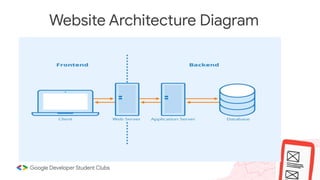
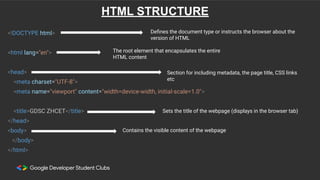
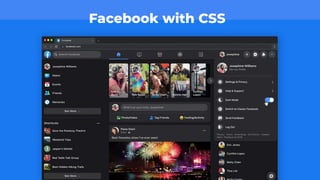
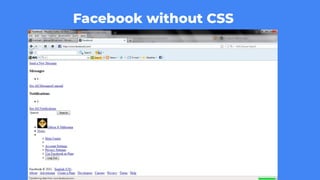
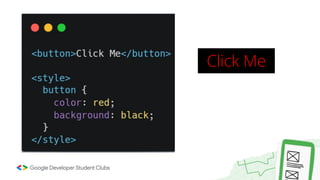
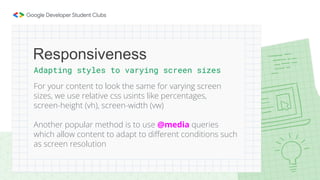
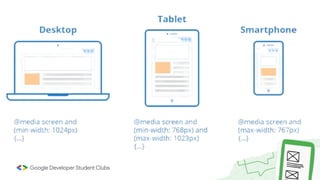
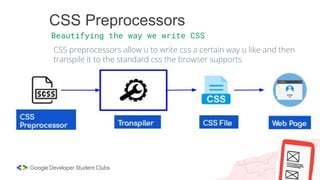
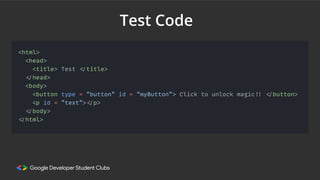
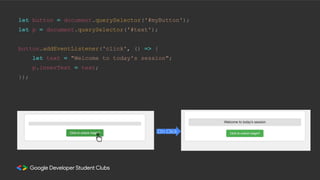
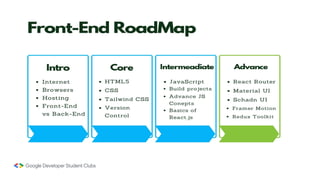
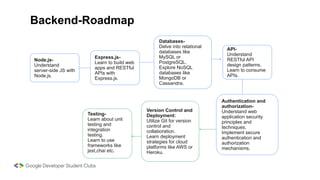
Web development involves building and maintaining websites and web applications using various technologies. It encompasses everything from creating simple static pages to complex dynamic applications. The first website created by Tim Berners-Lee in 1991 was not just a static page but an information hub. Web development enables e-commerce, online presence, communication, automation, and entertainment. Frontend development brings designs to life using HTML, CSS, and JavaScript, while backend handles server-side logic and databases. Databases store structured data for applications. Version control with Git and deployment strategies are important aspects of web development.