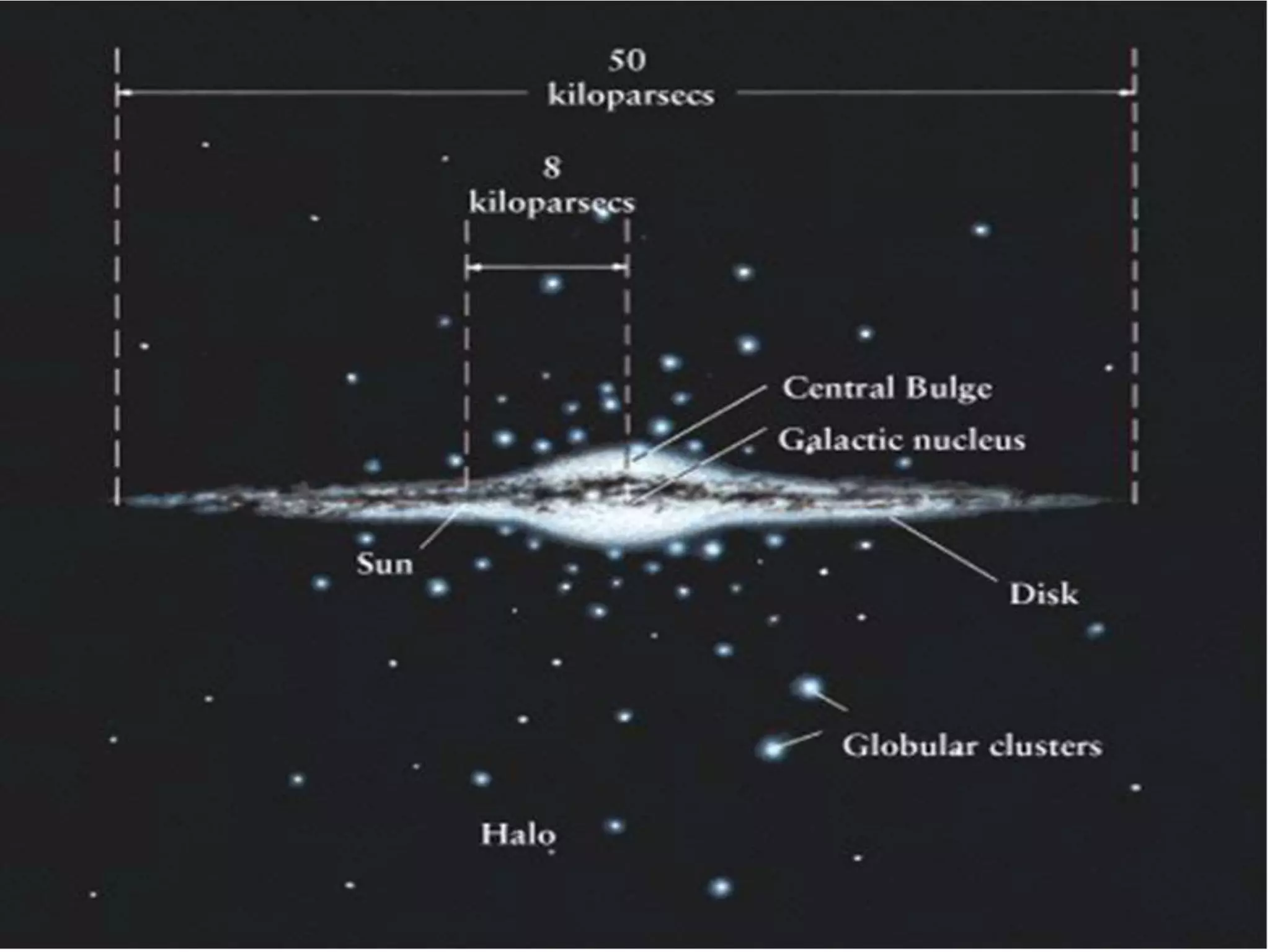
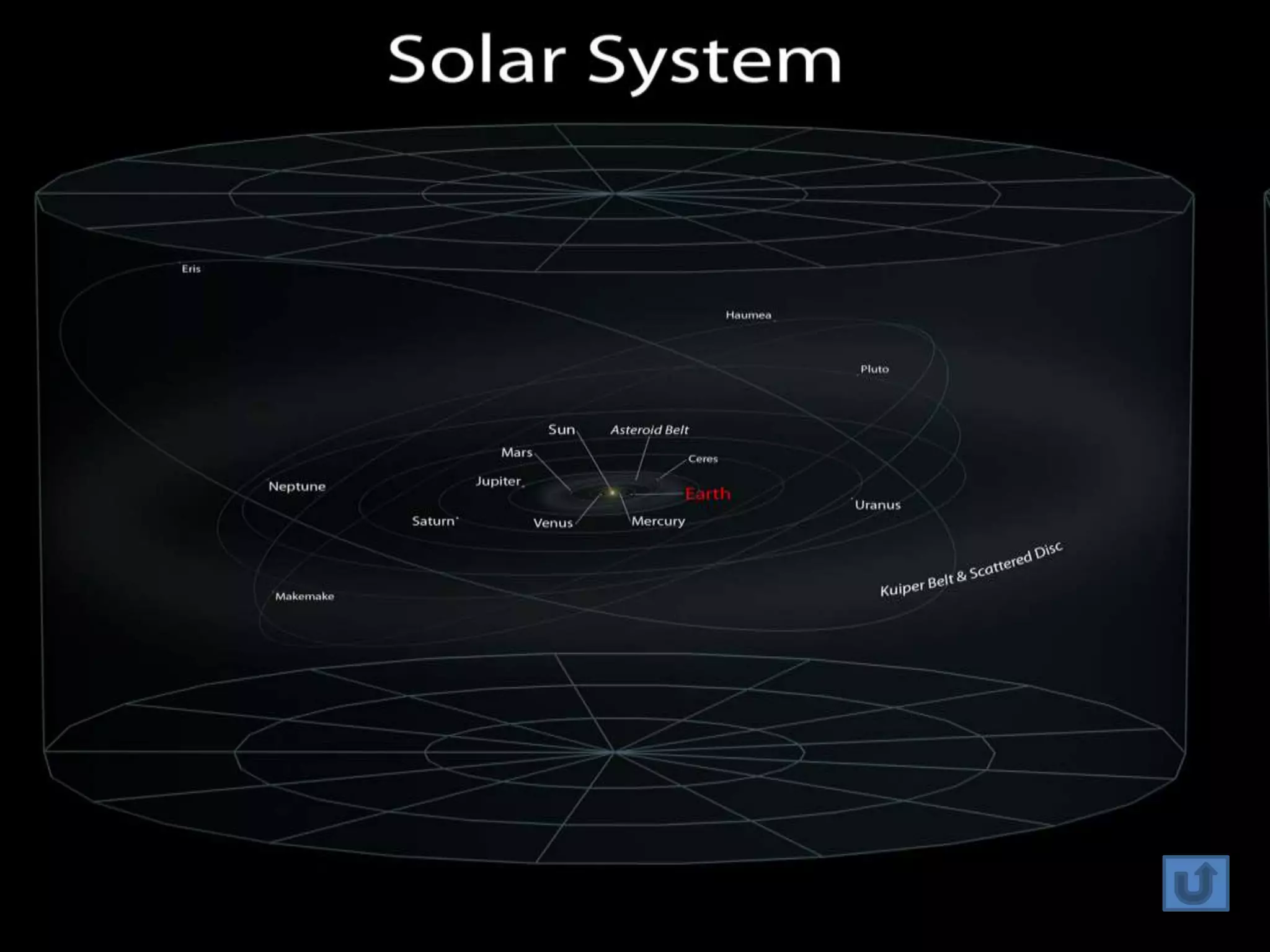
