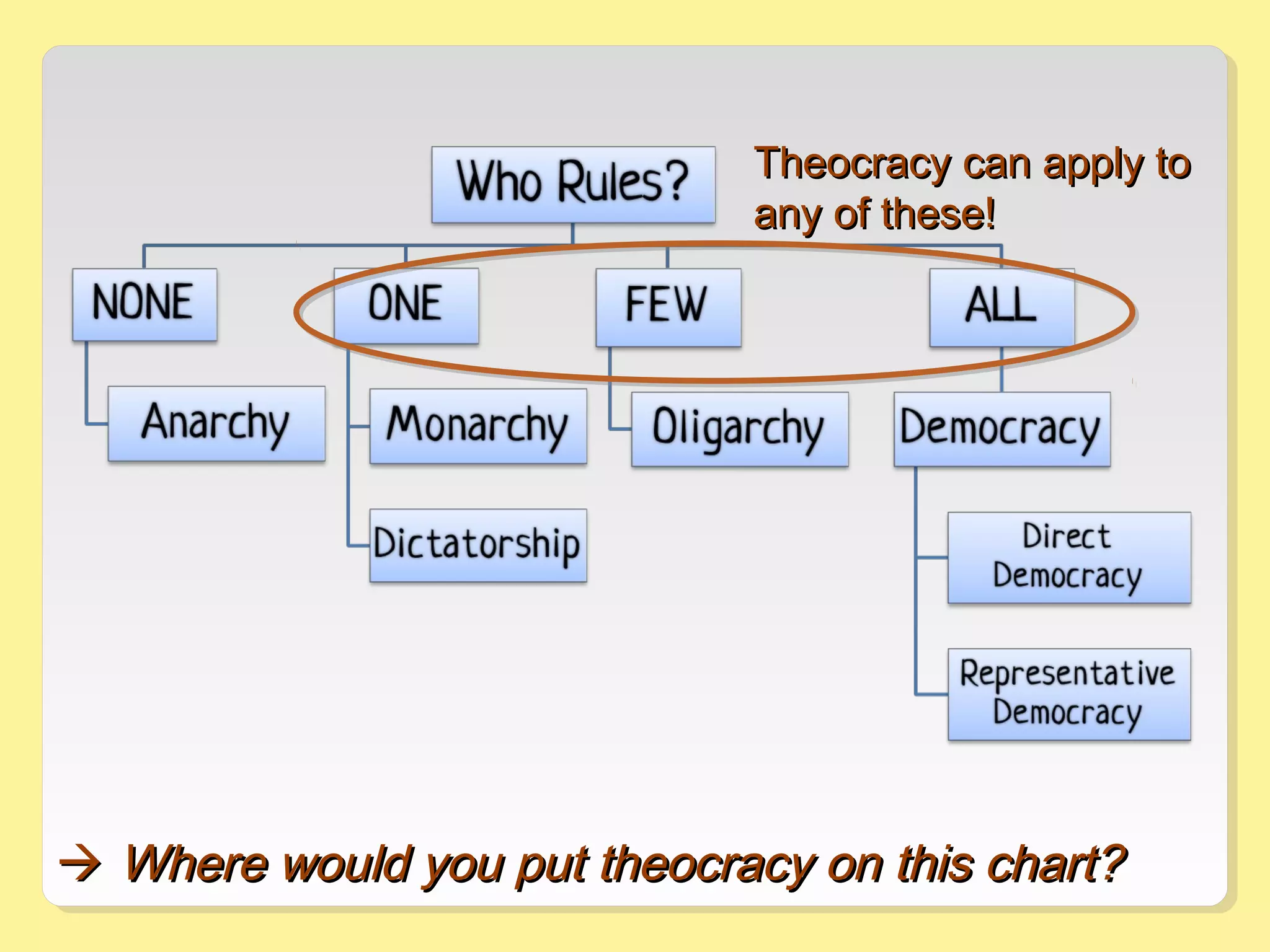
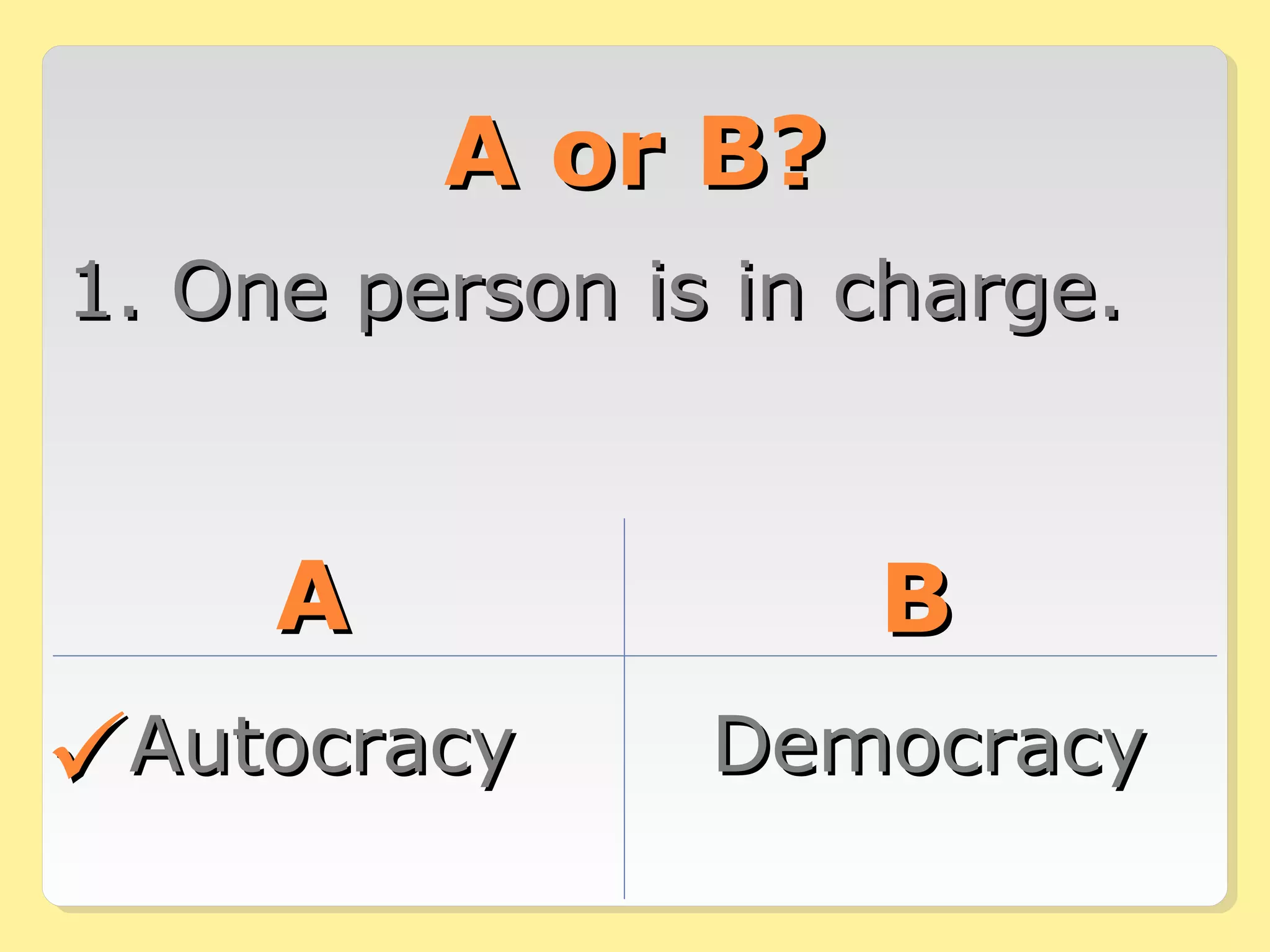
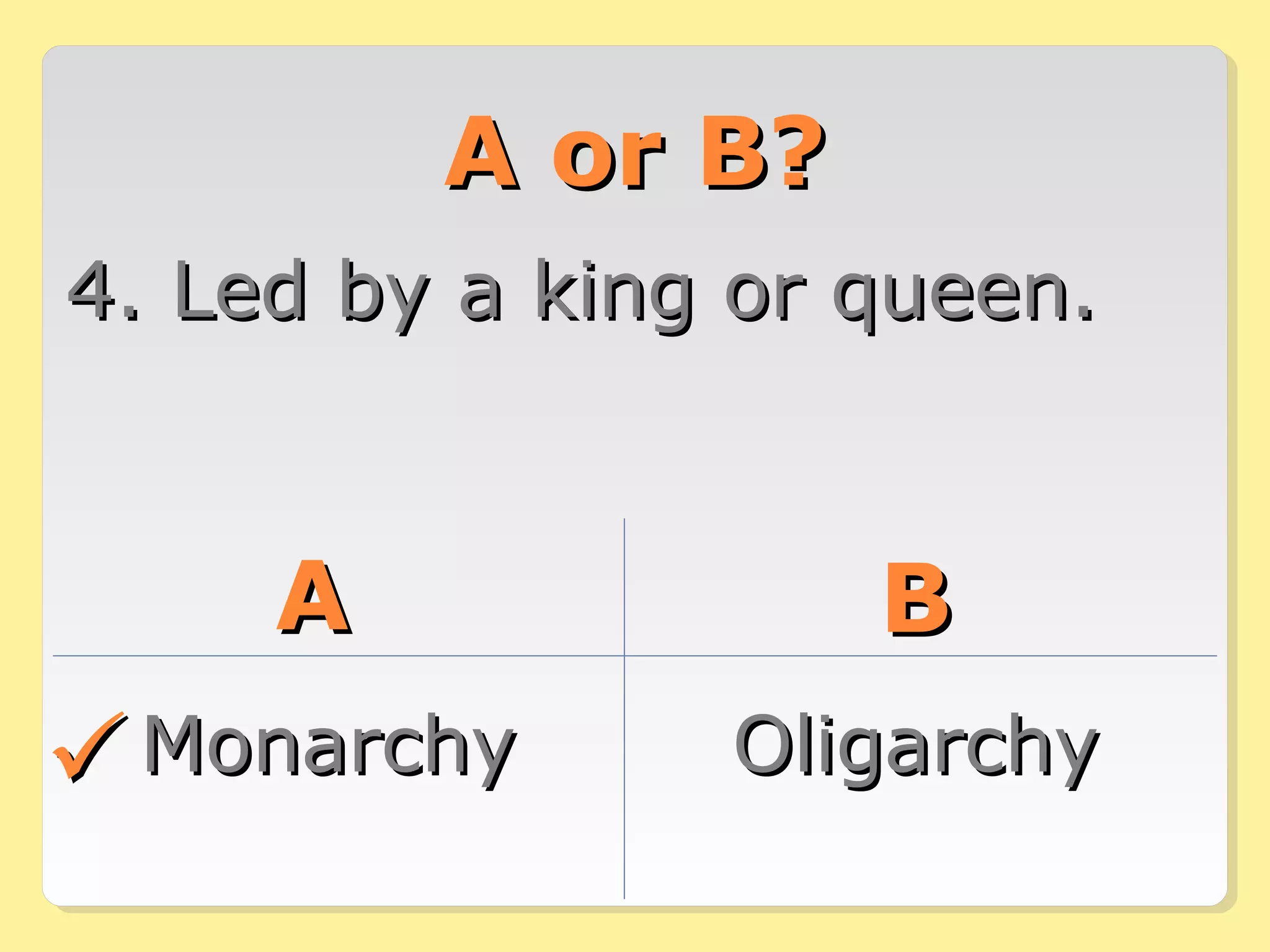
