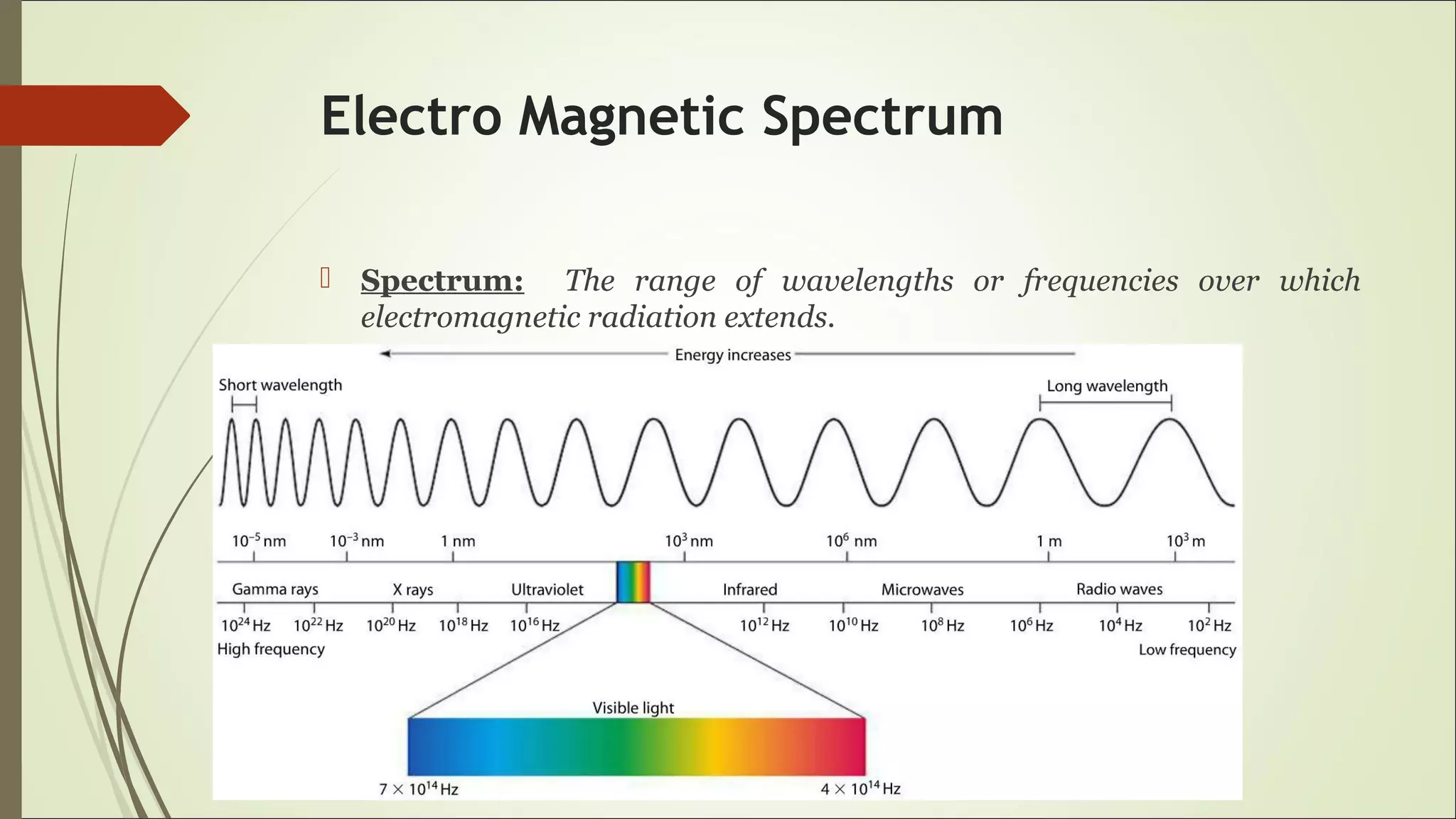
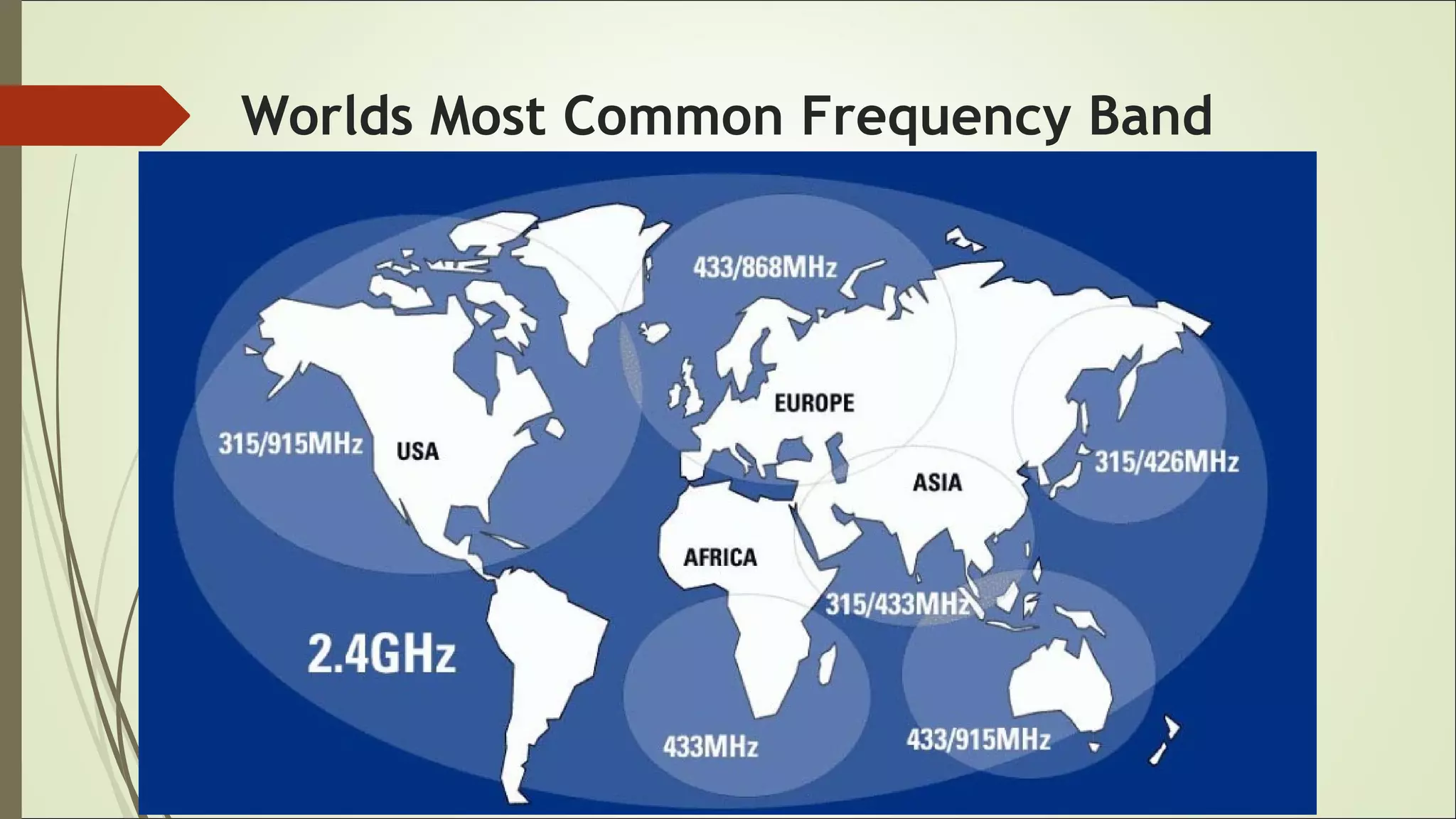
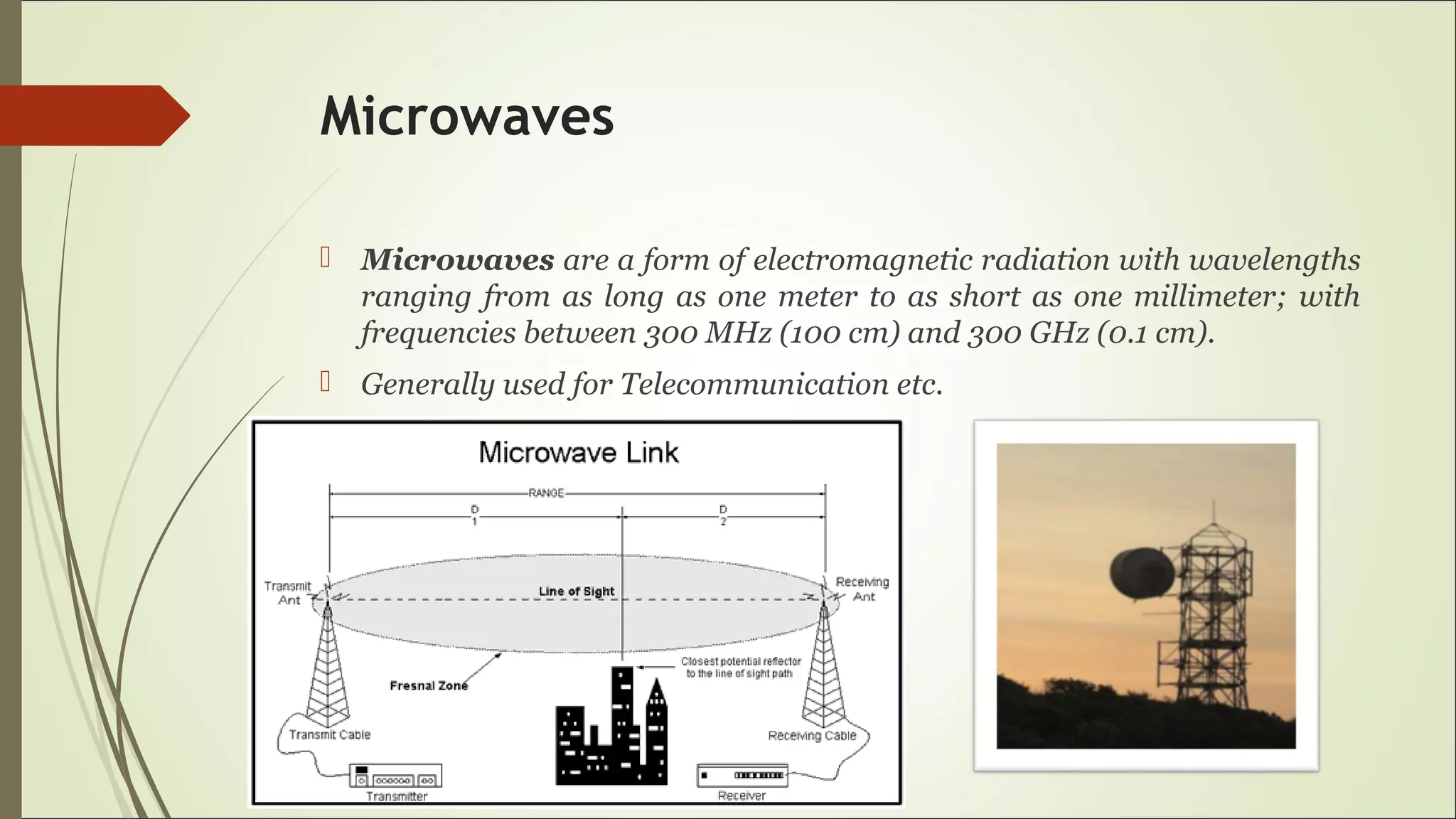
