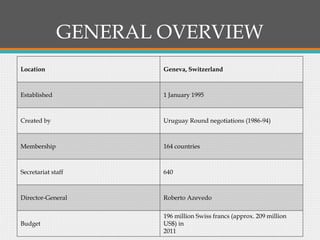
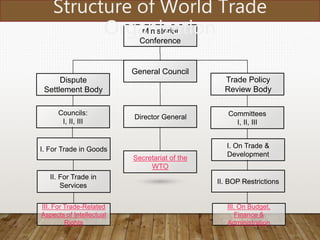
The World Trade Organization (WTO), established on January 1, 1995, regulates international trade to ensure it is smooth and predictable, evolving from the General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT) established in 1948. The organization has 164 member countries and addresses trade disputes while providing a platform for negotiations and monitoring national trade policies. Its structures include the General Council, Dispute Settlement Body, and Appellate Body, which handle dispute resolution and policy reviews among member nations.