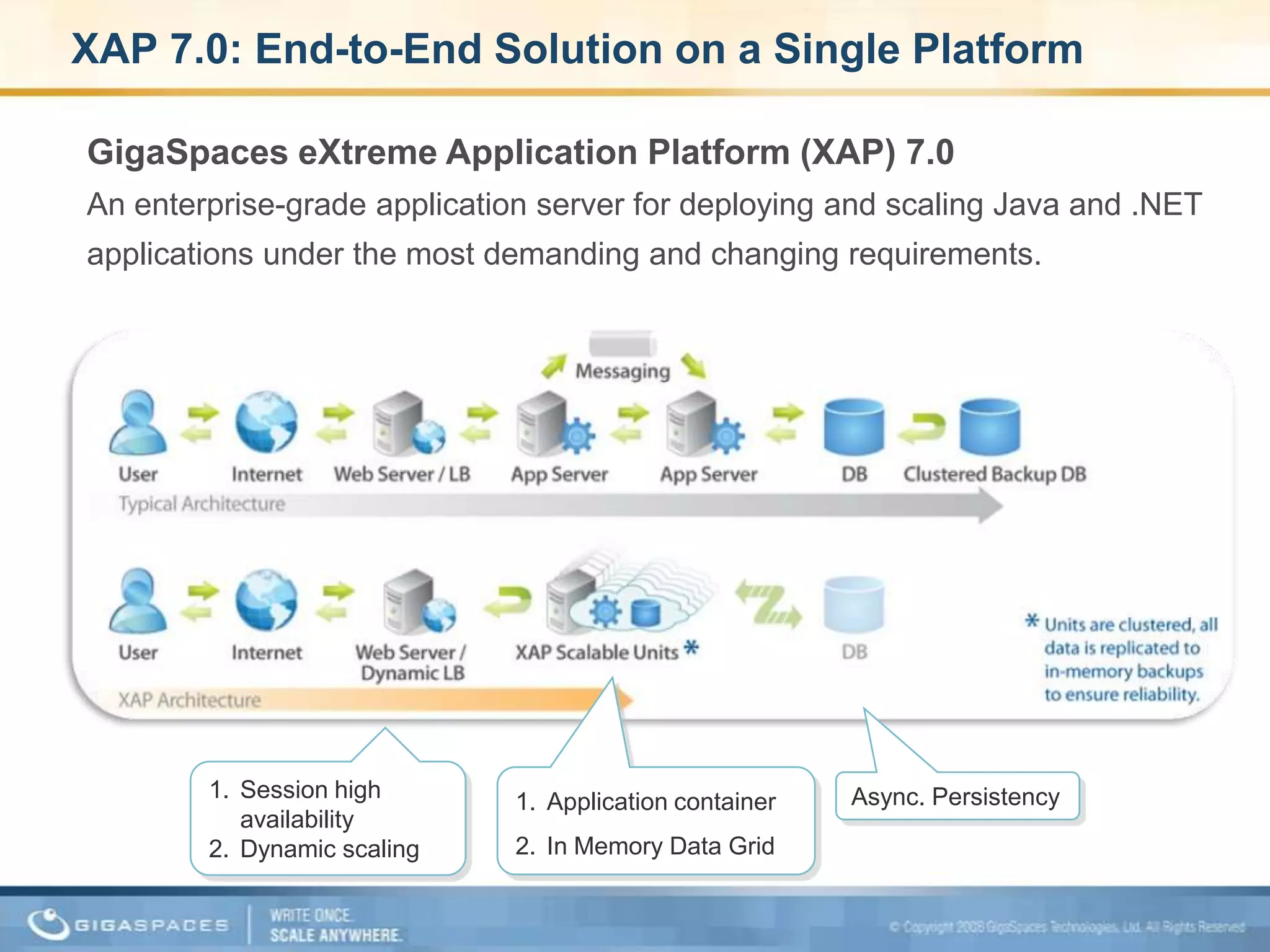
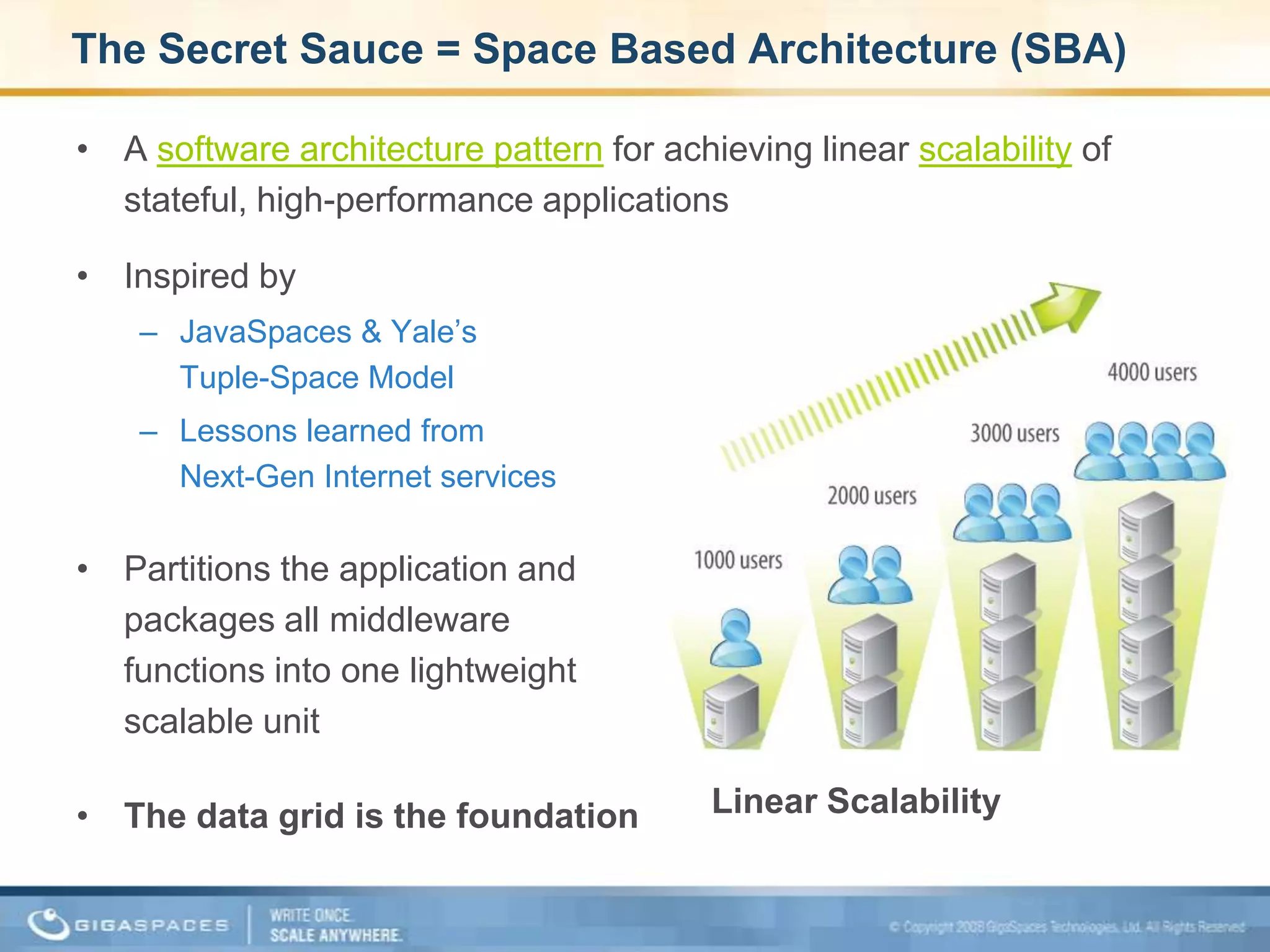
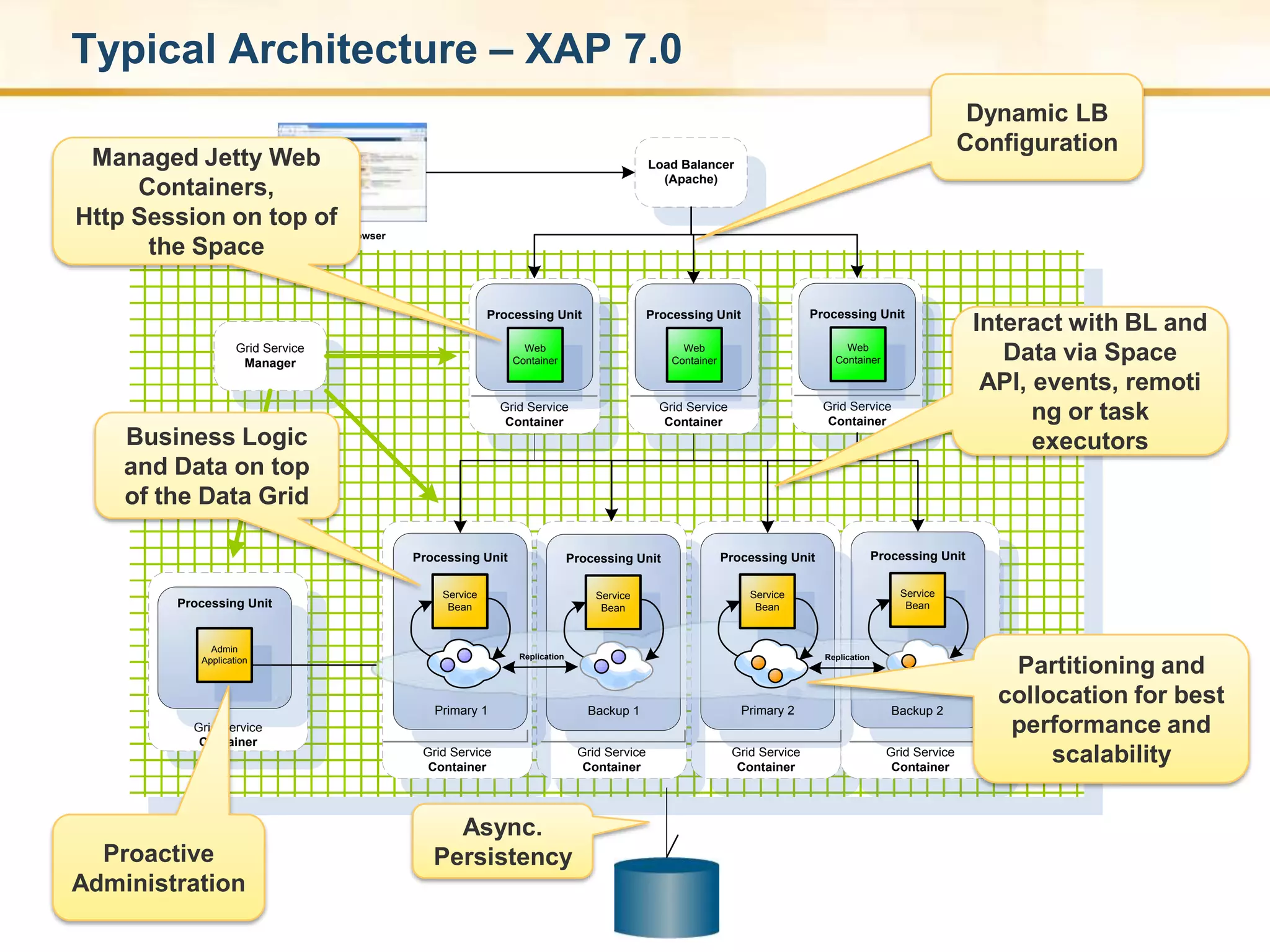
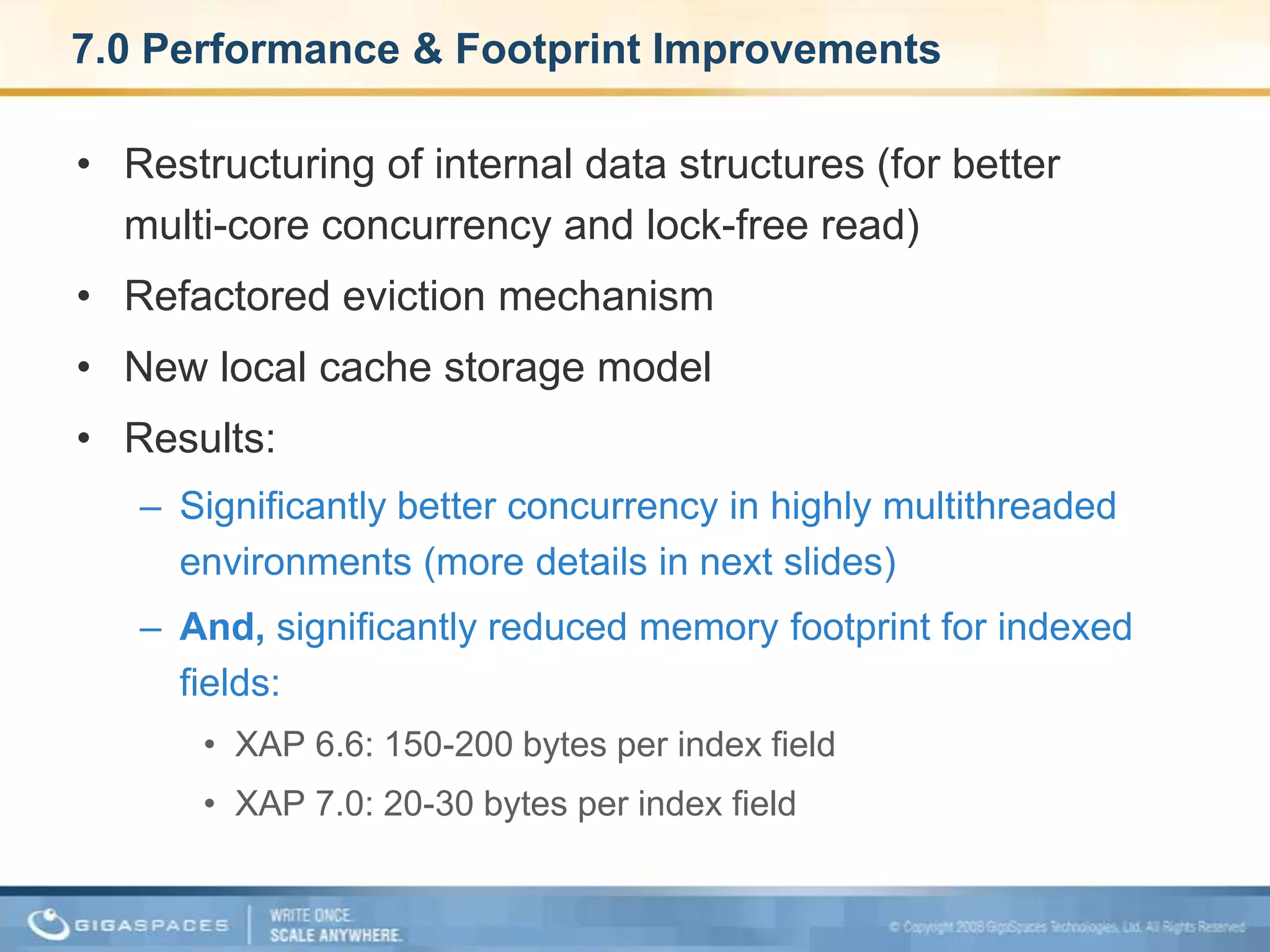