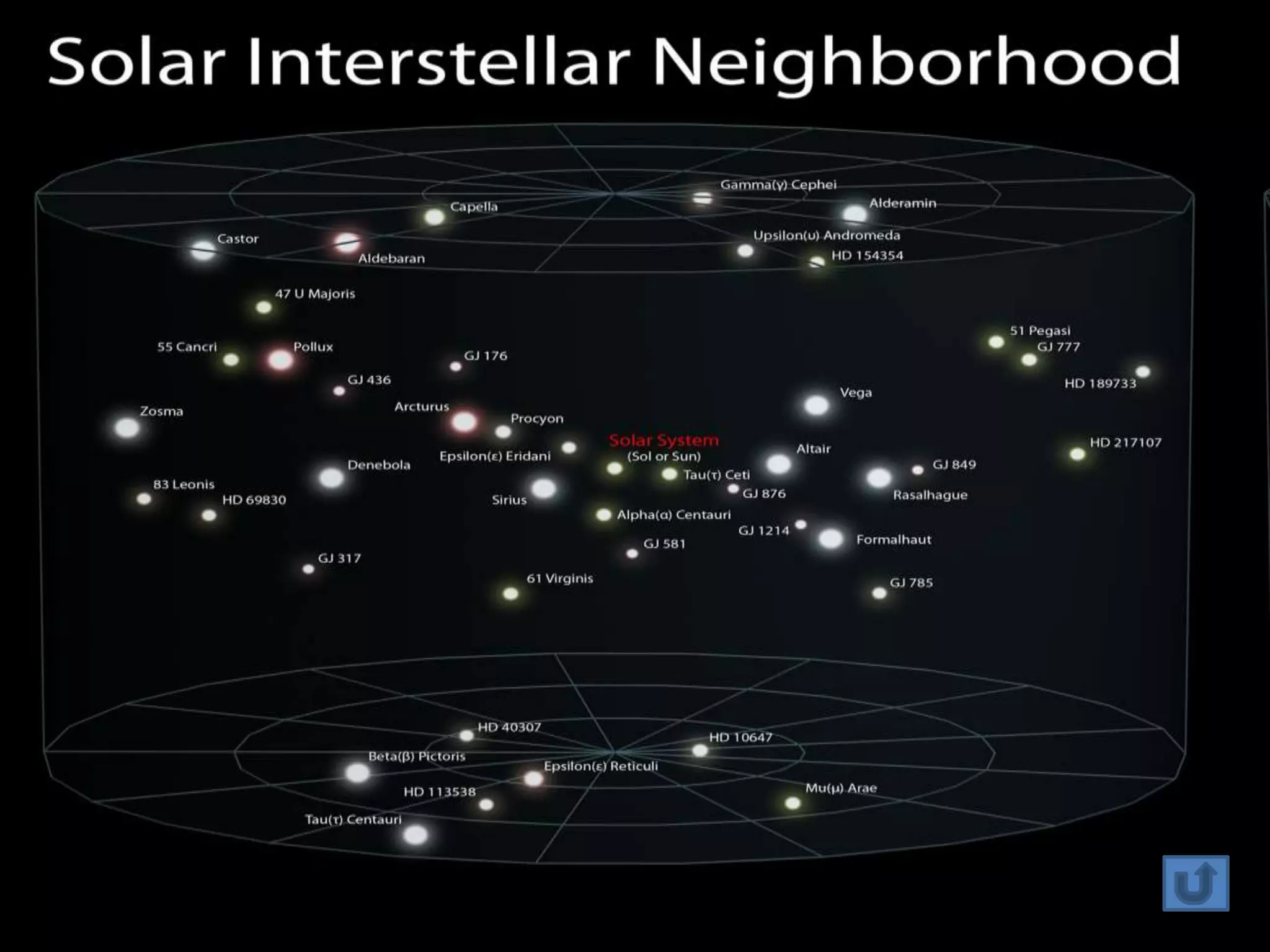
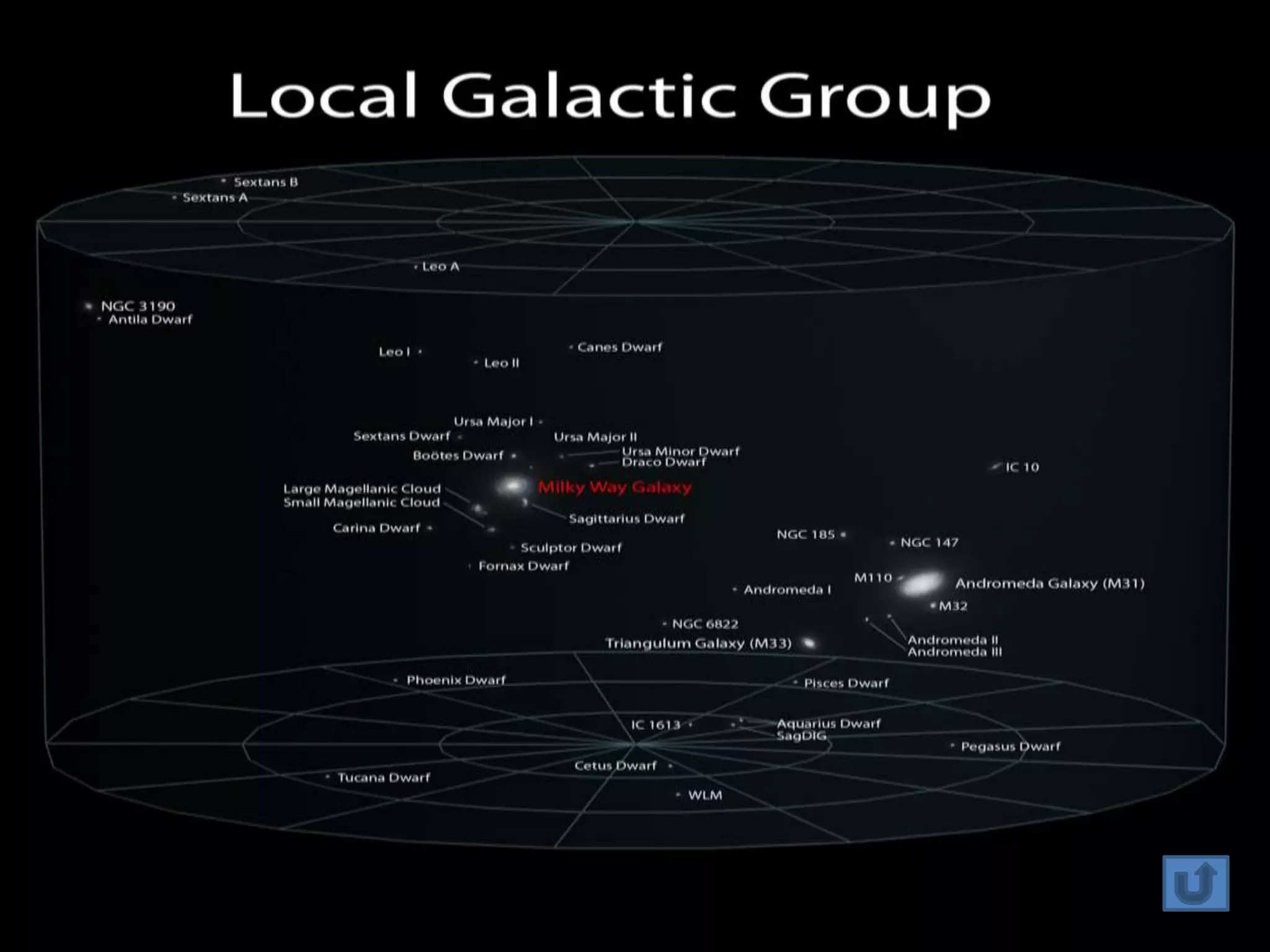
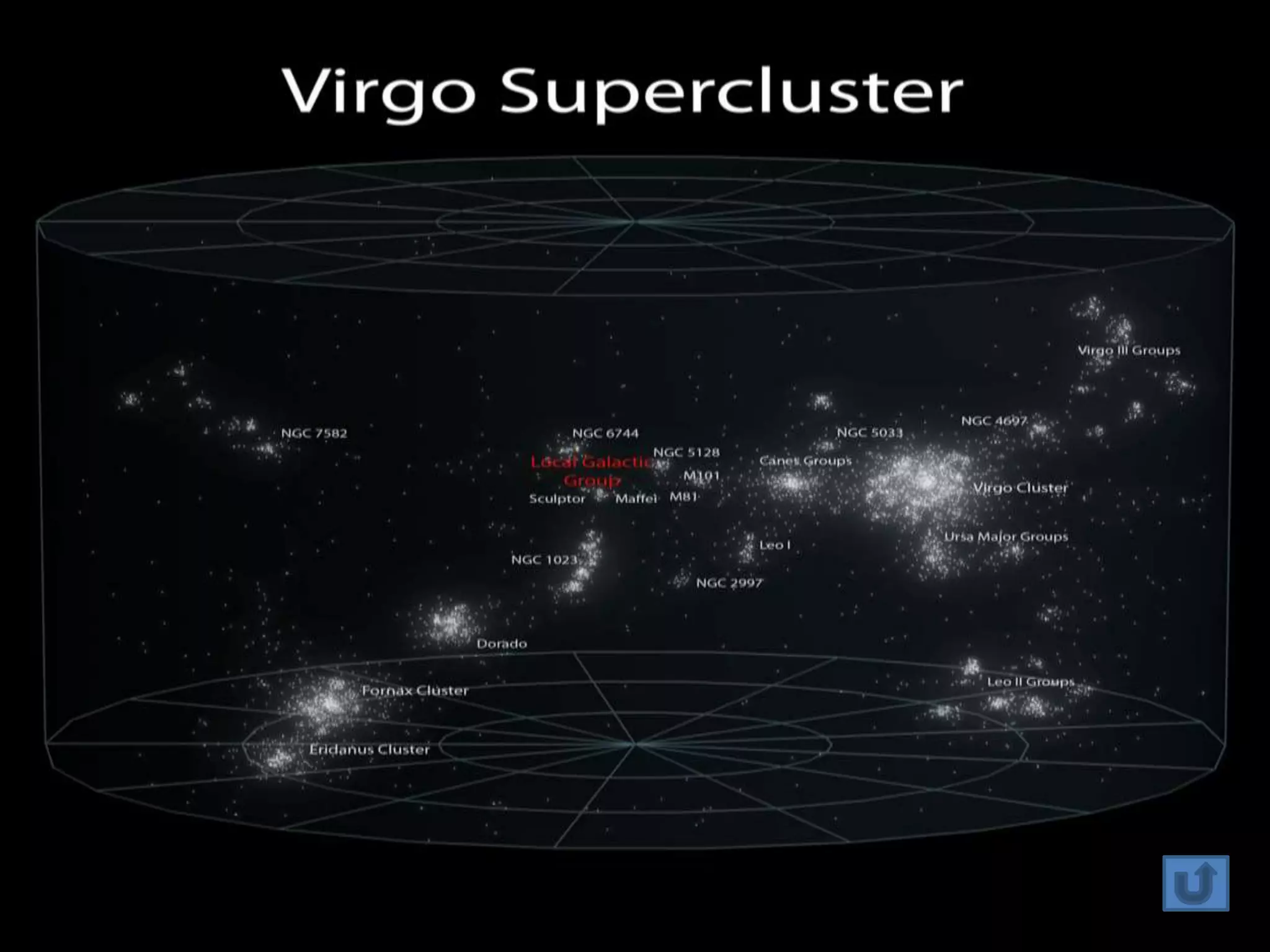
