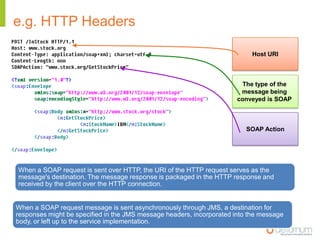
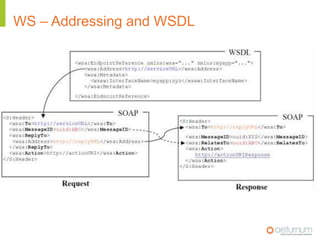
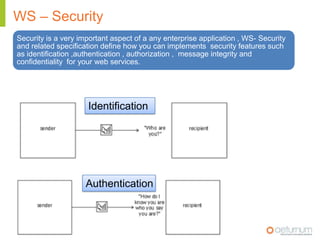
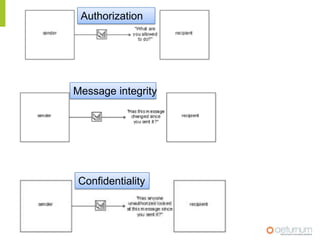
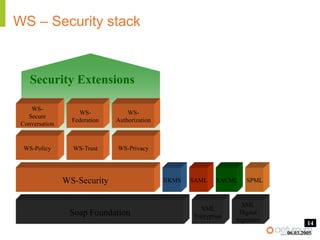
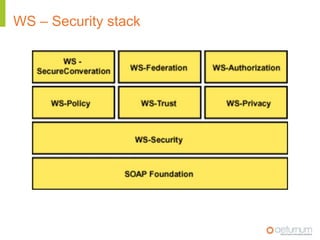
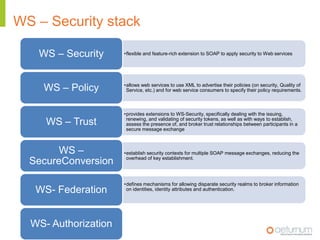
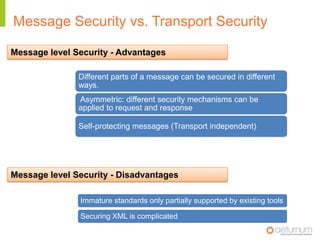
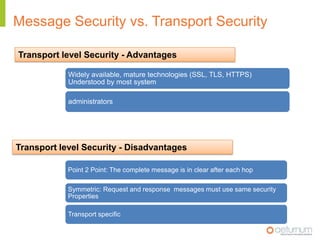
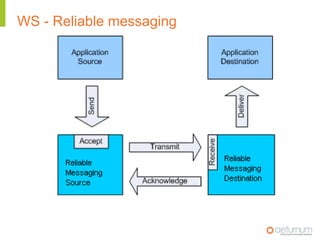
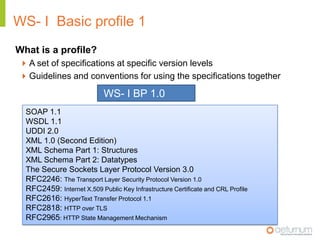
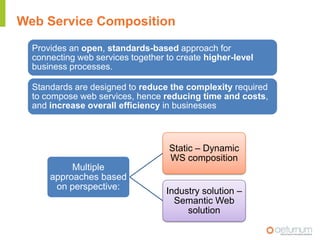
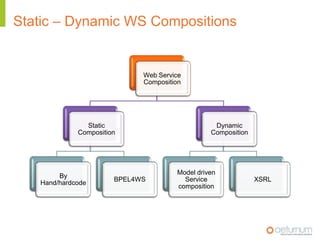
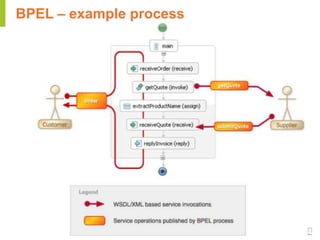
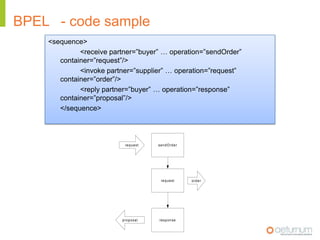
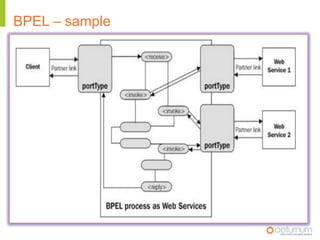
This document provides an overview of web service specifications and standards including SOAP, WSDL, WS-Addressing, WS-Security, WS-Reliable Messaging, and BPEL. It discusses how WS-Addressing specifies endpoints and message addressing, how WS-Security provides identification, authentication, authorization, integrity and confidentiality, and how WS-Reliable Messaging ensures reliable message delivery. It also summarizes WS-I goals of achieving interoperability and its Basic Profile 1.0 recommendations.