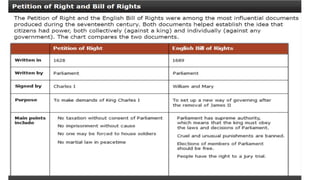
The document summarizes key events and developments in European history between the 16th and 18th centuries. It discusses the witchcraft trials of the 16th-17th centuries, the Thirty Years' War, revolutions in England including the English Civil War and Glorious Revolution, the wars of Louis XIV of France, the rise of Prussia under the Great Elector, and reforms in Russia under Peter the Great. These events helped shape the modern European state system based on Westphalia principles of national sovereignty.