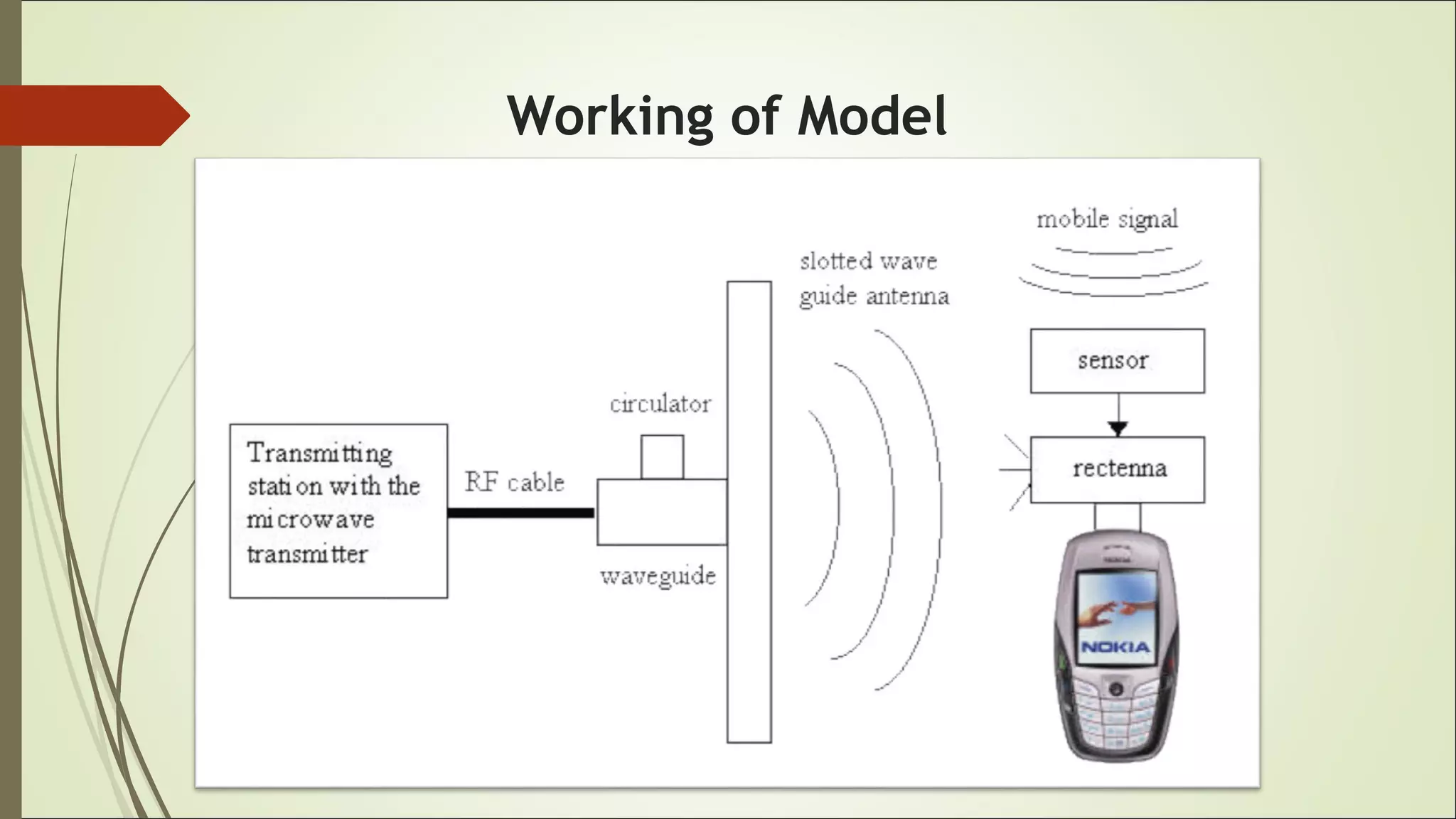
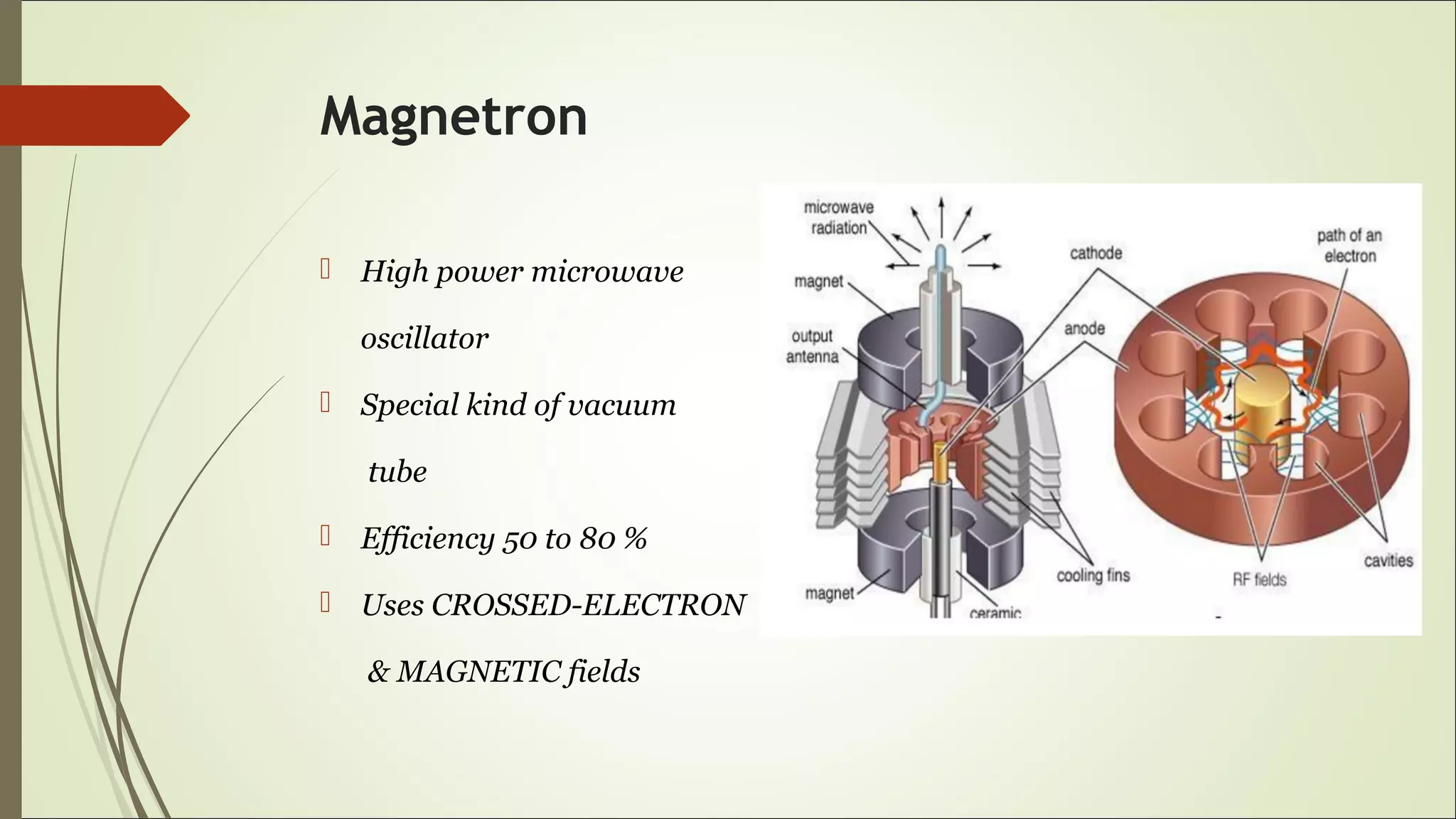
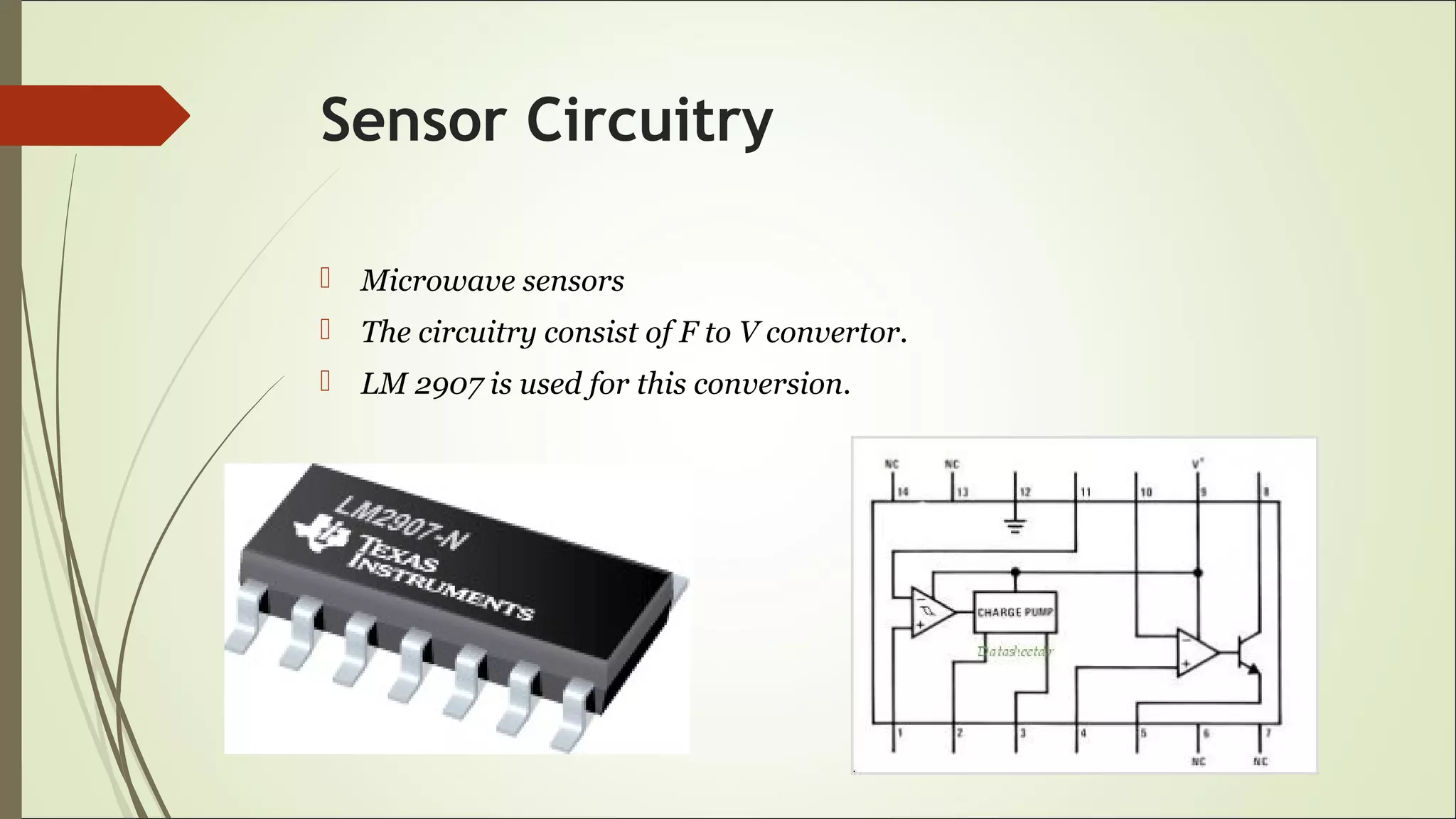
