The document discusses the World Trade Organization (WTO). It provides information on its objectives, functions, structure and agreements. Some key details include:
- The WTO was established in 1995 to replace the General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade and promote multilateral trade through agreements regulating international trade.
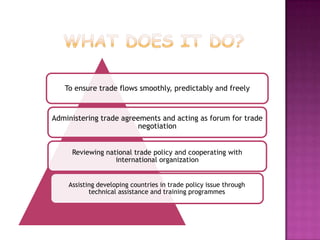
- It has 164 member countries and seeks to ensure trade flows freely by settling disputes and reviewing national trade policies.
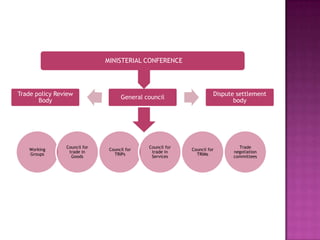
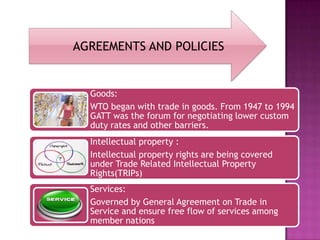
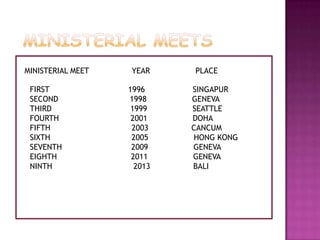
- The WTO agreements cover trade in goods, services, intellectual property, agriculture, textiles and dispute settlement. Ministerial meetings are held every two years.
- The WTO aims to reduce barriers to international trade and provide an open trading system but has also received criticism for negatively impact