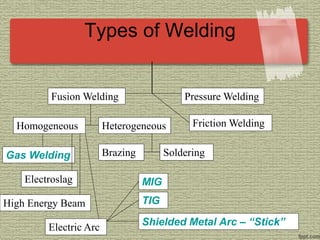
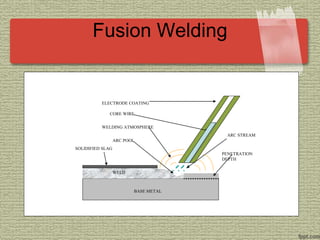
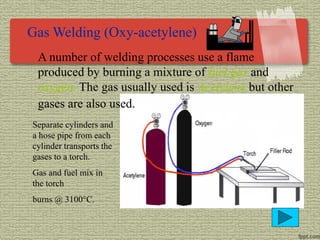
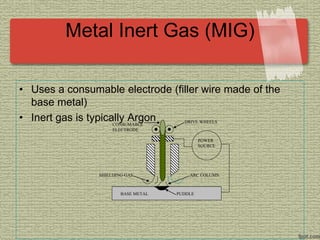
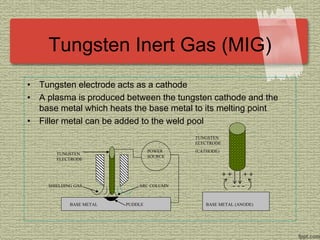
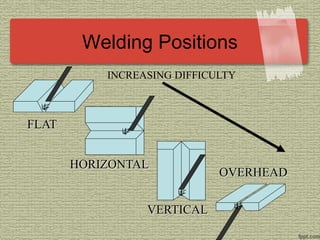
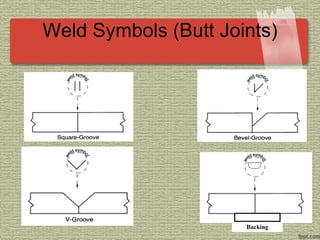
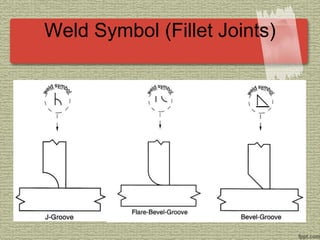
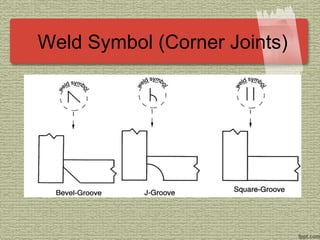
This document discusses various welding processes and principles. It describes welding as a process that joins materials by heating them to suitable temperatures with or without pressure. Some key welding types mentioned are fusion welding, pressure welding, gas welding, electric arc welding processes like MIG, TIG, and stick welding. The document explains concepts like weld fluxes, inert gases, and different welding positions. It provides examples of applications for welding in manufacturing and examples of common weld symbols.