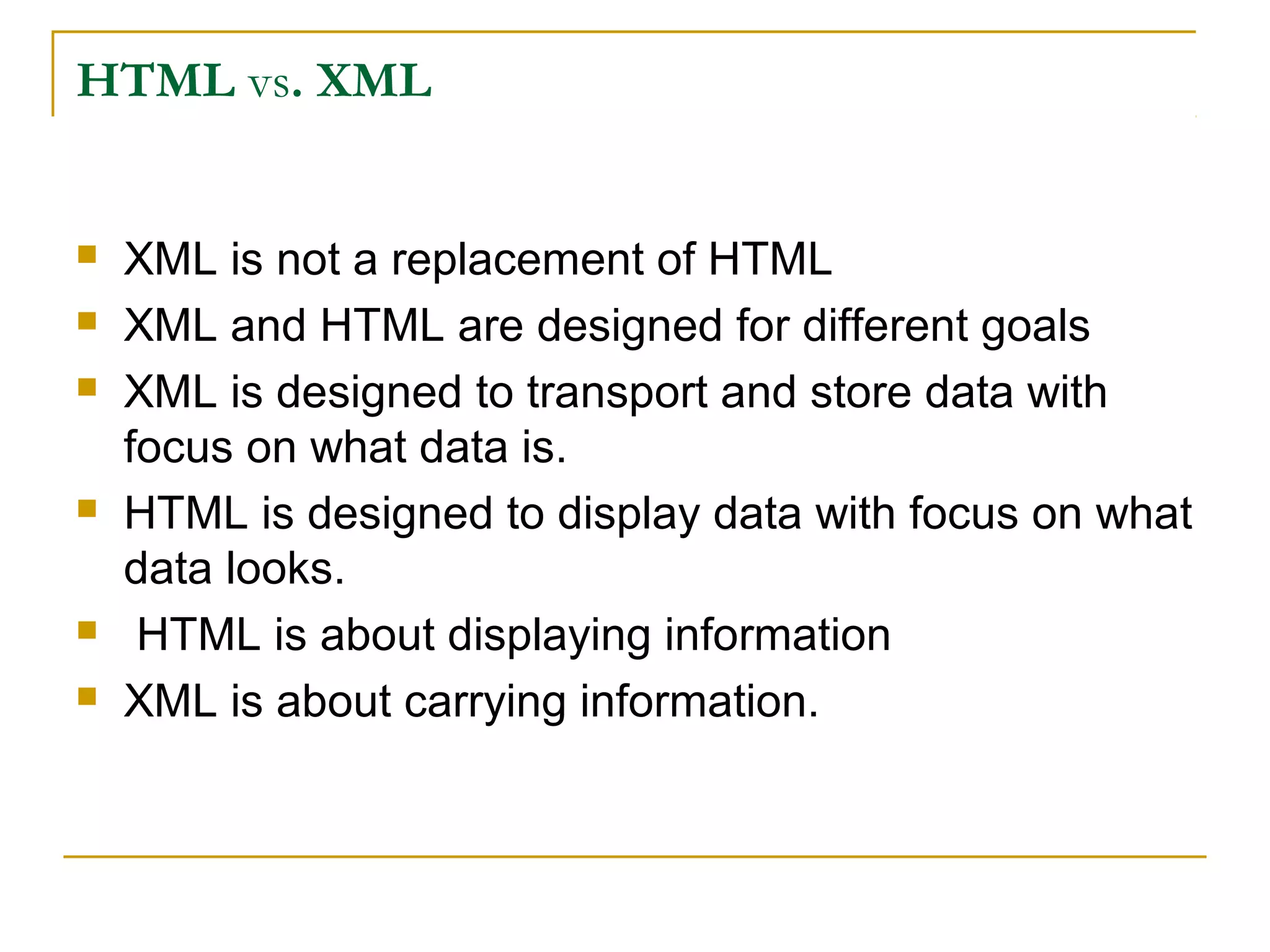
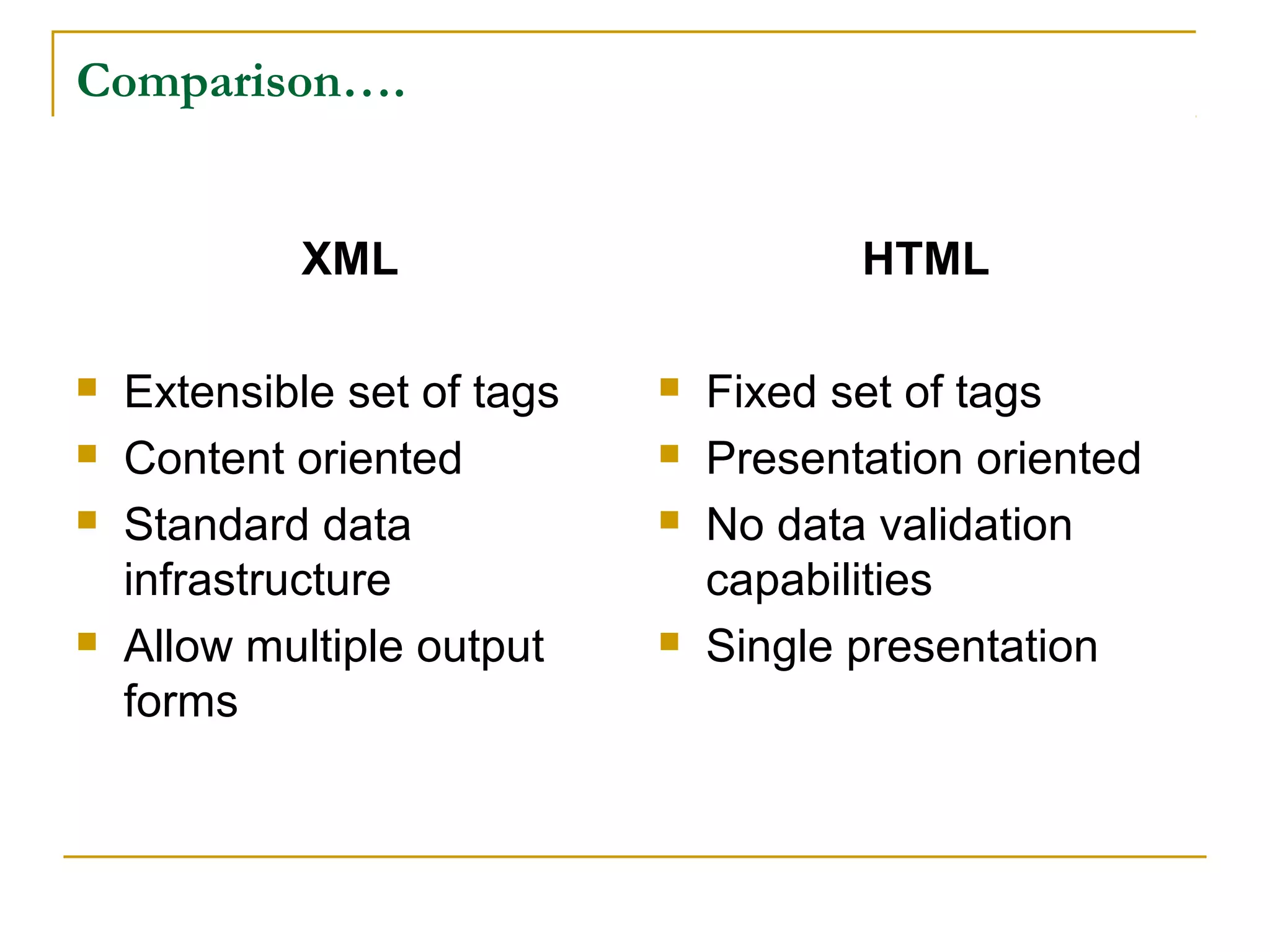
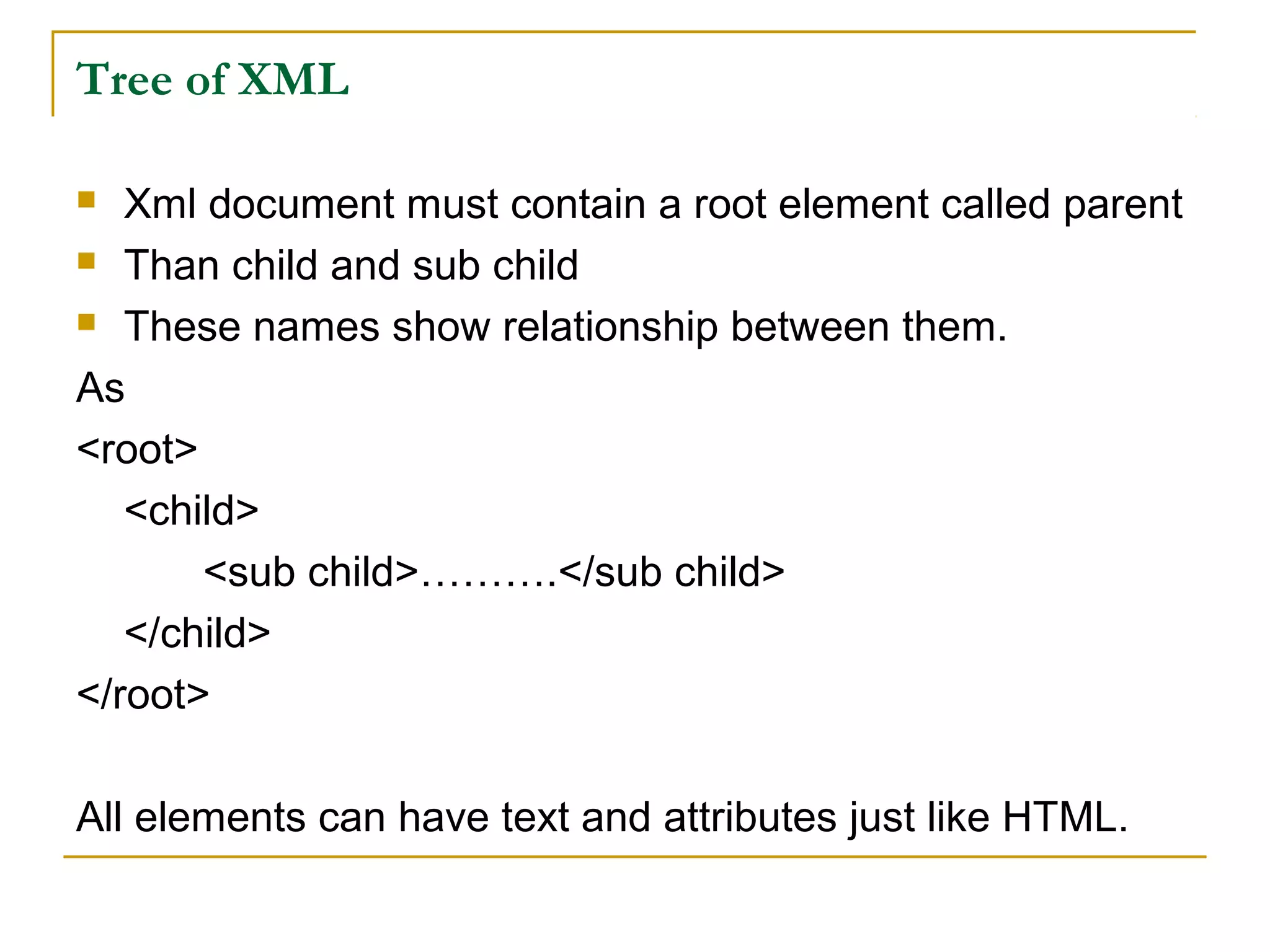
XML is a markup language similar to HTML but designed to carry data rather than display it. Unlike HTML, XML tags are user-defined rather than predefined. XML focuses on describing what data is, while HTML focuses on how data looks. XML allows data sharing across different applications and is commonly used to store and transport data on the web and in applications.