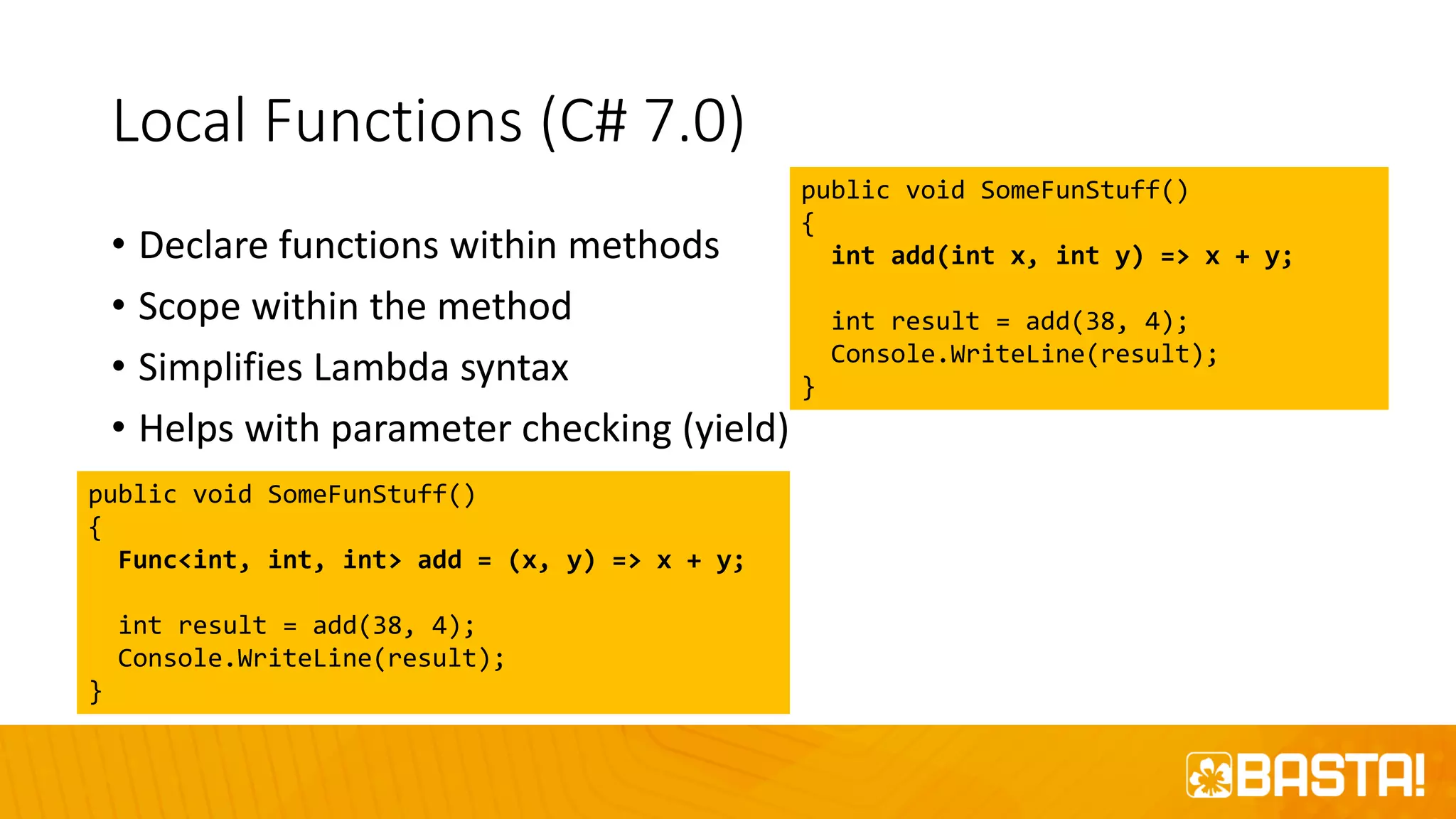
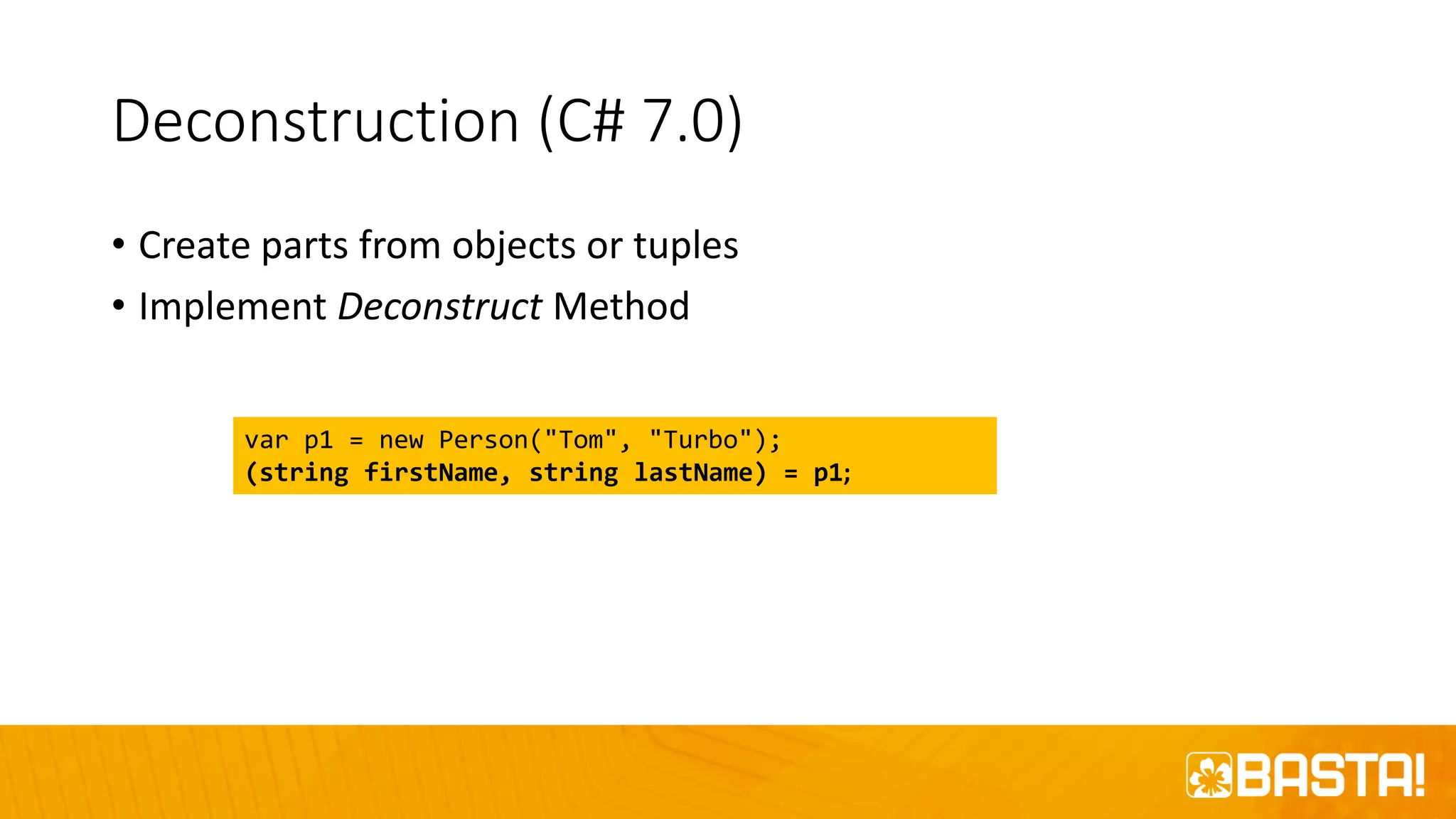
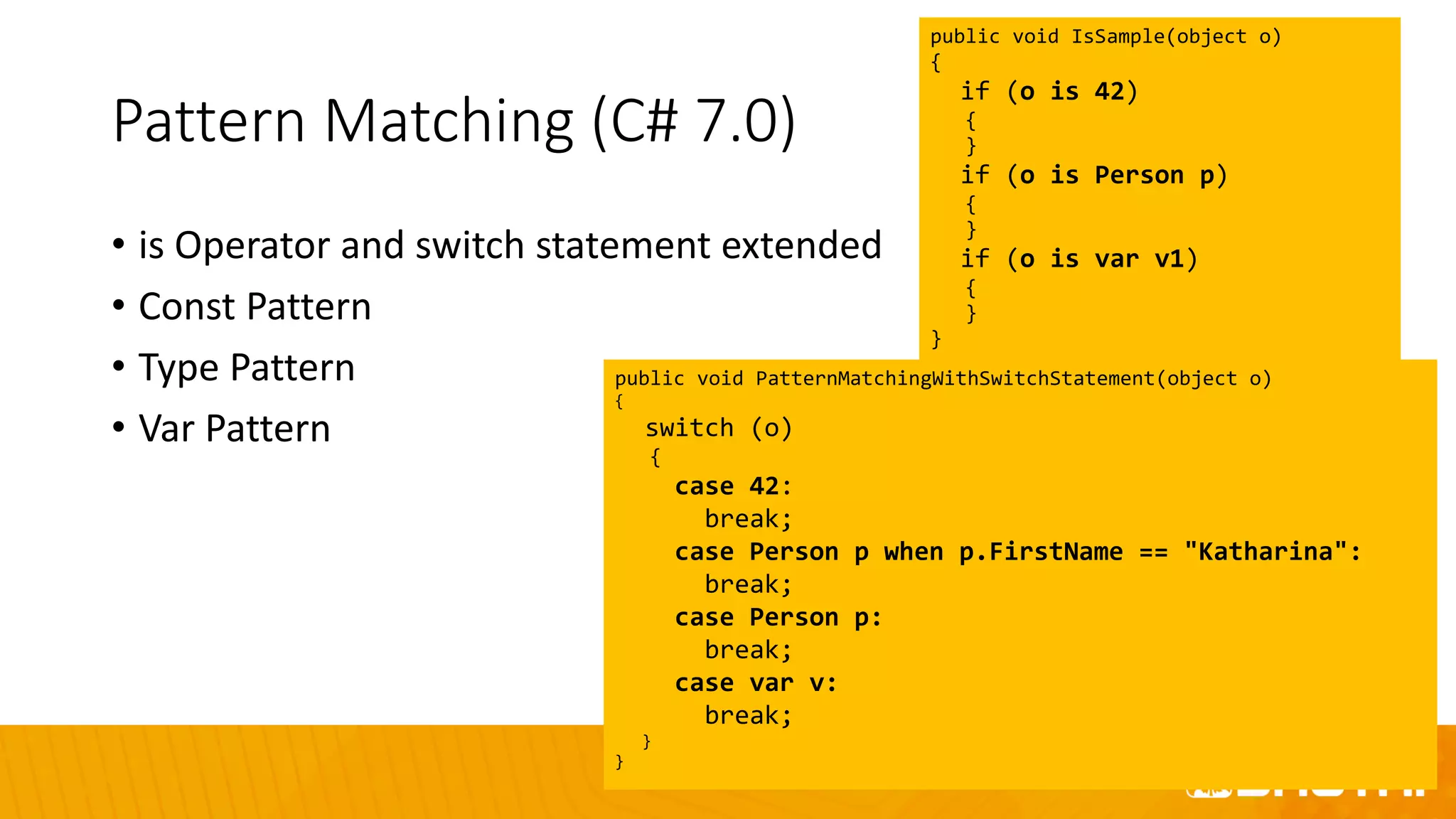
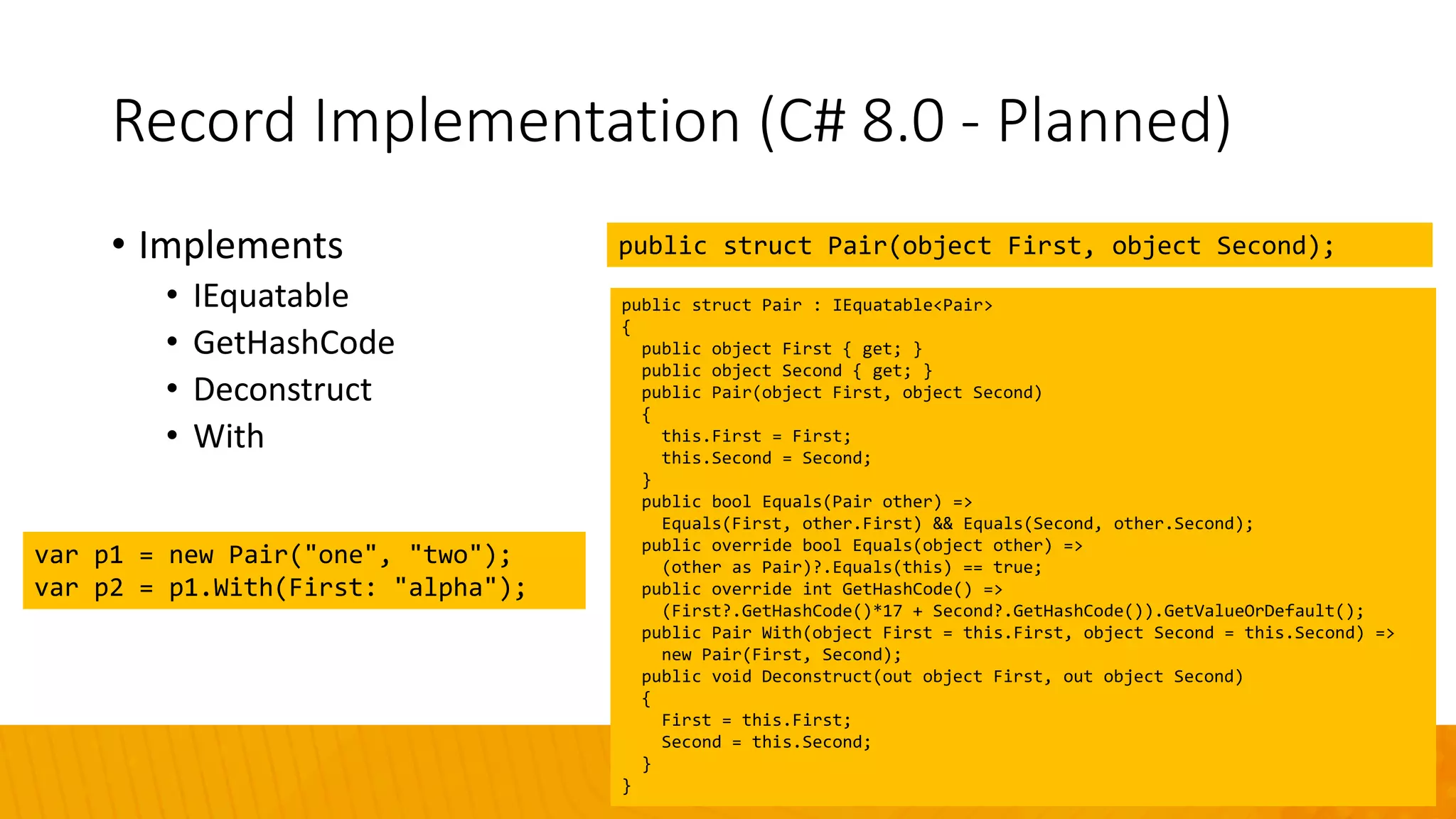
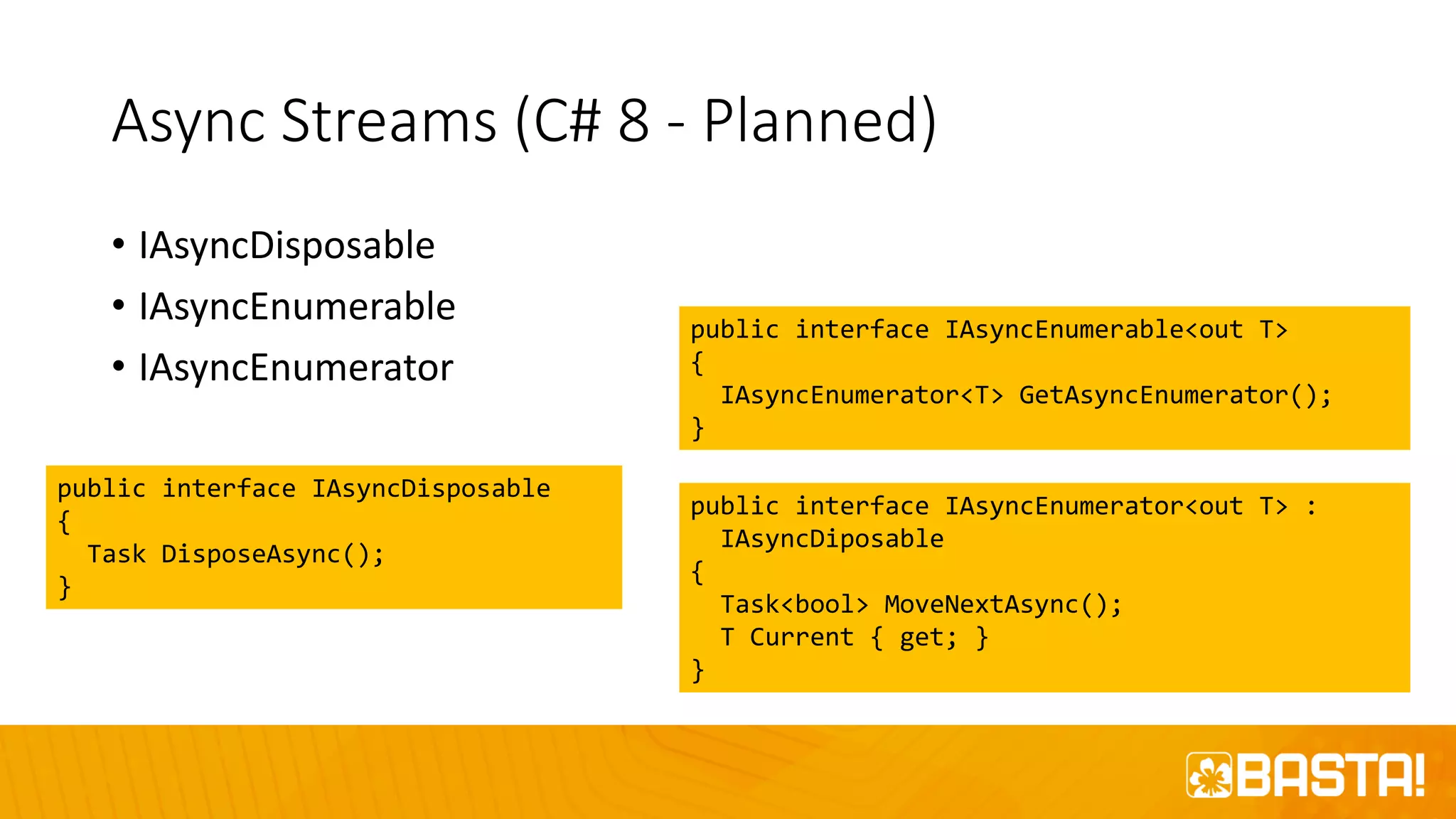
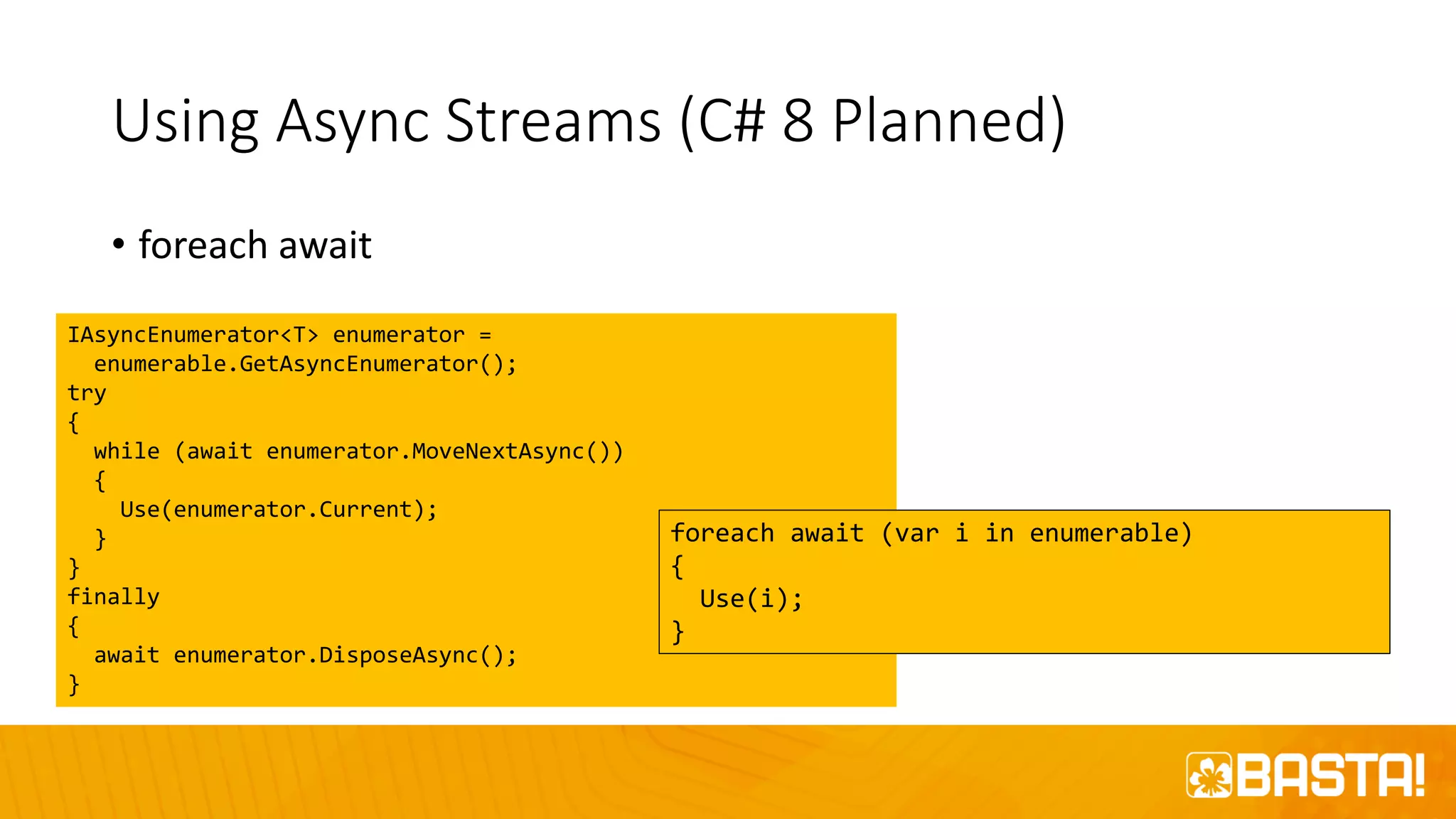
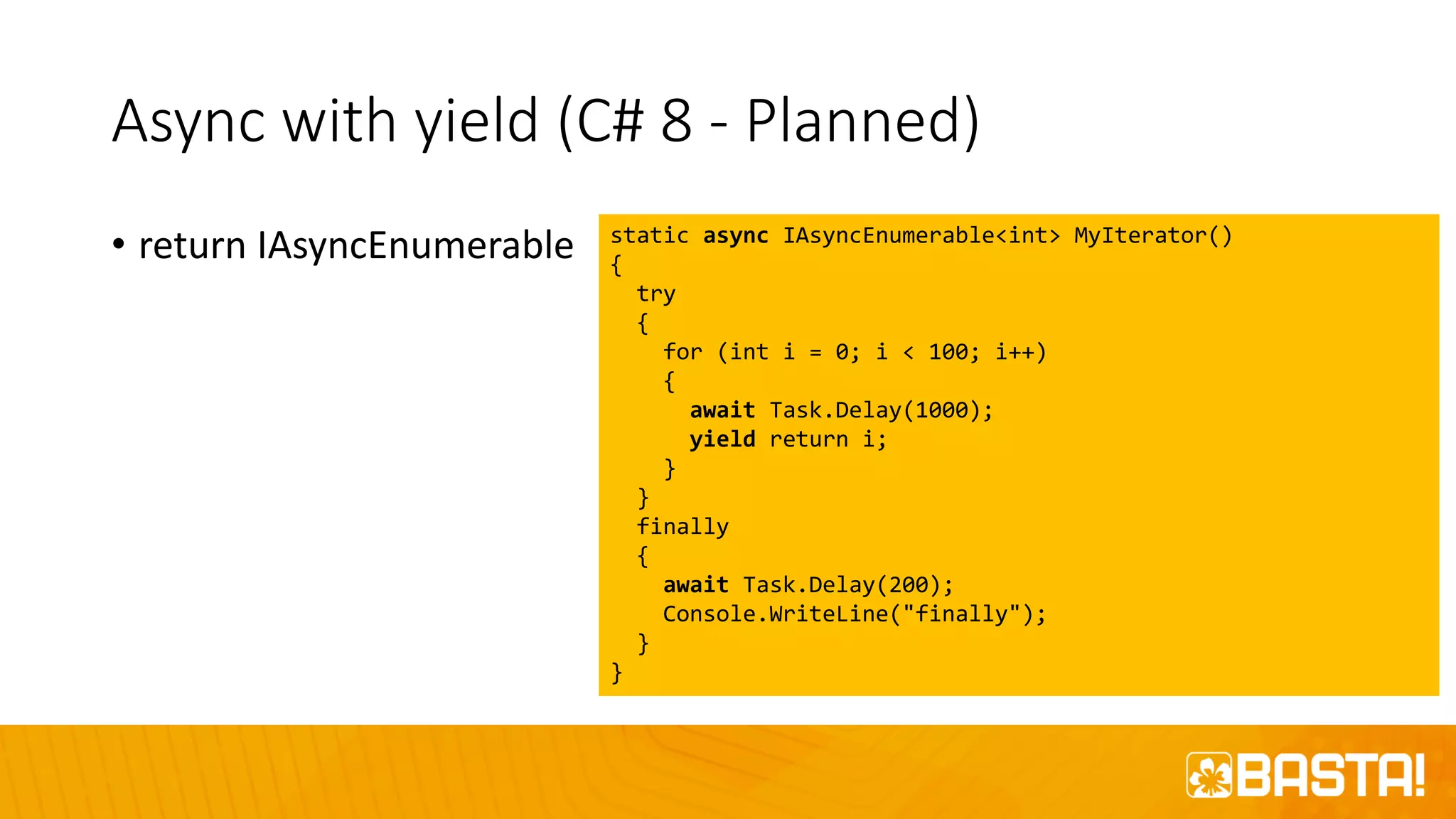