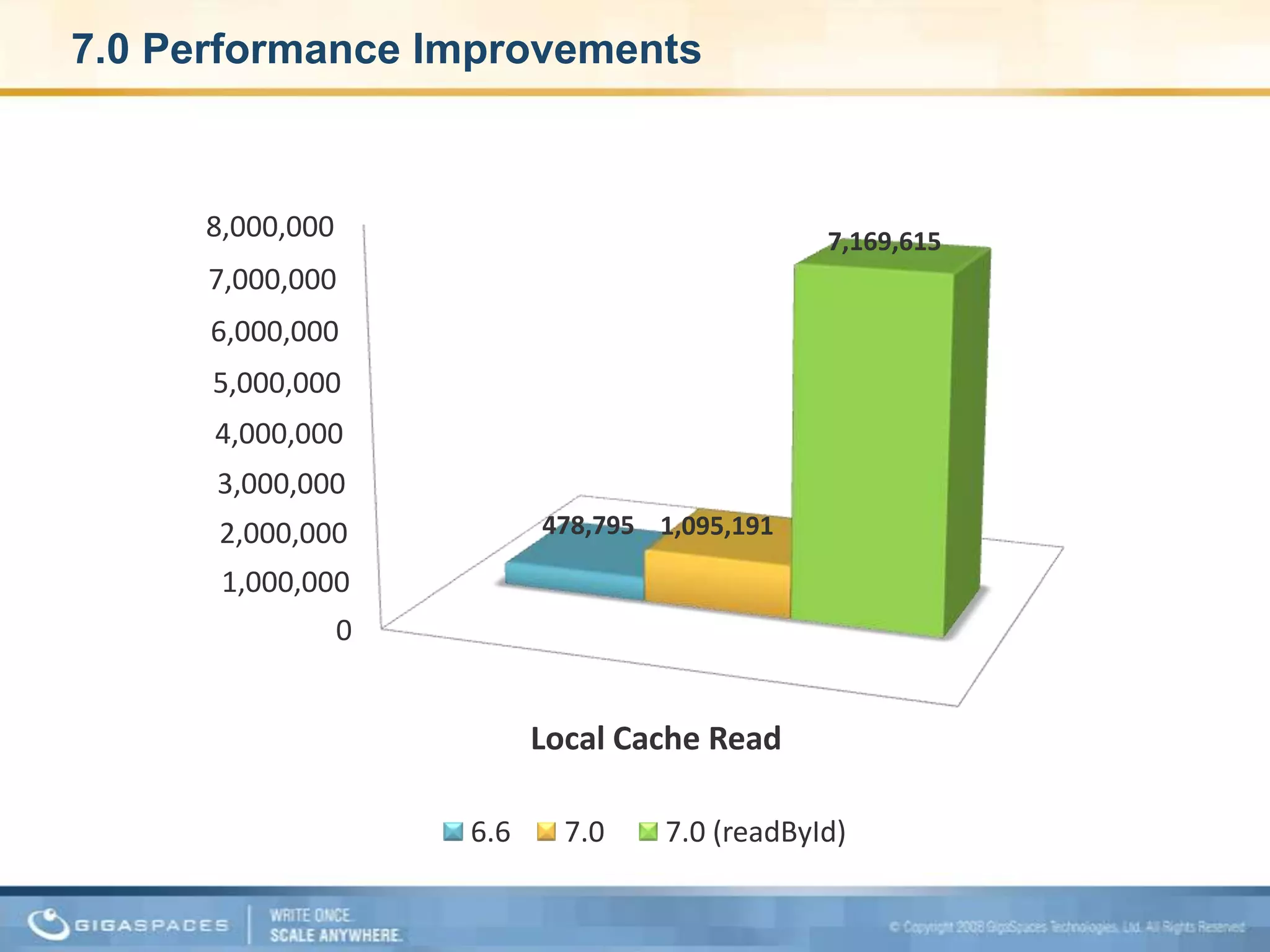
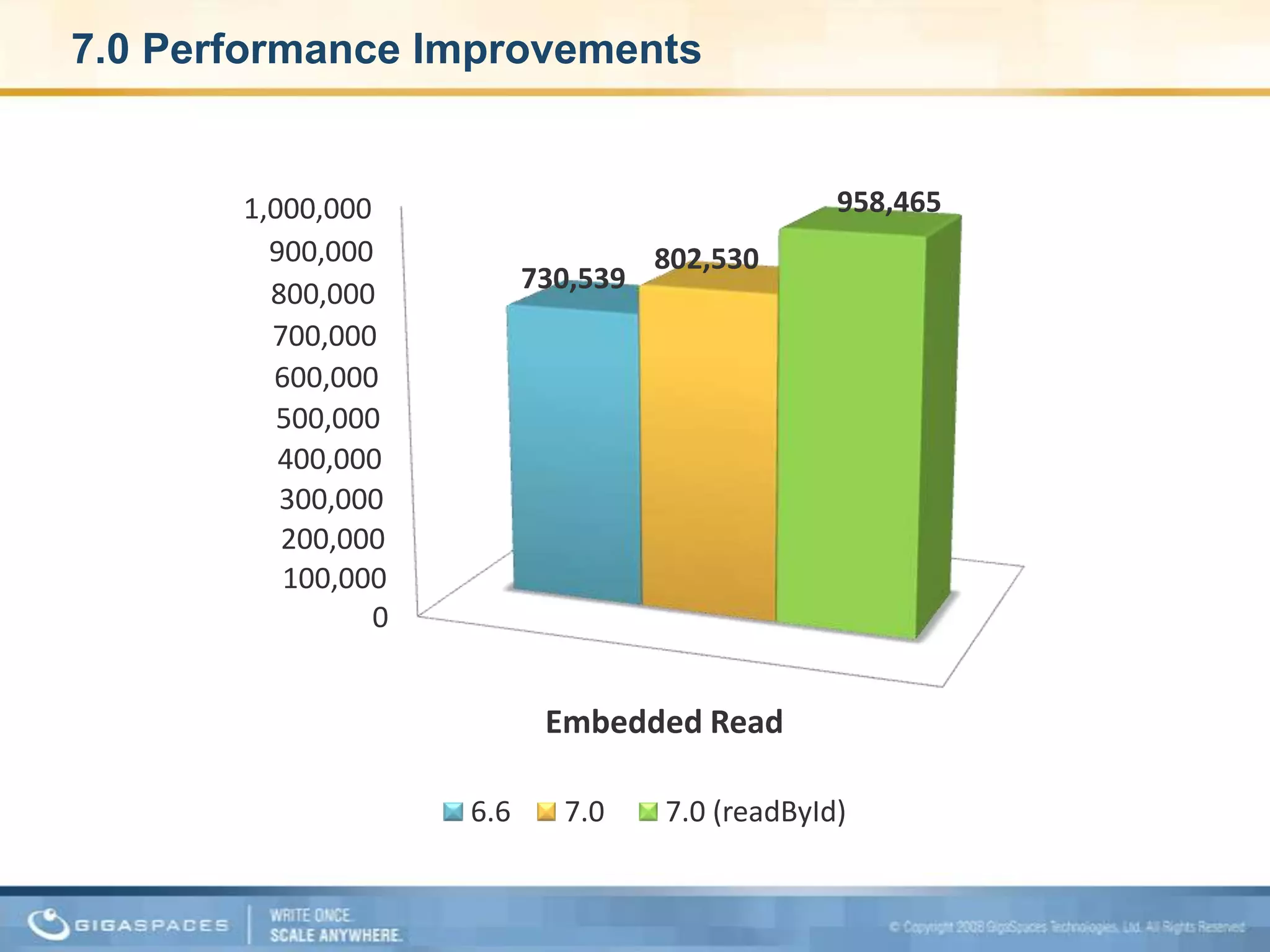
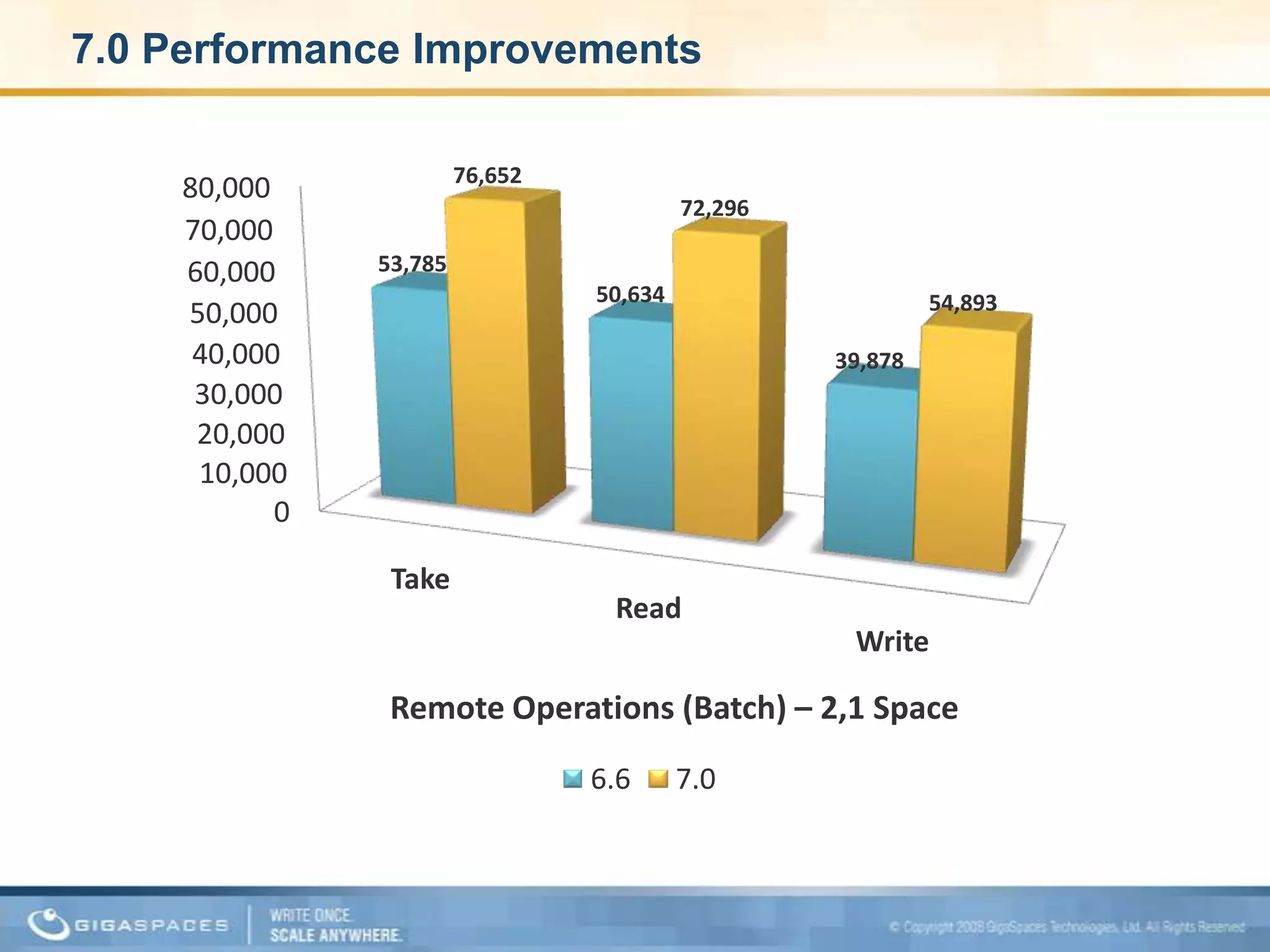
