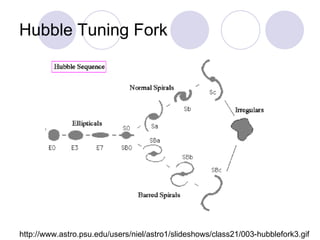
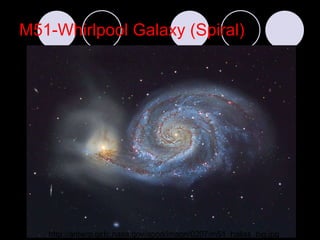
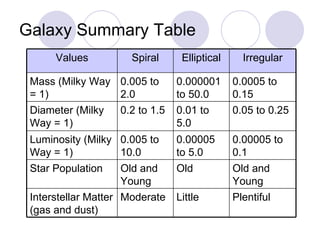
- Edwin Hubble developed a classification system for galaxies that included spiral, elliptical, and irregular galaxies. Spiral galaxies have spiral arms and central bulges, elliptical galaxies have spherical or egg-shaped structures, and irregular galaxies have no defined shape.
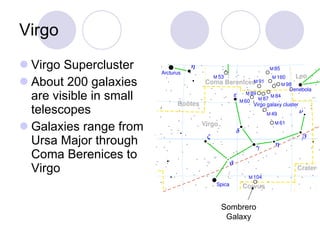
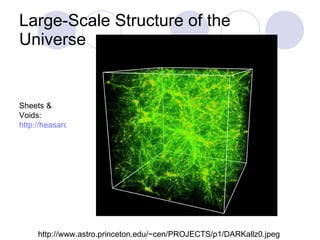
- Galaxies exist in groups and clusters held together by gravity, with galaxy clusters containing dozens to thousands of galaxies. Superclusters are clusters of galaxy clusters and are the largest known structures in the universe.
- The Milky Way is part of the Local Group, which also includes the Andromeda Galaxy and other dwarf galaxies. The Magellanic Clouds are two small, nearby galaxies that orbit the Milky Way.