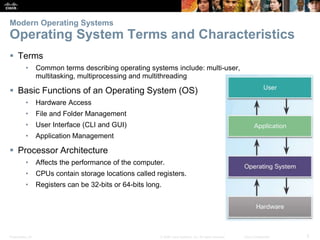
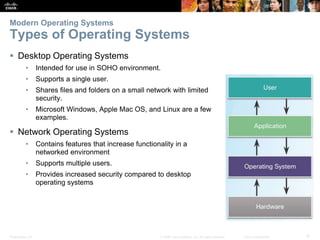
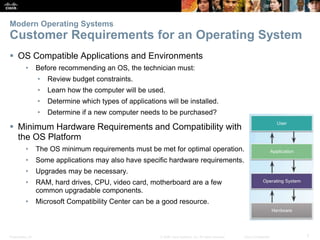
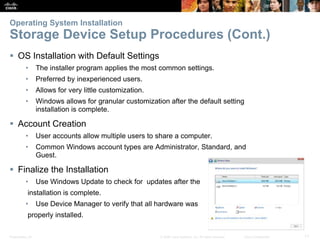
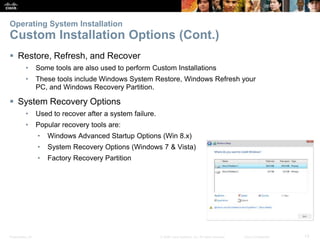
This document provides instructor materials for a chapter on installing Windows operating systems. The chapter covers modern operating systems, operating system installation, and includes a summary. It discusses operating system requirements, types of operating systems, hardware requirements, and the Windows installation process including partitioning drives, account creation, and configuration options.