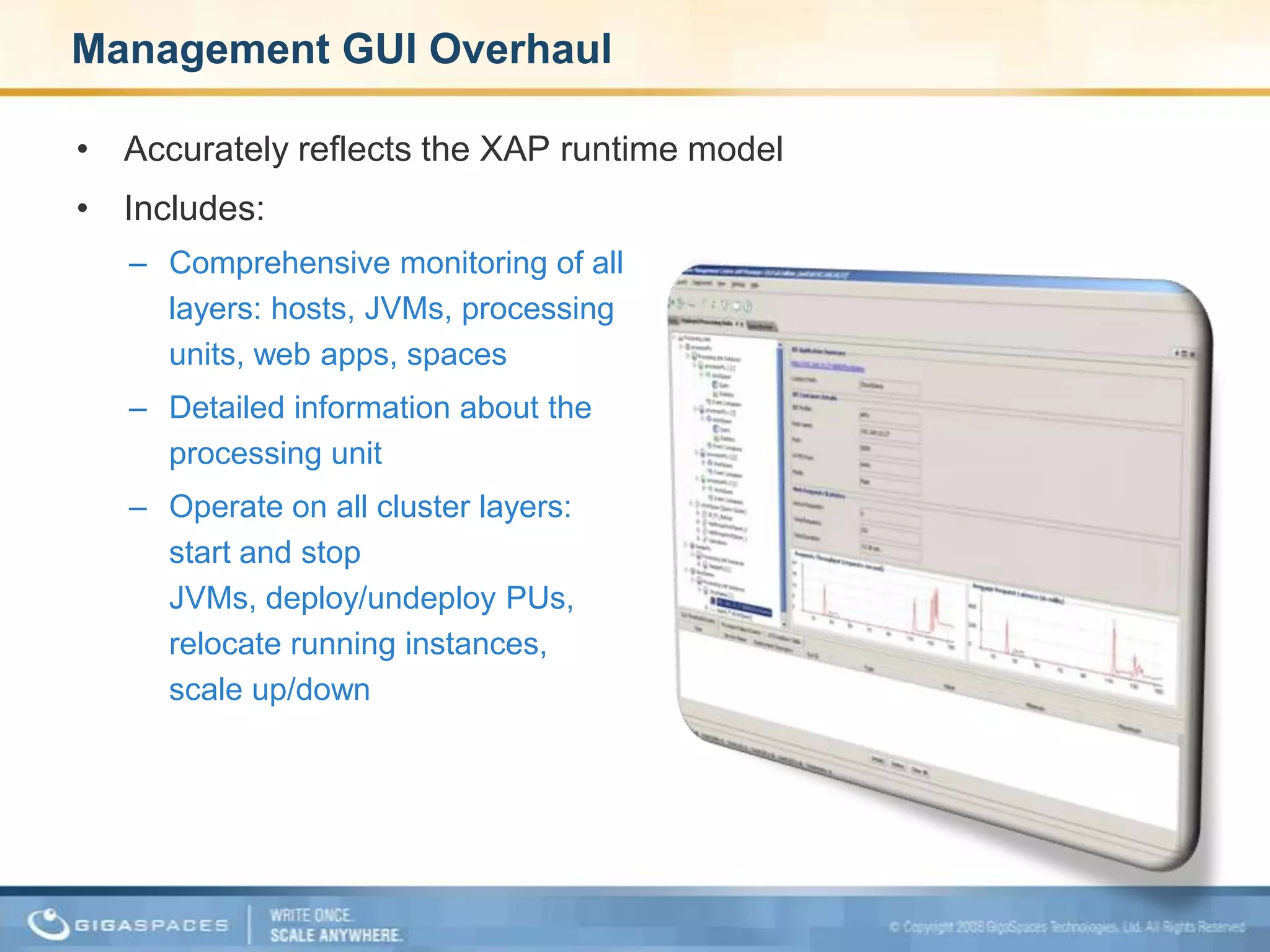
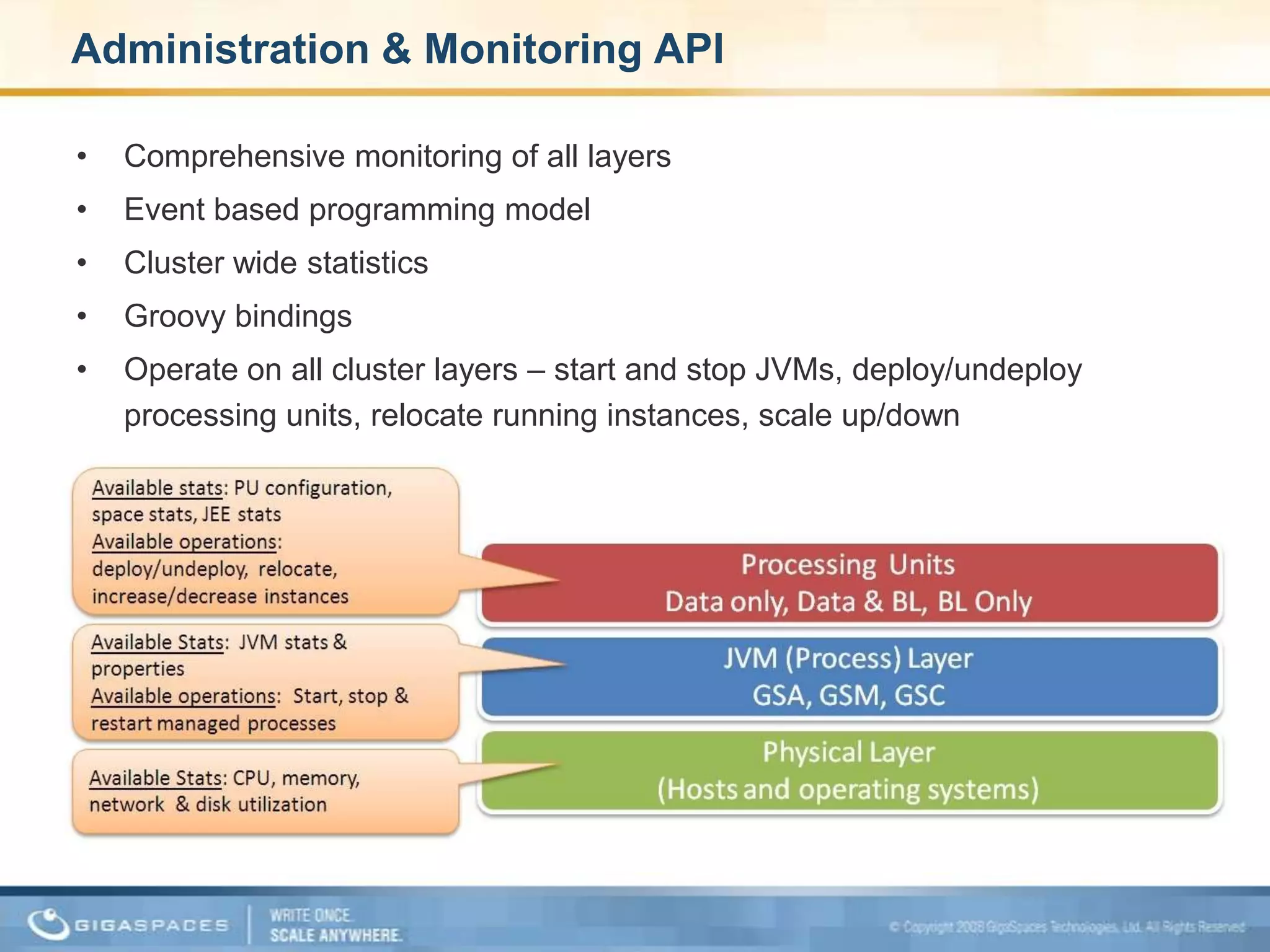
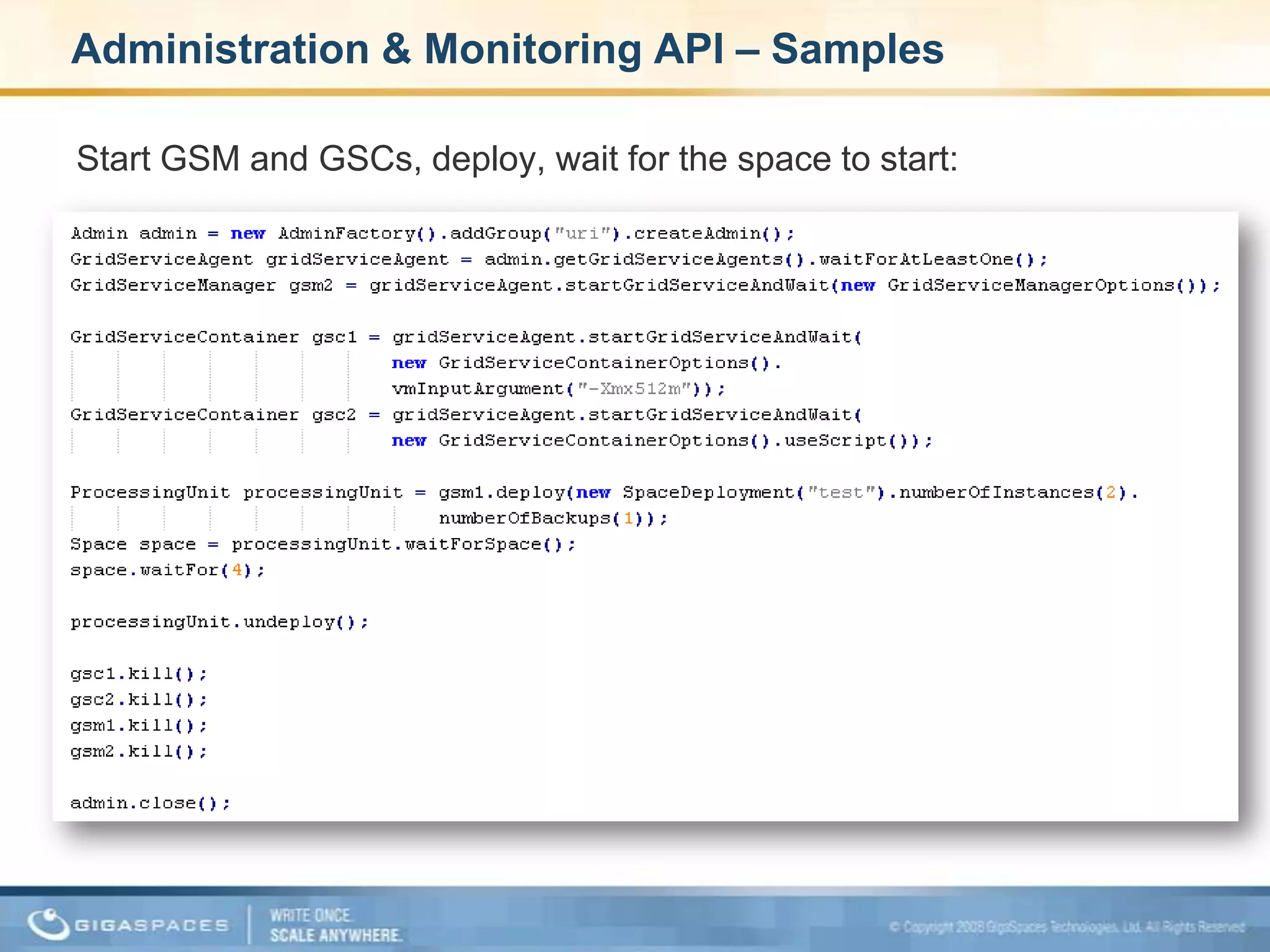
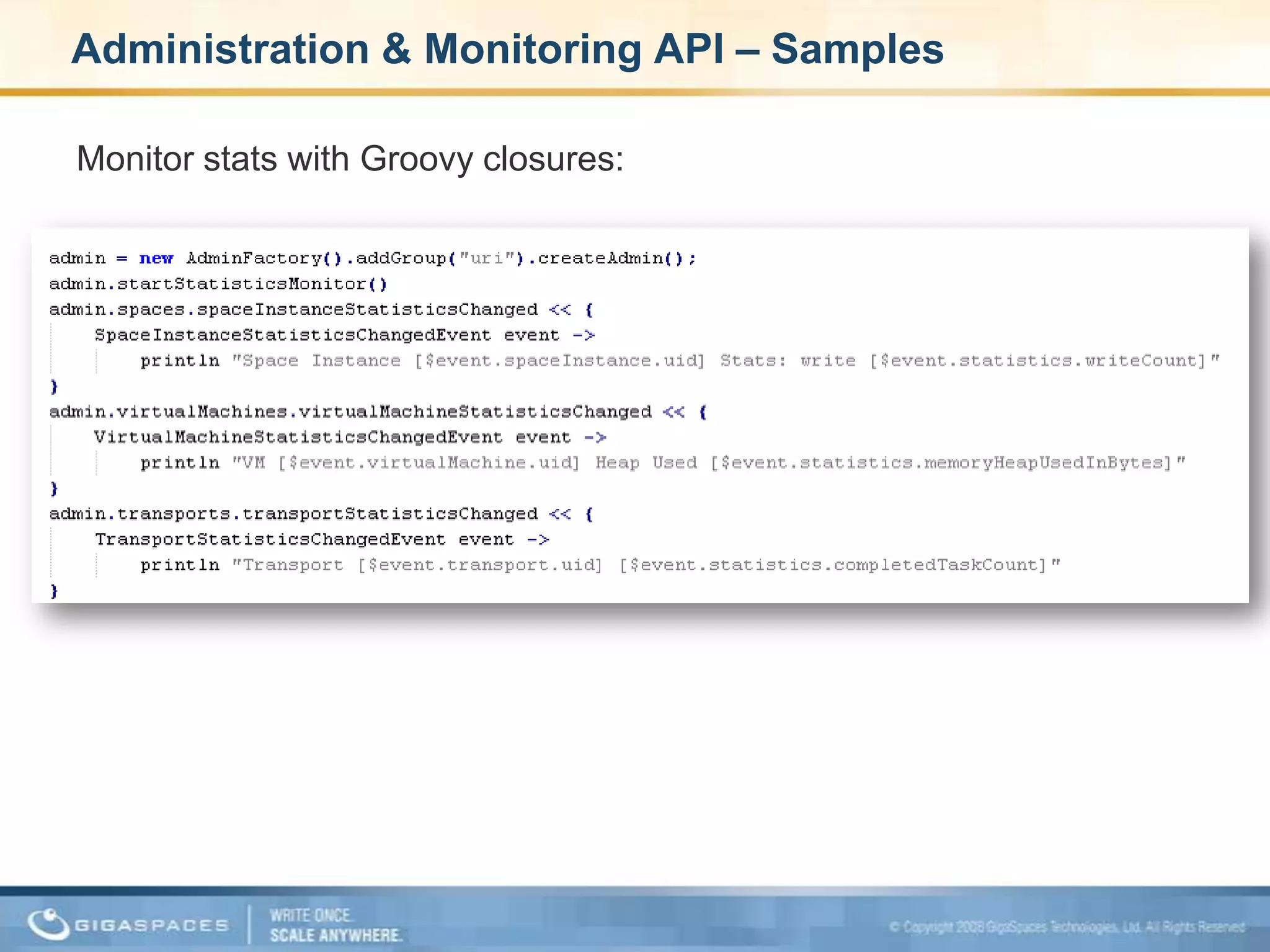
