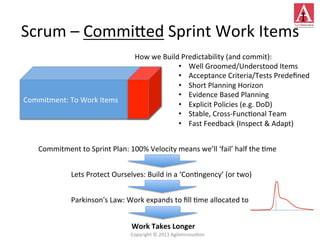
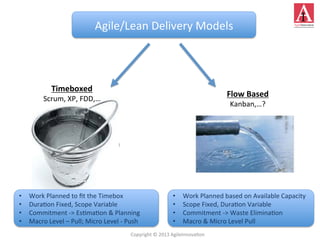
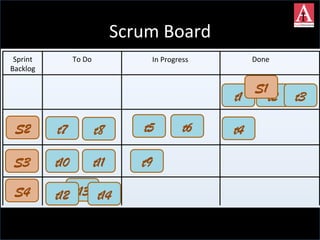
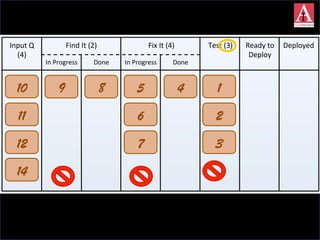
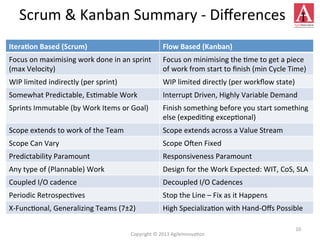
The document discusses different approaches to commitment in Scrum and Kanban frameworks for software development. In Scrum, teams commit to completing a fixed set of work items within a sprint, while in Kanban teams commit to achieving an overall goal and forecast work items. The document also notes some assumptions of Scrum that may not always be valid, such as all work being known and estimable. It provides an overview of key differences between timeboxed and flow-based approaches like Scrum and Kanban respectively.