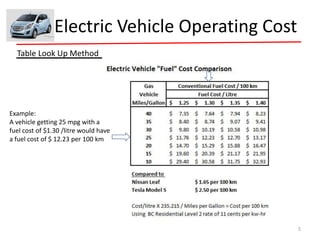
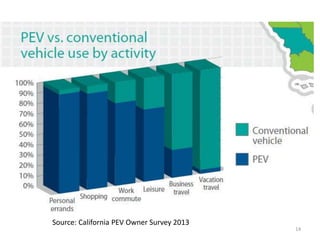
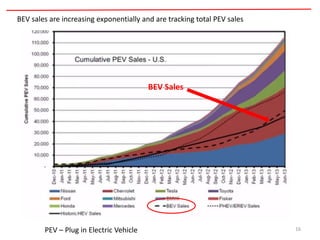
The document discusses the advantages of electric vehicles over gas-powered vehicles. It notes that electric vehicles have no emissions, low operating costs that are typically 15% of the cost of gas vehicles, require no oil changes, have 98% fewer moving parts, virtually no brake pad replacements, and are expected to have twice the useful life of internal combustion engine vehicles. It also provides data showing the increasing sales and models of electric vehicles.