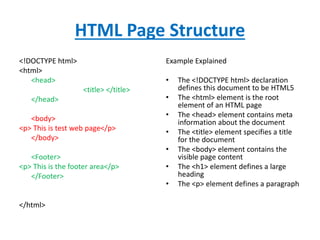
This document provides an introduction to various technologies used to build websites and web applications. It discusses markup languages like HTML, CSS and XML which are used for frontend design. It also covers programming languages and technologies used for backend development like Perl, Java, and .NET. The document then gives an overview of HTML including its structure, tags and common elements like headings, paragraphs and lists. It also discusses XML, CSS, web servers and databases which are fundamental components of web technology.