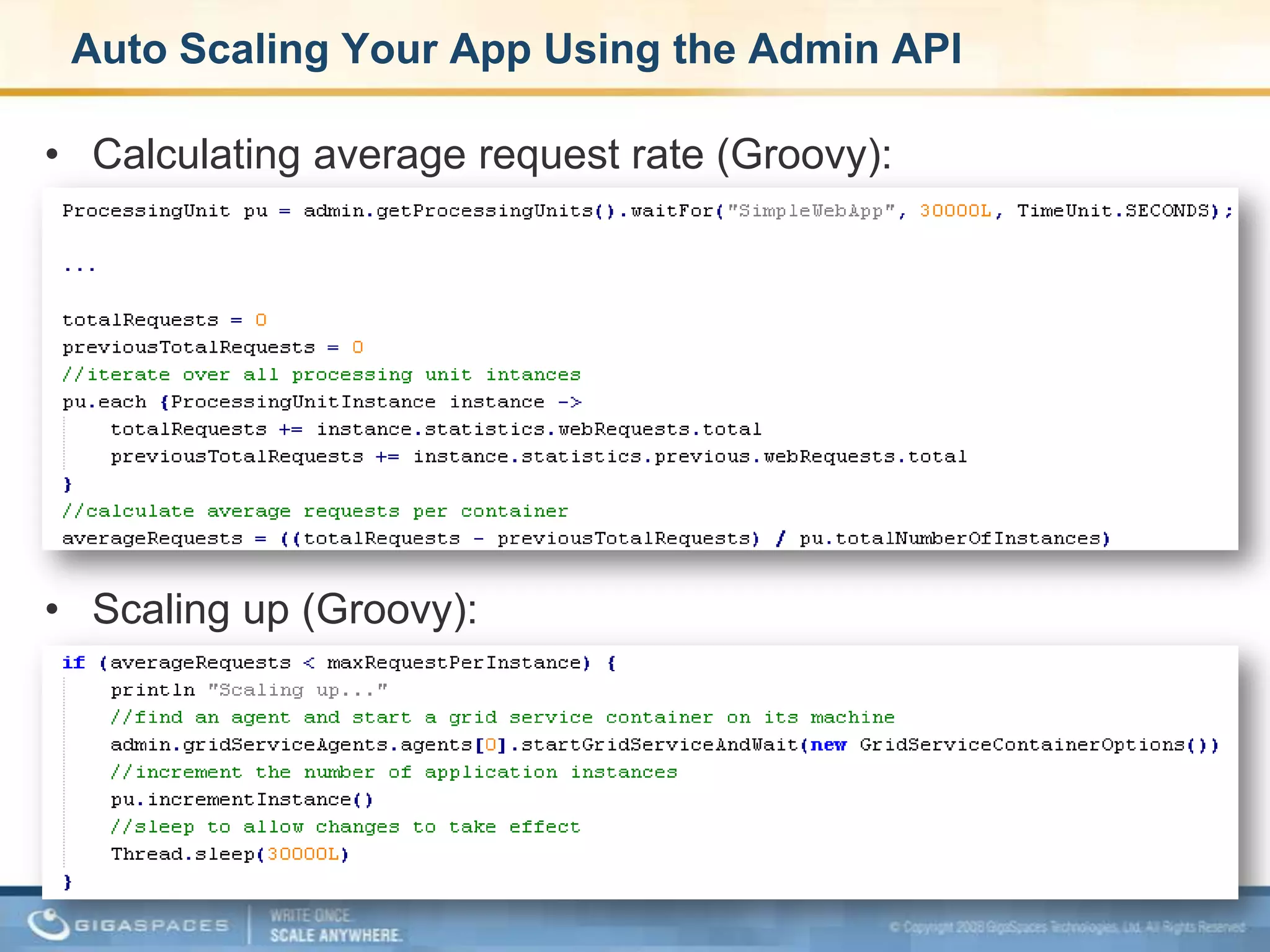
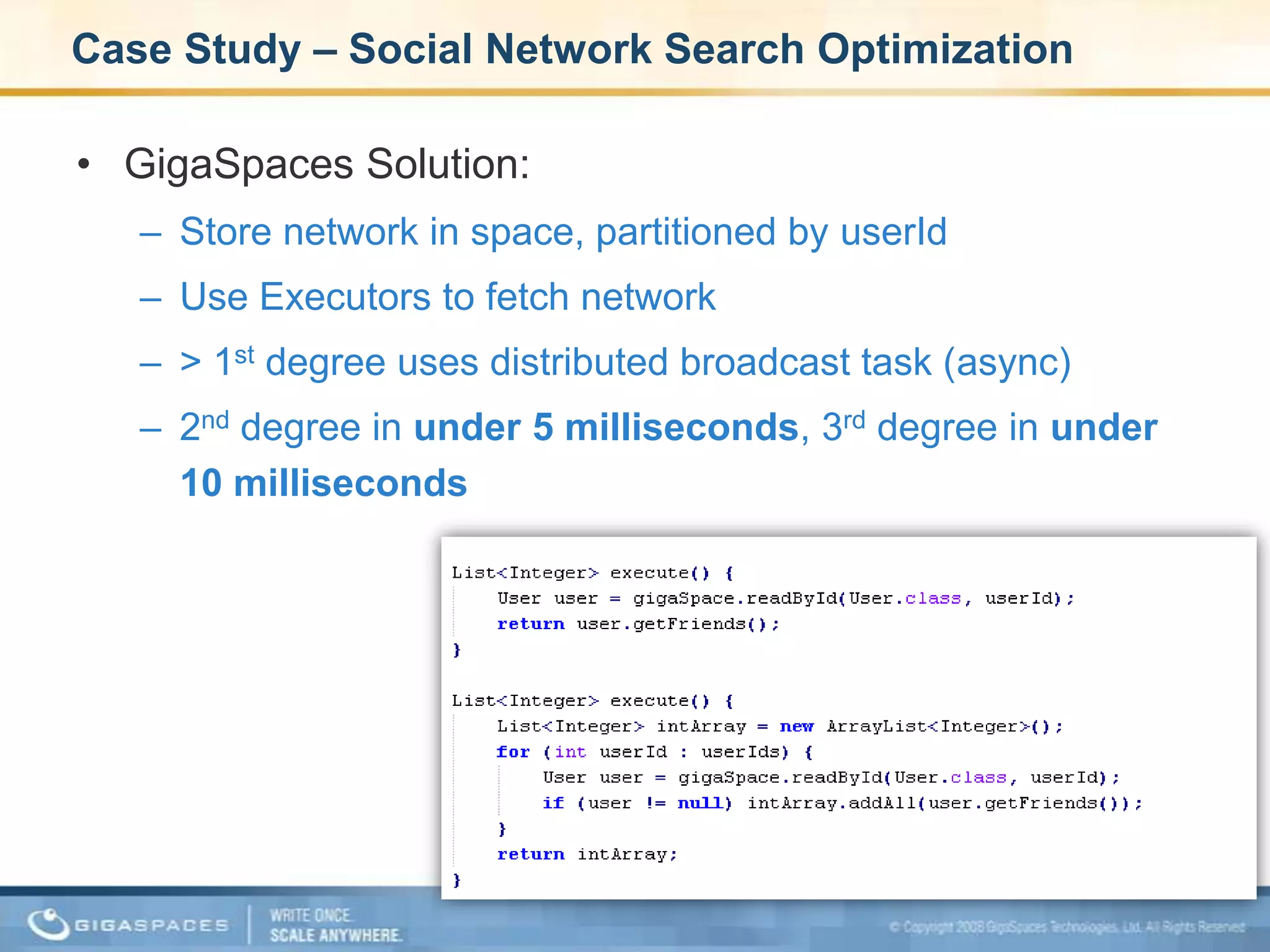
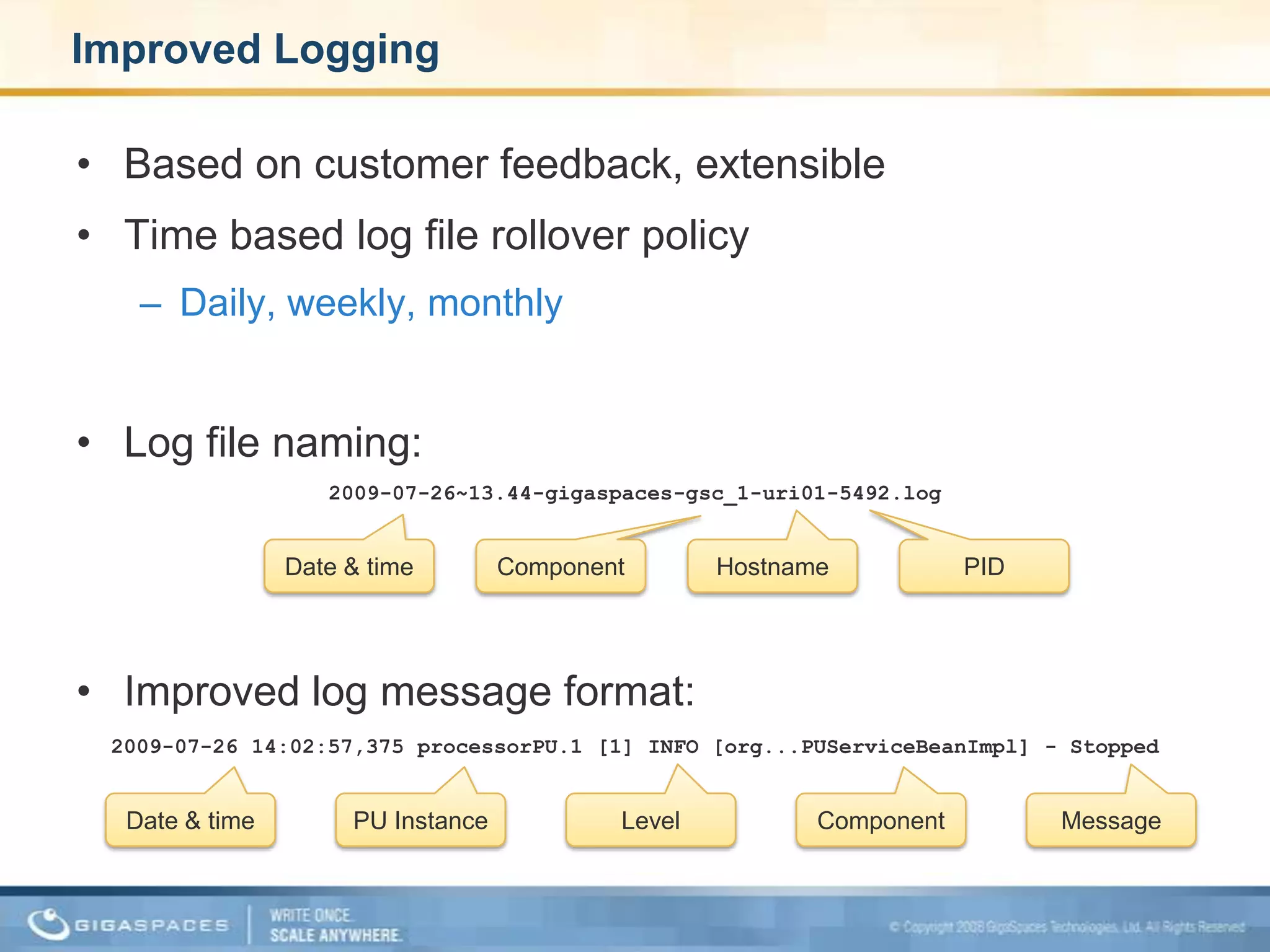
