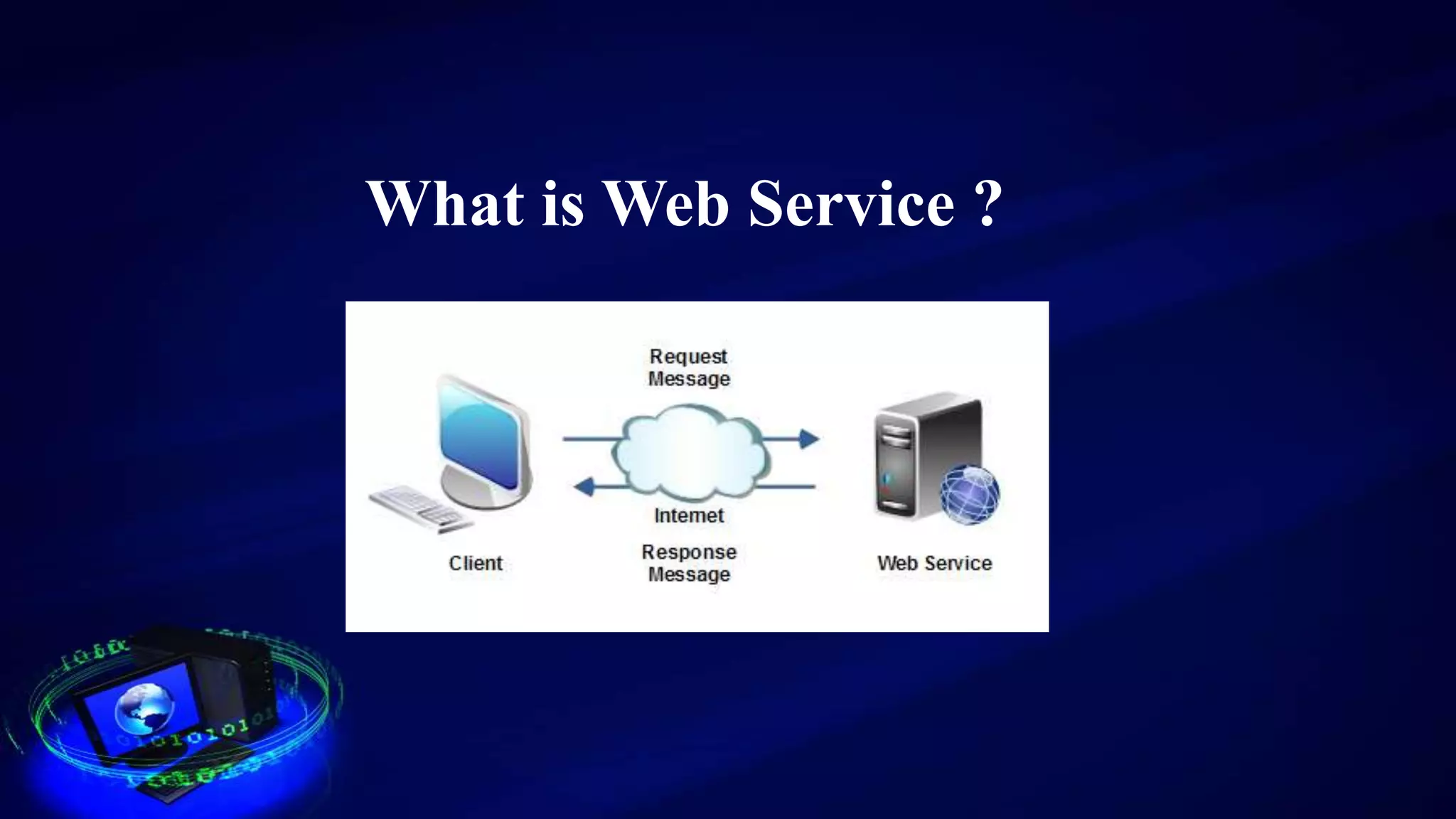
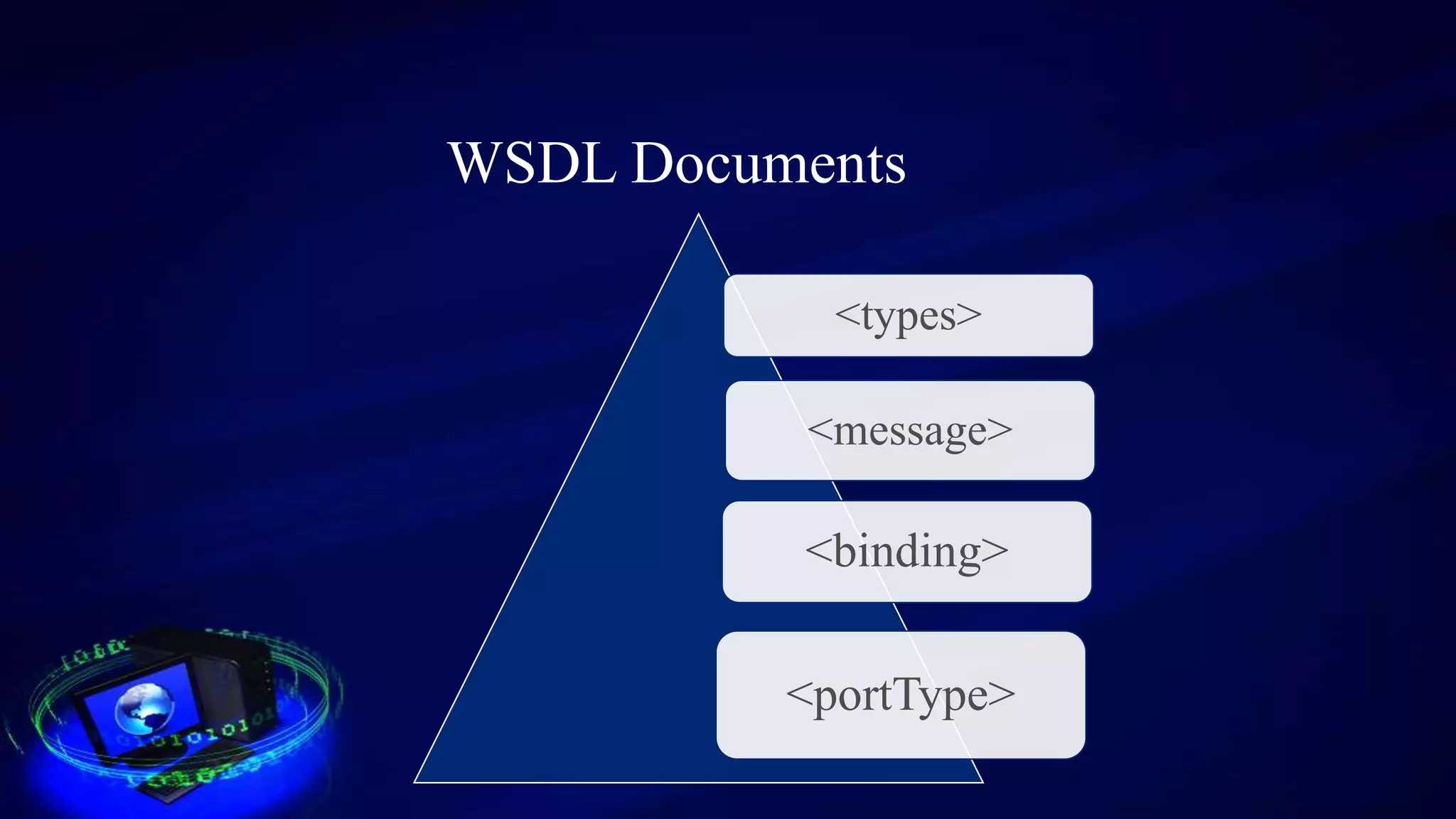
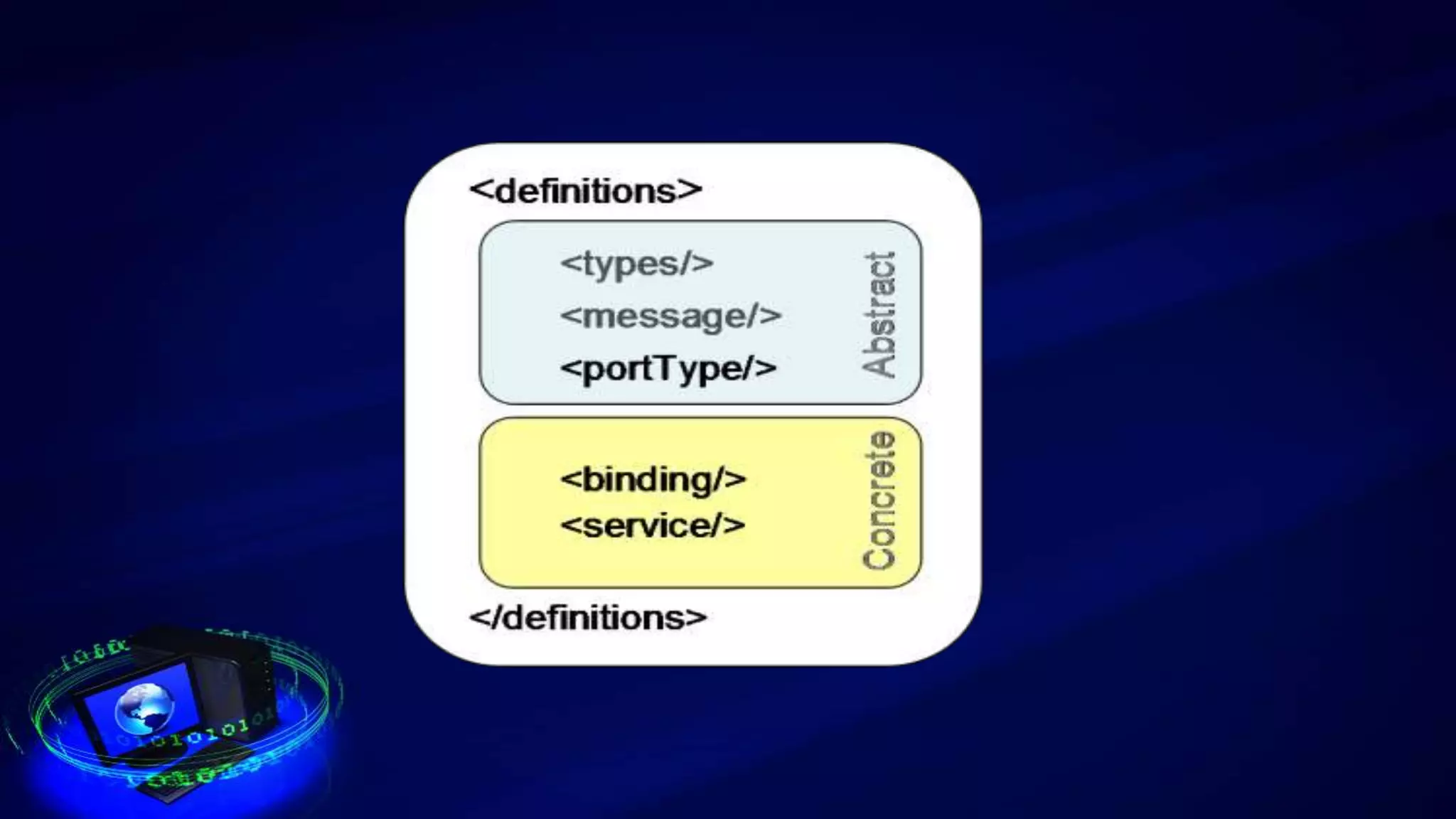