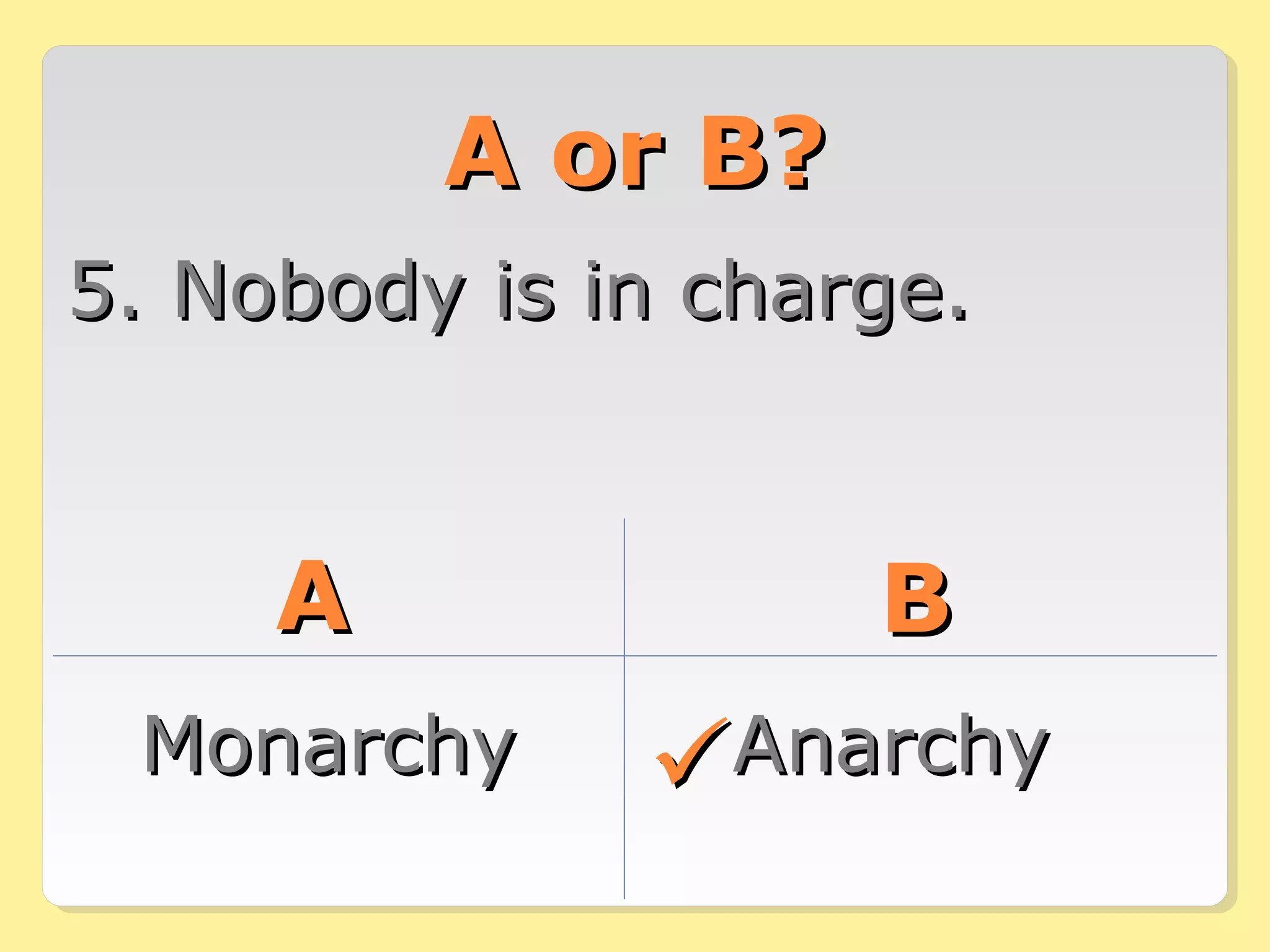
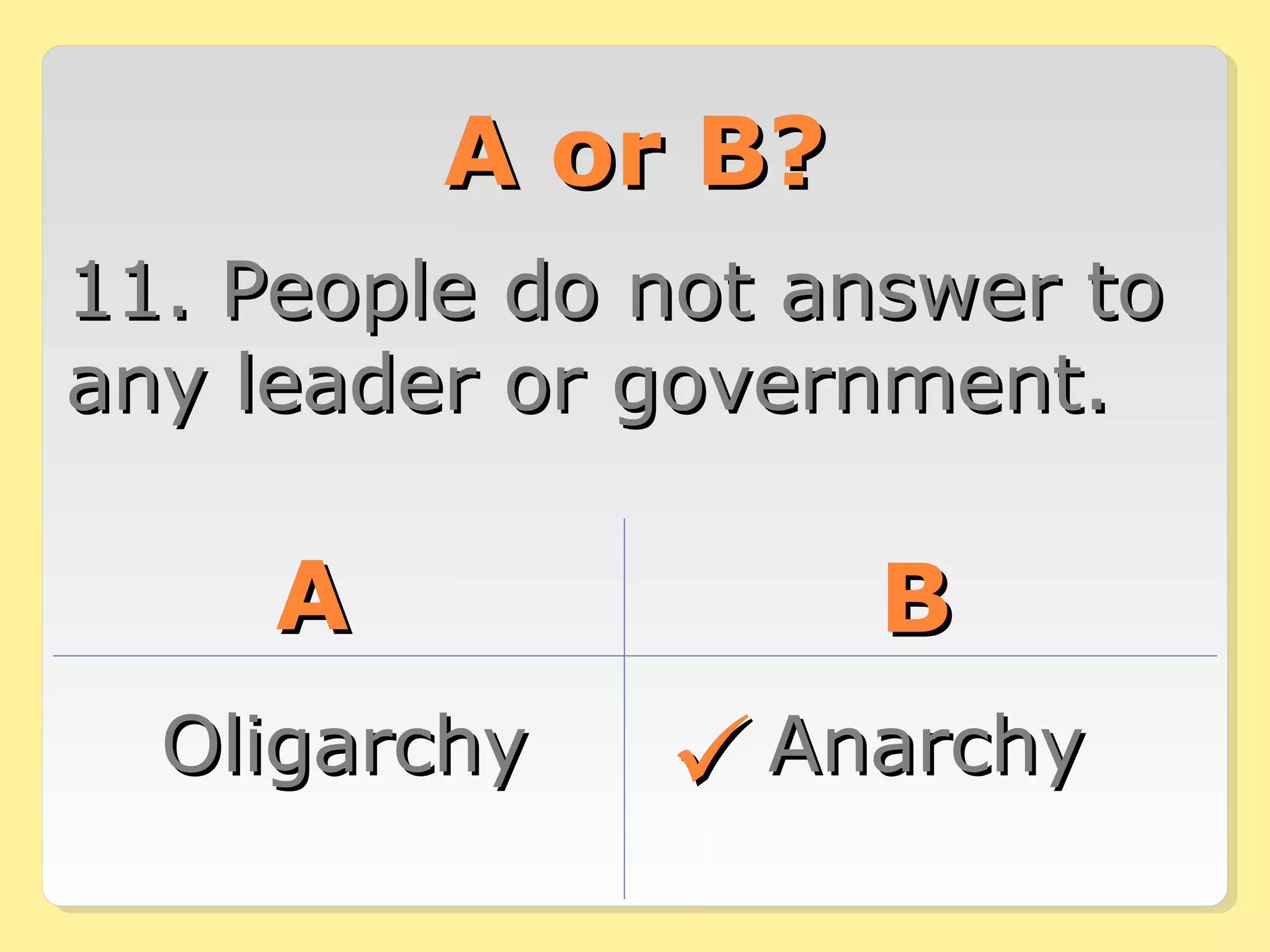
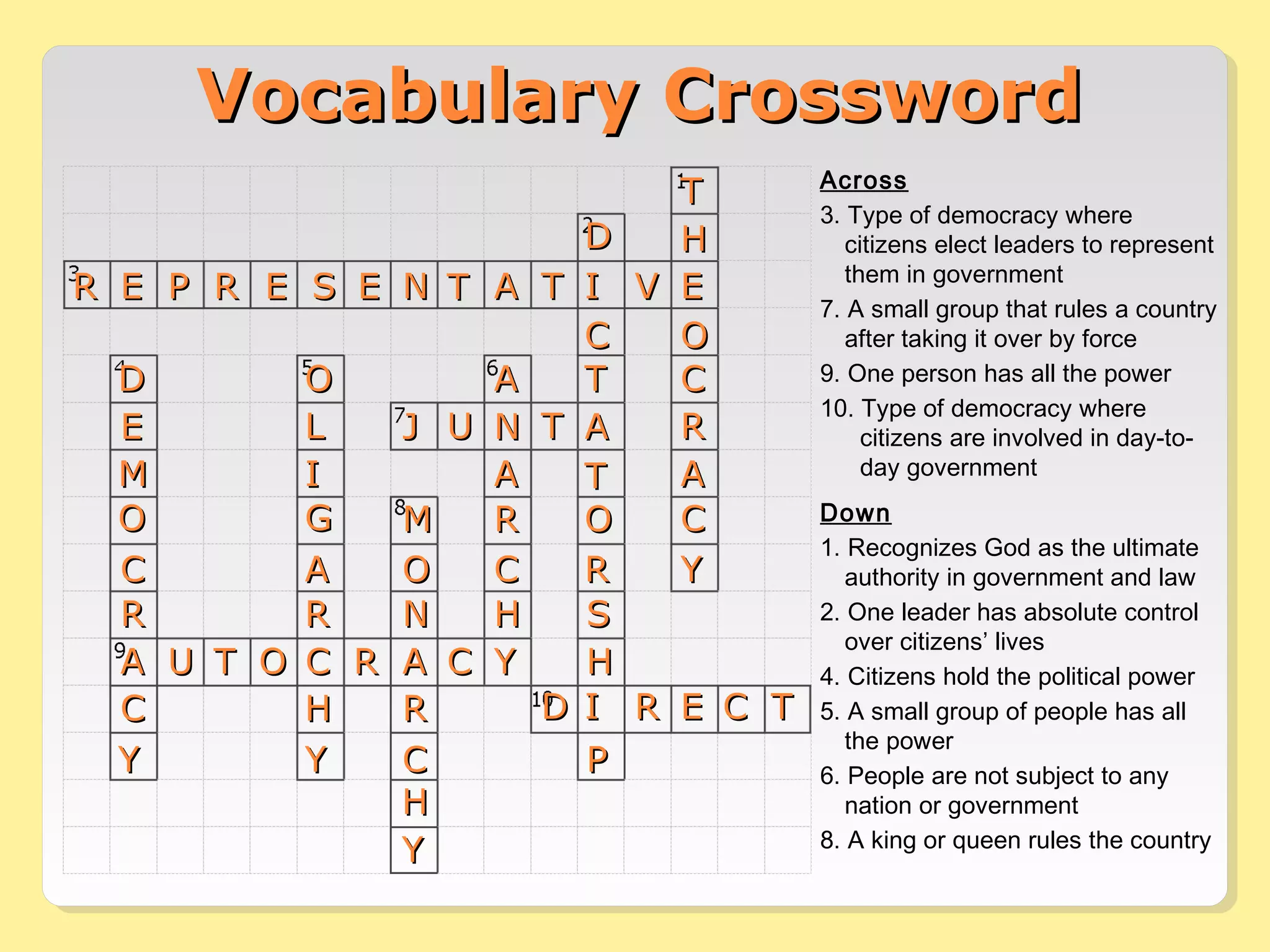
This document provides information about different forms of government through graphics, mini-quizzes, and activities. The graphics include a chart on different forms of government like democracy, dictatorship, and monarchy. The mini-quizzes ask users to identify characteristics of governments and match them with the correct form. The activities involve identifying the forms of government for different real-world countries and determining whether statements about governments are true or false.