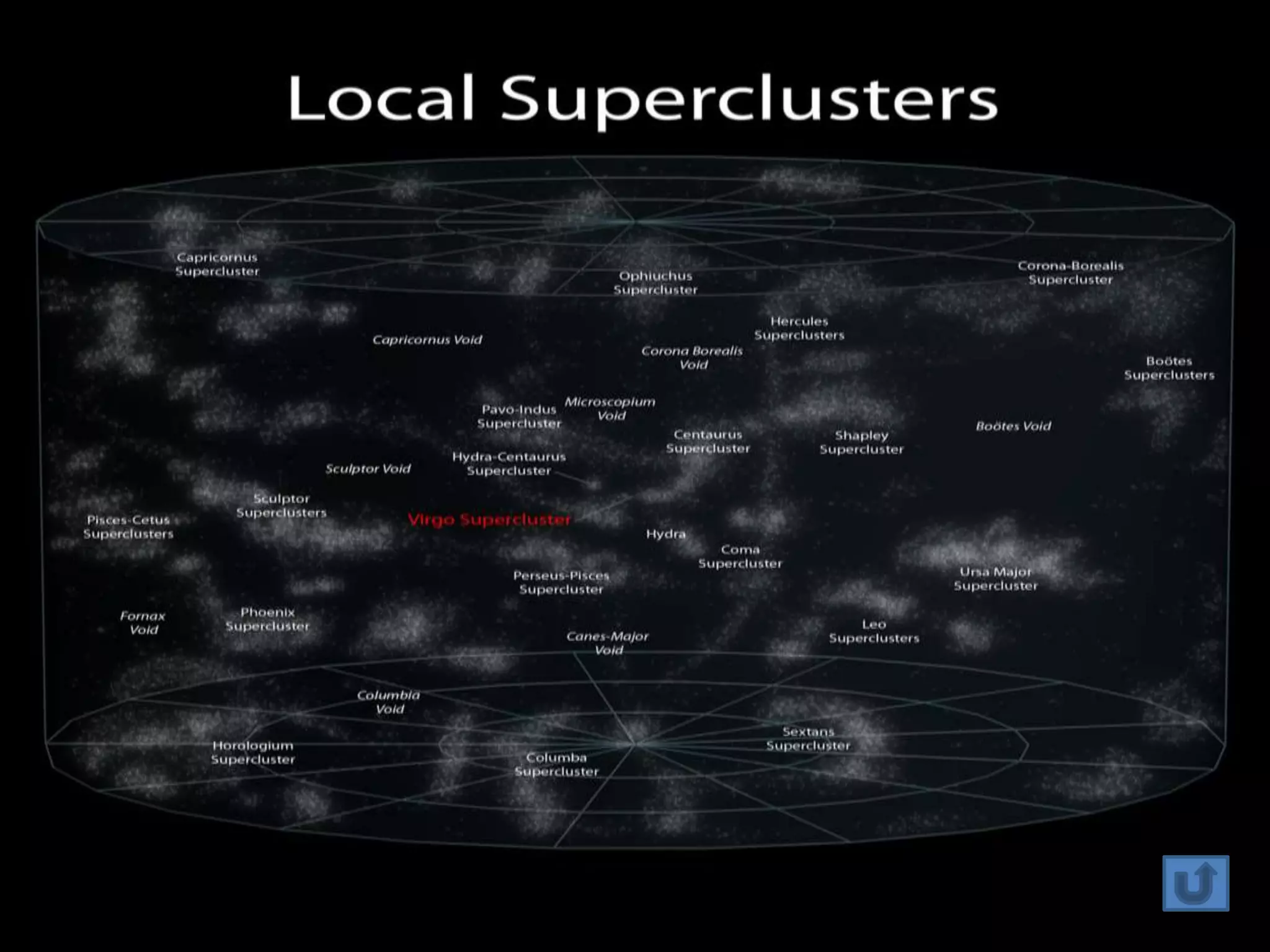
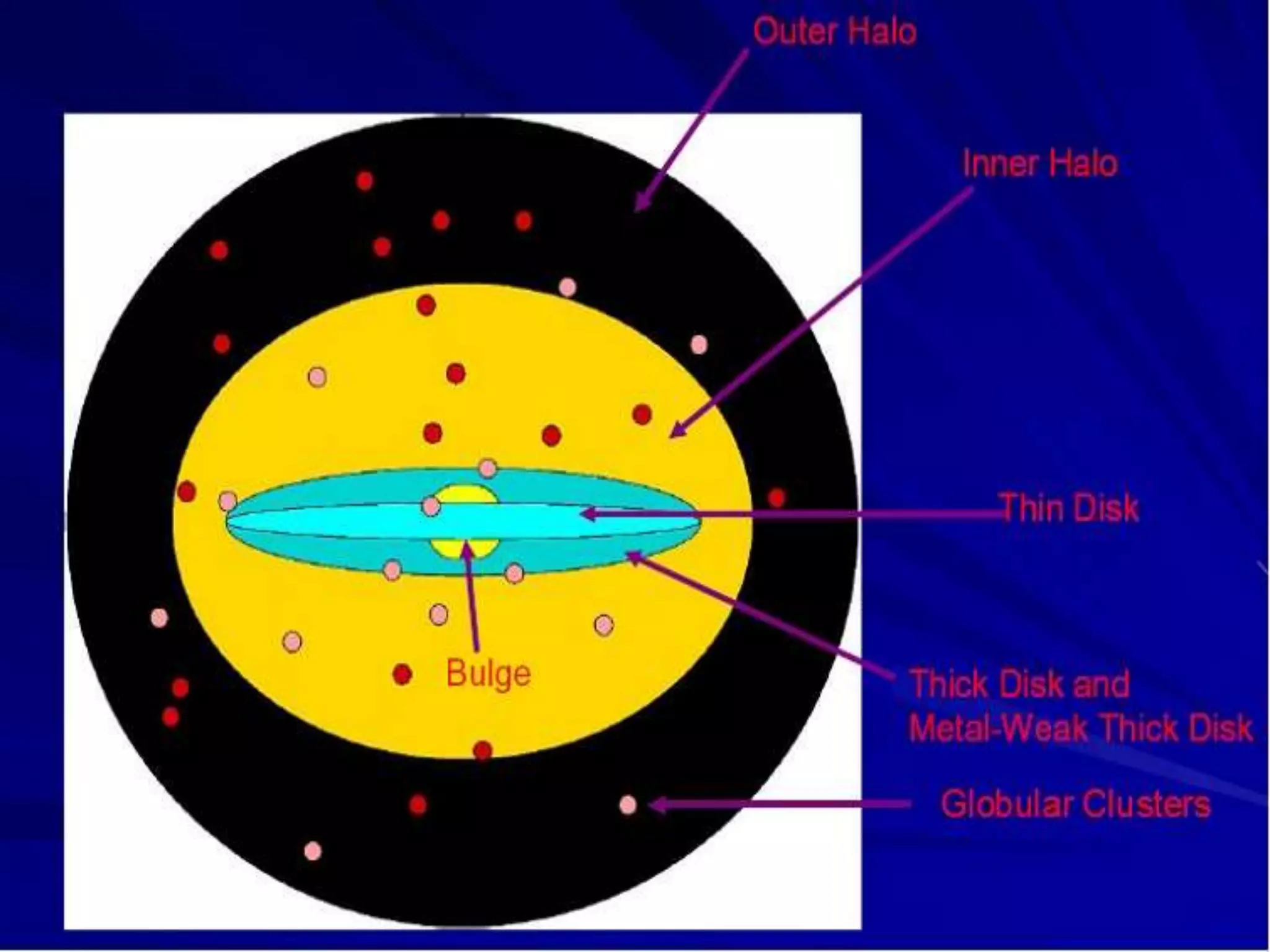
The document discusses the Milky Way galaxy and its discovery and mapping over time by various astronomers from Galileo to Hubble. It then covers theories about galaxy formation from collapsing dust clouds and collisions. Finally, it describes different types of galaxies like elliptical, spiral, and starburst galaxies and lists some examples, as well as the parts that make up a typical galaxy.