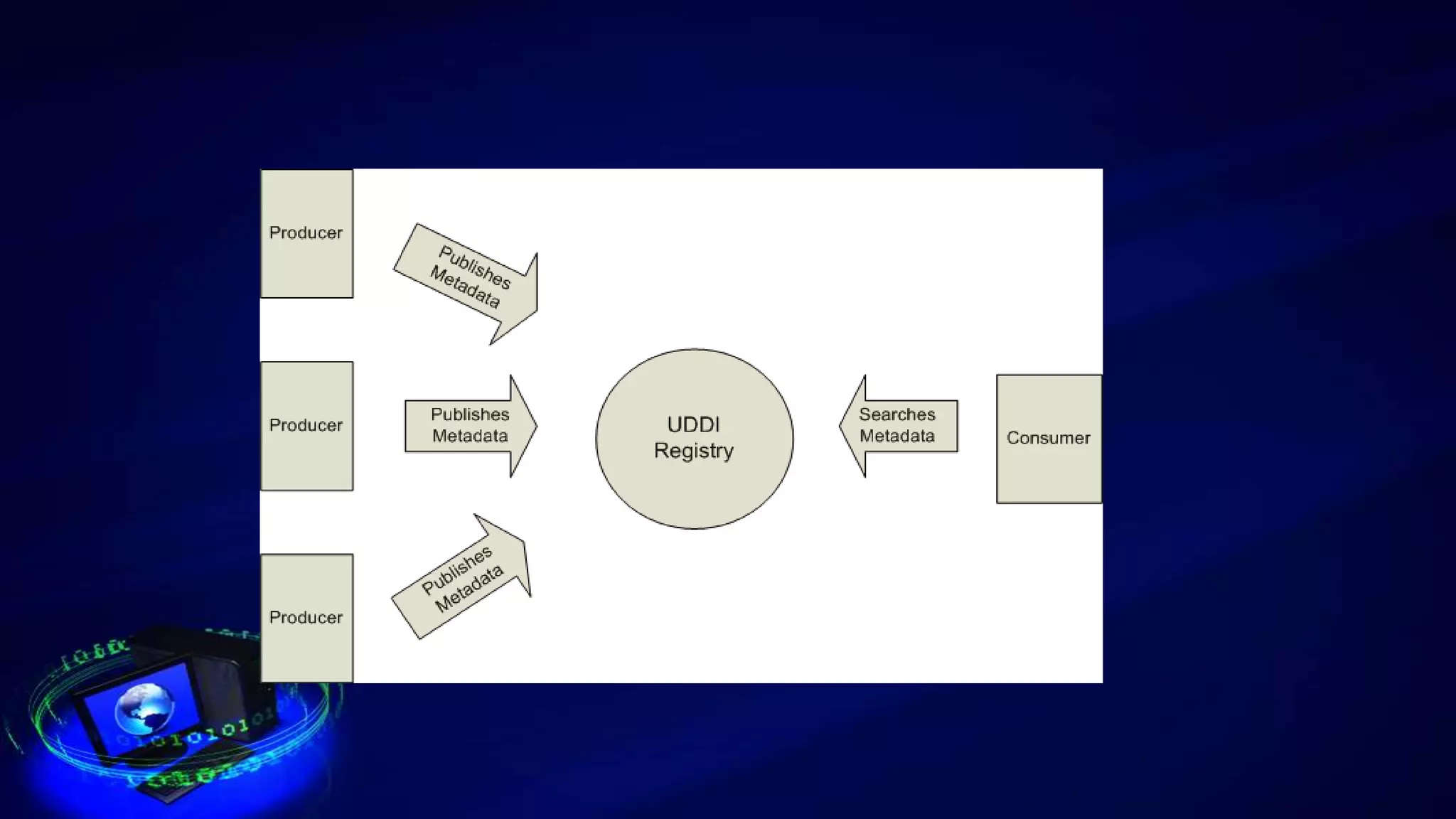
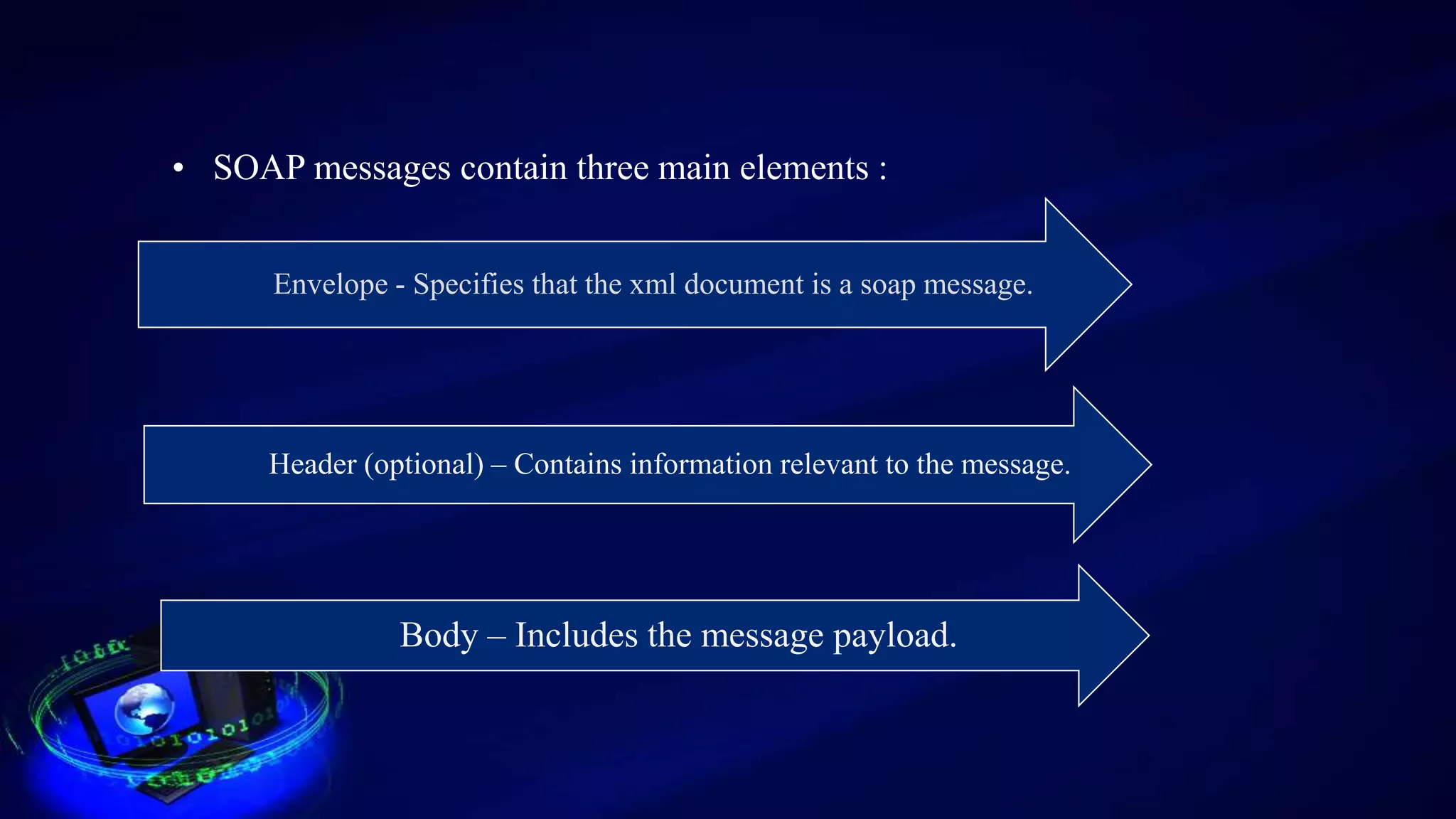
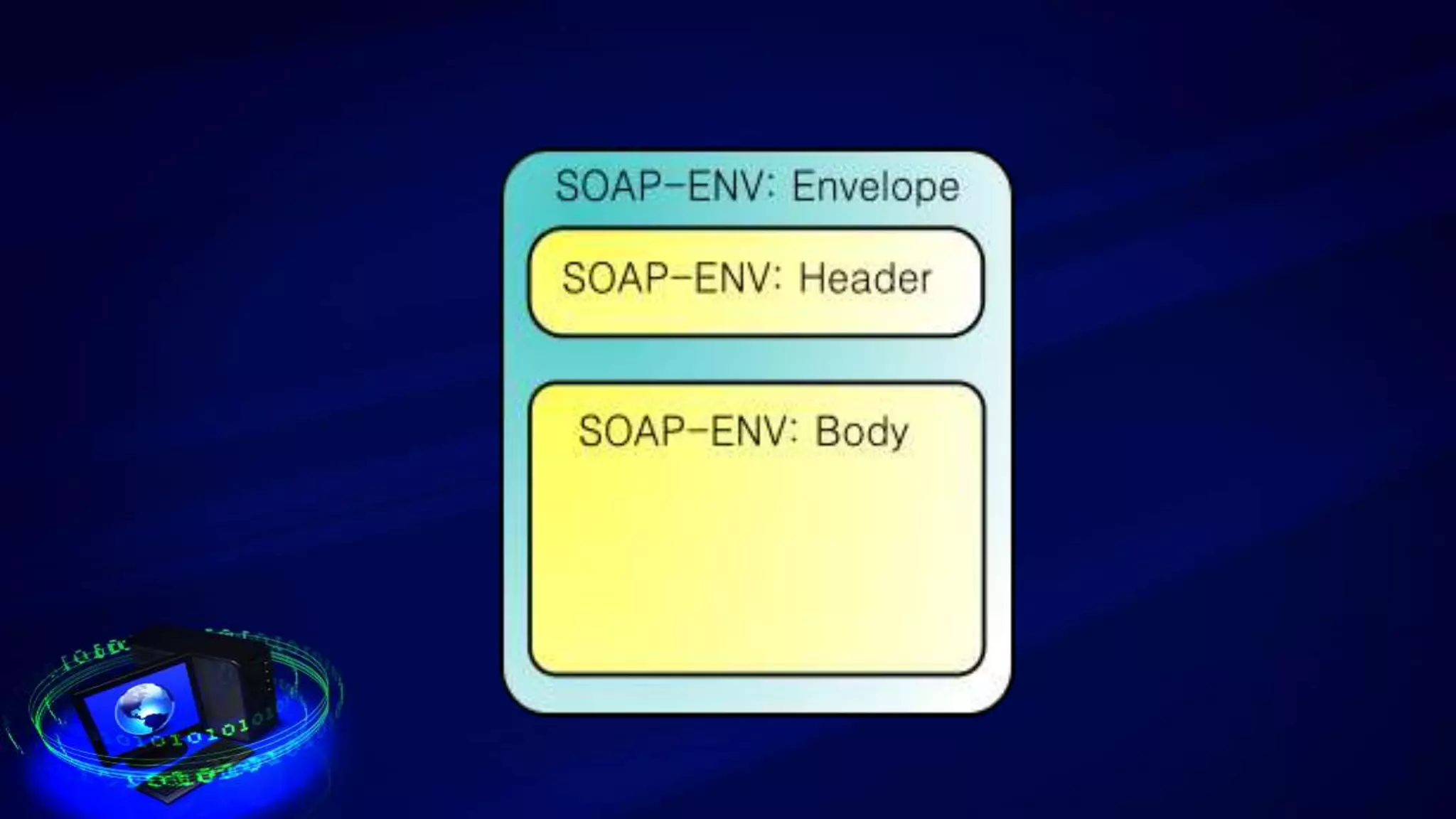