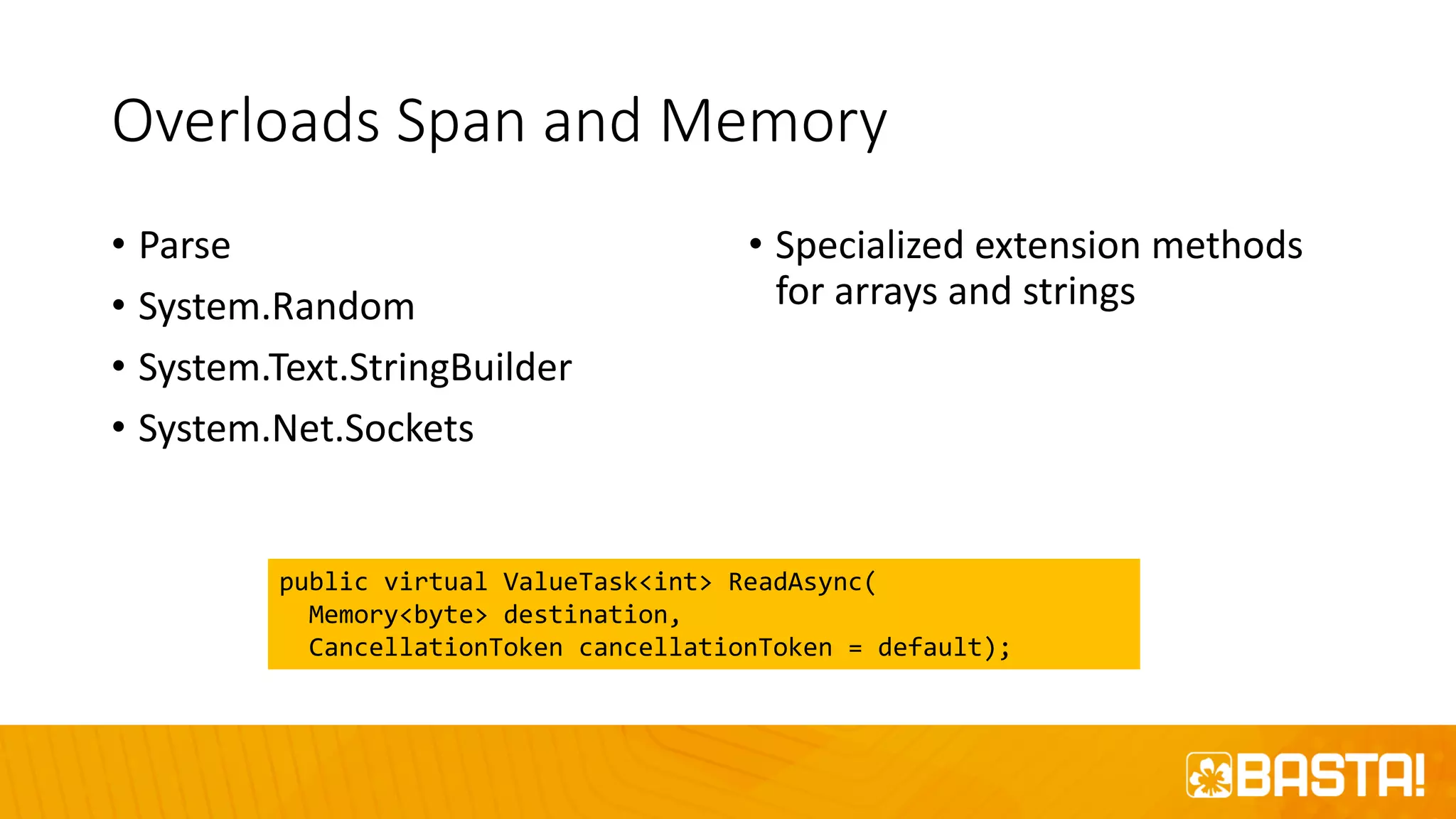
The document discusses the evolution of C# programming language, focusing on features from versions 7.0 to 8.0, including productivity enhancements, performance improvements, and new features to reduce errors. Key