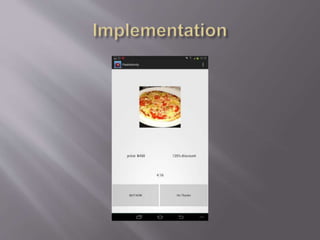
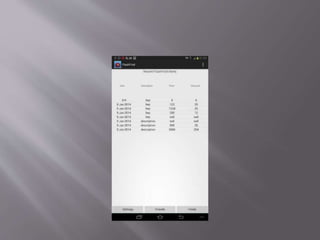
The document discusses an augmented reality (AR) application developed by students which enhances user experiences by providing real-time information and notifications while addressing concerns like battery drainage and application efficiency. The project utilizes various development tools, including Eclipse and Android Studio, and incorporates hardware and software sensors for functionality. Key features of the application include the use of a low pass filter for improved accuracy, as well as a push notification system to conserve battery life.
















![ [1] Mr. Raviraj S.Patkar, Mr. S. Pratap Singh, Ms. Swati V. Birje,”
International Journal of Advanced Research in Computer Science and
Software Engineering,” IEEE Transanction, 5, May 2013.
[2] Naresh Kumar N, Prof. Mohan K, “GCM Service Driven
Communication With An Android Application in Cloud Computing,” in
proceeding, 5, May 2013.
[3] Poonam, Prof. (Dr.) Yusuf Mulge, “Remote Temperature Monitoring
Using LM35
sensor and Intimate Android user via C2DM Service,” in proceeding, 6,
June 2013.
[4] Zhi Xu, Kun Bai, Sencun Zhu, “Inferring User Inputs On Smartphone
Touchscreens Using On-board Motion Sensors,” in proceeding, April 16–
18, 2012.
[5] Shahid Ayub, Alireza Bahraminisaab, Bahram Honary,” A Sensor
Fusion Method for Smart phone Orientation Estimation,” in proceeding,
June, 011.
[6] Hamed Ketabdar, Mehran Roshandel, Kamer Ali Yüksel, “Towards
Using Embedded Magnetic Field Sensor for Around Mobile Device 3D
Interaction,” in proceeding, May, 2012.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/worldexplorer-140529020745-phpapp02/85/World-explorer-20-320.jpg)