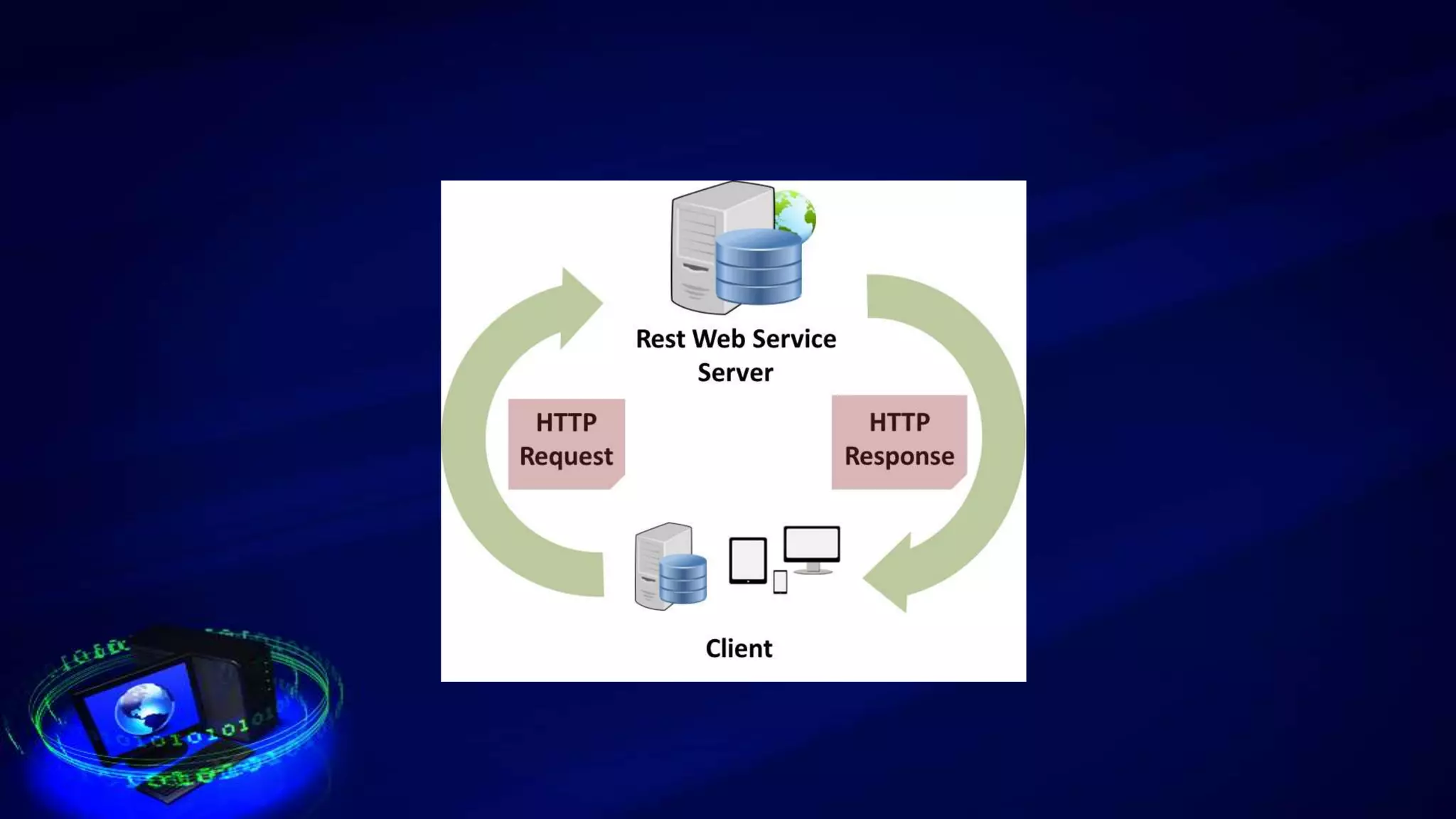
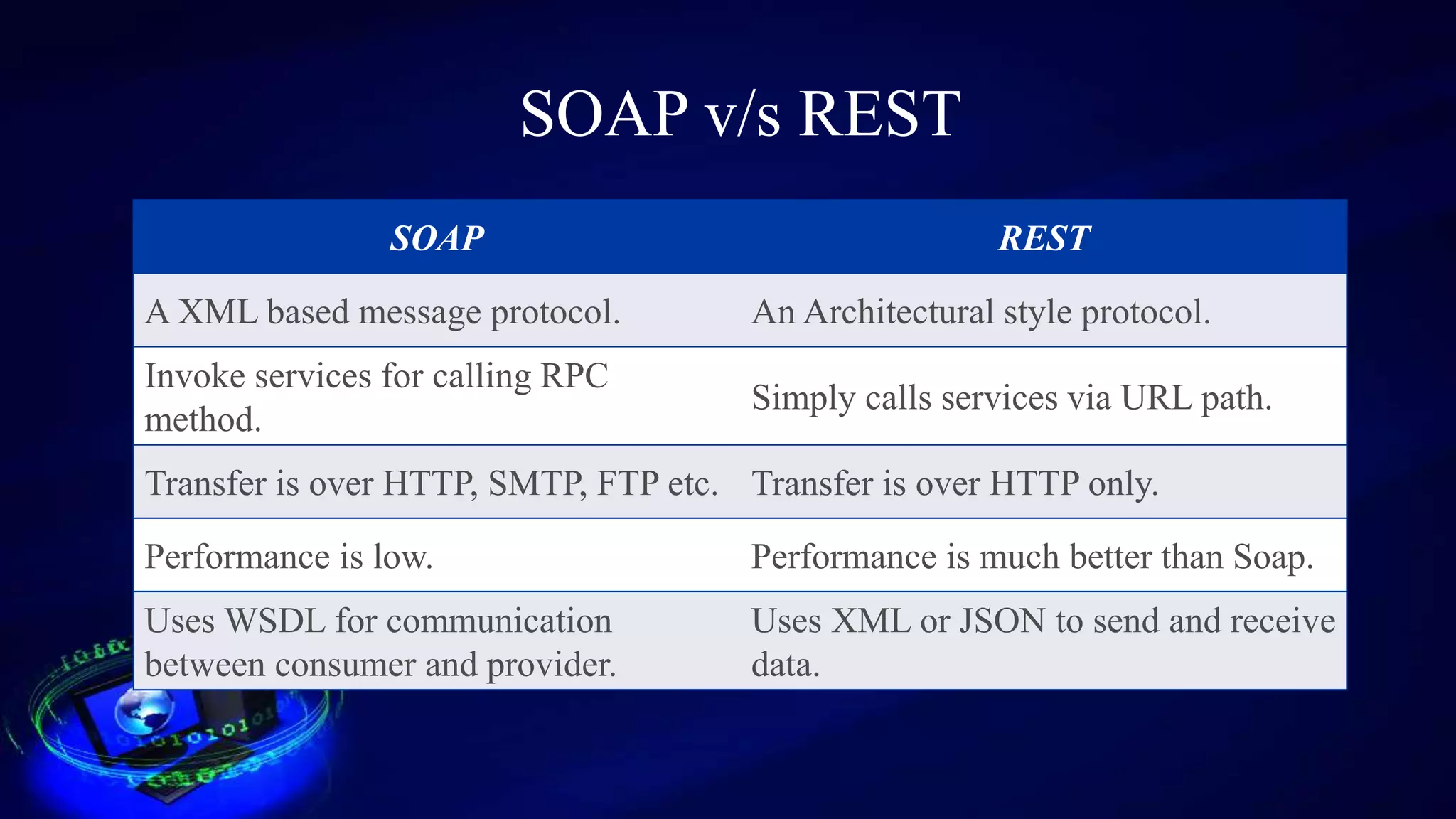
This document provides an introduction to web services, including how they are classified and tested. It discusses how web services use XML, SOAP, WSDL, and UDDI to enable communication over the internet. The two main classifications of web services are SOAP and REST. SOAP uses XML and WSDL to define services as remote procedure calls, while REST uses standard HTTP methods to manipulate resources. The document outlines reasons for testing services and common test approaches, including functional, performance, security, load, and regression testing. It also lists some popular tools for testing web services and compares key differences between SOAP and REST.