topics include expressions, local functions, async streams, nullable reference types, and pattern matching. It also highlights future plans for C# along with resources for further information and training.














![ArrayPool
• Reduce work needed by Garbage Collector
• Pool of arrays managed by ArrayPool
int[] arr = ArrayPool<int>.Shared.Rent(length);
//... use array
ArrayPool<int>.Shared.Return(arr, clearArray: true);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/csharp-180220110625/75/C-What-s-Next-23-2048.jpg)


![Returning Value Types By Reference
• ref return (7.0)
• ref local (7.0)
• ref readonly return (7.2)
• ref readonly local (7.2)
public ref int GetItem(int index)
{
return ref _items[index];
}
public ref readonly int GetReadonlyItem(int index)
{
return ref _items[index];
}
ref int x = ref GetItem(4);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/csharp-180220110625/75/C-What-s-Next-26-2048.jpg)


![Slicing (ranges) – C# 7.3 Planned
• Operator ..
var slice = source[5..10];
switch (codePoint)
{
case 1536..1541:
break;
foreach (var item in 3..5)
{](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/csharp-180220110625/75/C-What-s-Next-30-2048.jpg)



![Null Conditional Operator (C# 6)
• Reduce Null-Checks
int? length = customers?.Length;
Customer first = customers?[0];
int? count = customers?[0]?.Orders?.Count();
public void OnPropertyChanged([CallerMemberName] string propertyName = null) =>
PropertyChanged?.Invoke(this, new PropertyChangedEventArgs(propertyName));](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/csharp-180220110625/75/C-What-s-Next-34-2048.jpg)