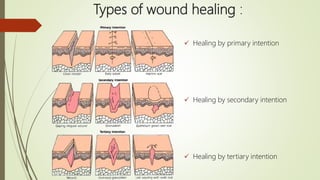
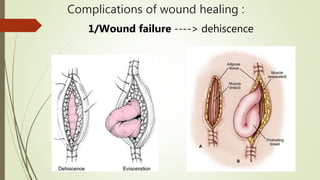
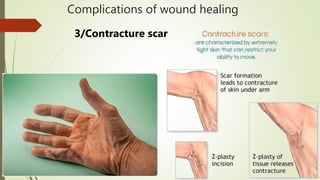
This document summarizes wound healing and its complications. It describes three types of wound healing: primary, secondary, and tertiary intention. The components and stages of wound healing are outlined. Factors that affect wound healing, such as age, nutrition, cortisone, and infection are discussed. Complications of wound healing include dehiscence, disfigurement, contracture, hypertrophic and keloid scarring, and infection. The document provides an overview of the wound healing process and potential problems that can arise.