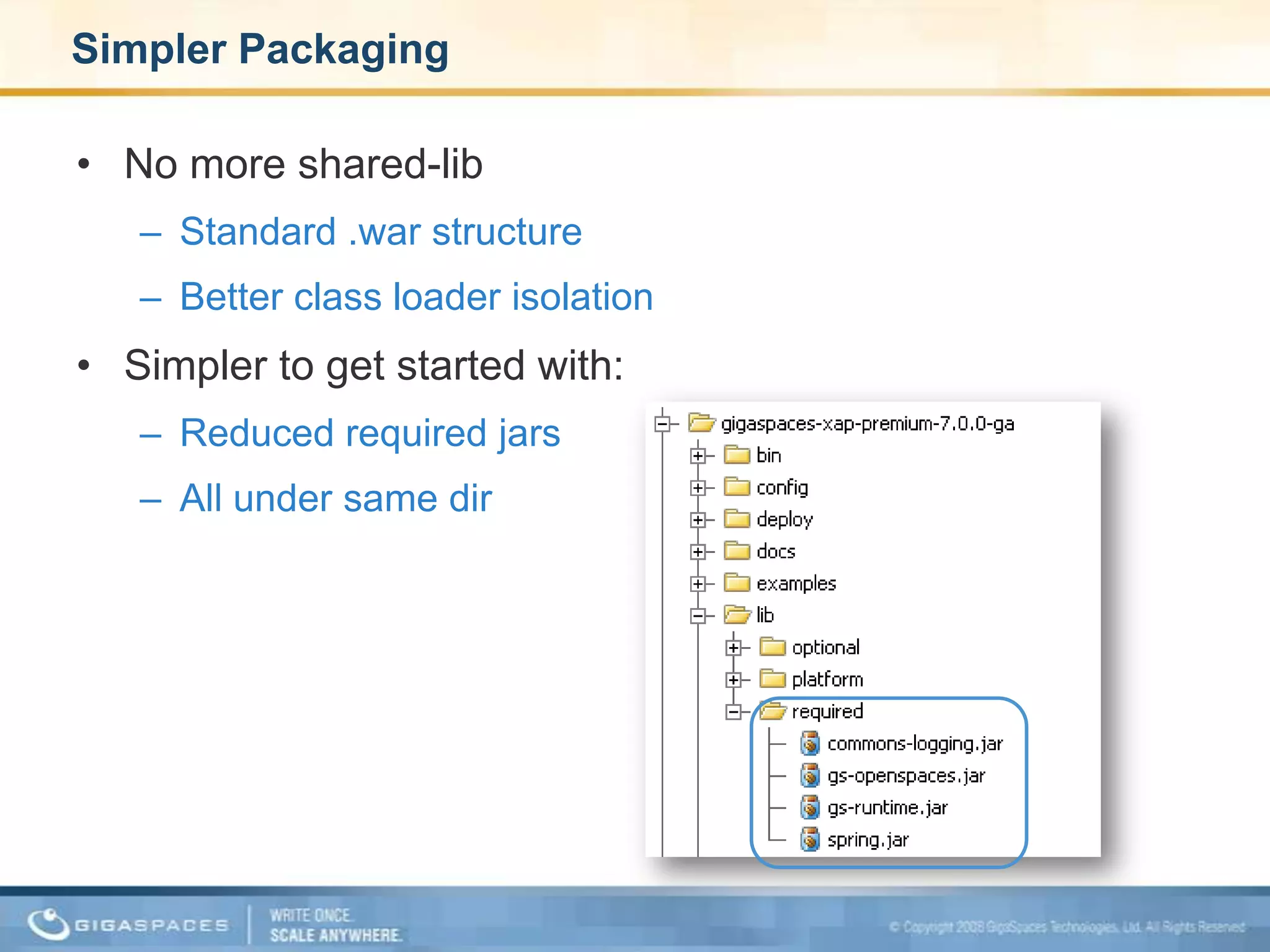
XAP 7.0, launched on July 28, 2009, is an enterprise-grade application server designed for deploying and scaling Java and .NET applications with improved performance, scalability, and management capabilities. The update includes a significant overhaul of the management GUI, new administration and monitoring APIs, and enhancements to the data grid and task execution features. Additionally, the release simplifies API usage and packaging while improving memory utilization, allowing for more efficient handling of multithreaded environments.