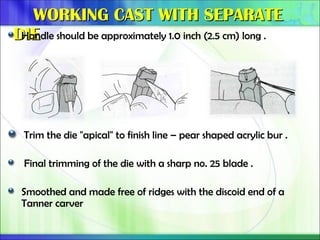
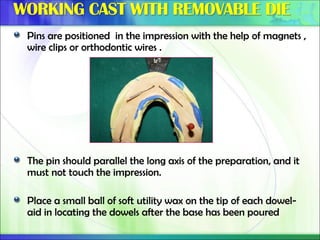
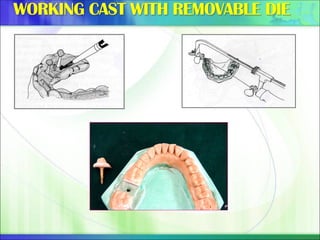
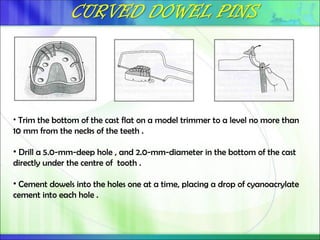
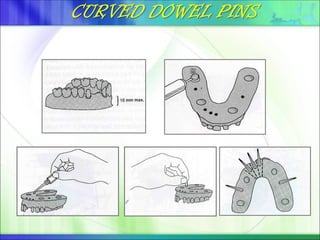
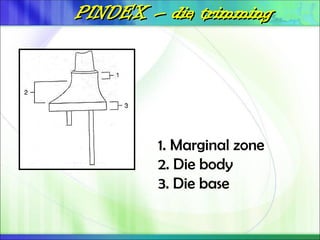
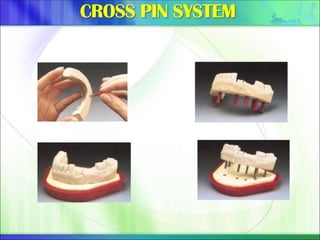
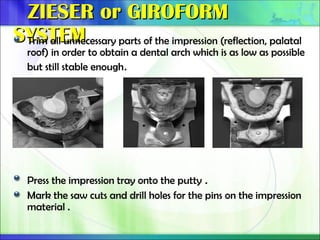
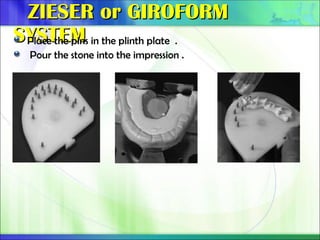
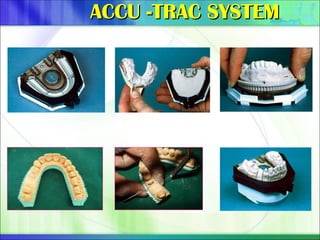
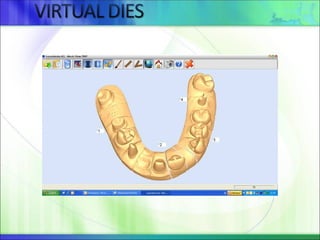
Die - the positive reproduction of the form of a prepared tooth in any suitable substance (GPT-5).
The die for the fixed restoration also must meet certain requirements:
It must reproduce the prepared tooth exactly.
- All surfaces must be accurately duplicated, and no bubbles or voids can be accepted.
Desirable characteristics of a die material:
- accuracy
- reproduce fine detail and sharp margins
- strength
- hardness
- ease of manipulation
- production of die in a short time
- suitable to all types of impression materials
- non-injurious to health
- good color contrast
Classification - Newmann and Williams , 1969
a) METAL DIES :
- Silver and copper amalgam - must condense into a rigid material. Affected by heat. 10-12 hours to harden.
- Electroplated dies
- Copper , 10-15 hour process
- Silver - hydrocyanic gas can be produced
- Bismuth-tin Alloy spray gun at 138 degrees C to impression. Difficult to spray in narrow confined areas
The use of electroformed gold copings as the core of fixed oral prostheses was first introduced by Rogers & Armstrong in 1961 .
DISADVANTAGE :
- Highly toxic electrolyte , need for large expensive equipment .
In 1970 Wismann developed thiosulfate electrolyte system .
In 1991 a new, much smaller system developed by Gramm Technik - less expensive .
- Electrodeposition of 24-Kt gold copings directly onto a stone die would seem to offer the potential for less distortion and misfit .
Thicknesses of 0.2mm
The areas to be plated are first coated with finely powdered silver or graphite .
The impression is then placed in an electroplating bath .
A layer of pure metal is deposited on the impression and is supported with Type IV stone or resin.
performed slowly – TYPICALLY TAKES 8 hrs .
silicone impression materials are difficult to electroplate evenly –low surface energy .
Polyether - hydrophilic nature, imbibe water and become distorted - cannot be plated accurately
STONE DIES :
- Type IV and Type V gypsum products .
- The materials are capable of reproducing a 20-um-wide line as prescribed by ADA specification No. 19 .
- Setting and thermal expansion compensate for the casting shrinkage .
- Gypsum's greatest disadvantage is its relatively poor resistance to abrasion .
- To overcome this disadvantage - DIE HARDENER
Materials like colloidal silica , cyanoacrylate , gum arabic , calcium hydroxide , polystyrene - added or coated to gypsum to improve abrasion resistance .
Methods- soaking or boiling dies , coating , air thinning , brush thinning , shaking .
Composition of a typical die hardener :
- Methyl Ethyl ketone or any solvent = 75%
acrylic resin or Methyl Methaacrylate = 25%
Little effect on the hardness of the stone, they improve abrasion resistance .
Slight increase in setting expansion.
Abrasion resistance most improved by impregnate the surface of the die with a low-viscosity resin such as cyanoacry