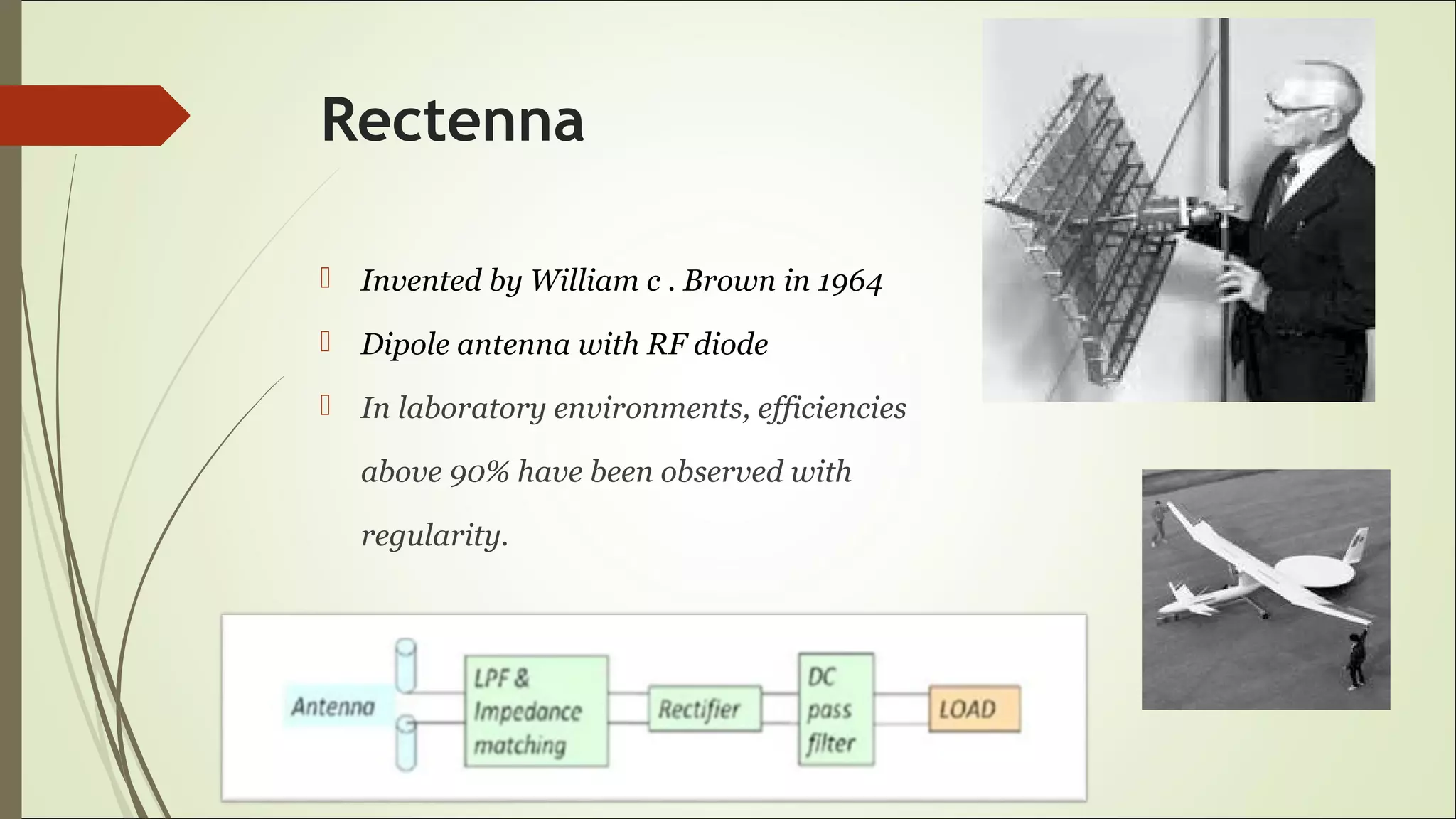
This document proposes a wireless mobile charging system using microwaves. It would allow phones to charge automatically as users talk, eliminating the need for physical charging cables. The system would consist of a transmitter using a magnetron and slotted waveguide antenna to broadcast microwaves. Receivers on phones would contain a sensor and rectenna to detect and convert the wireless energy into electricity to charge the battery. While this could provide more convenient charging anywhere, concerns include potential health effects of radiation exposure and higher system costs compared to wired charging.