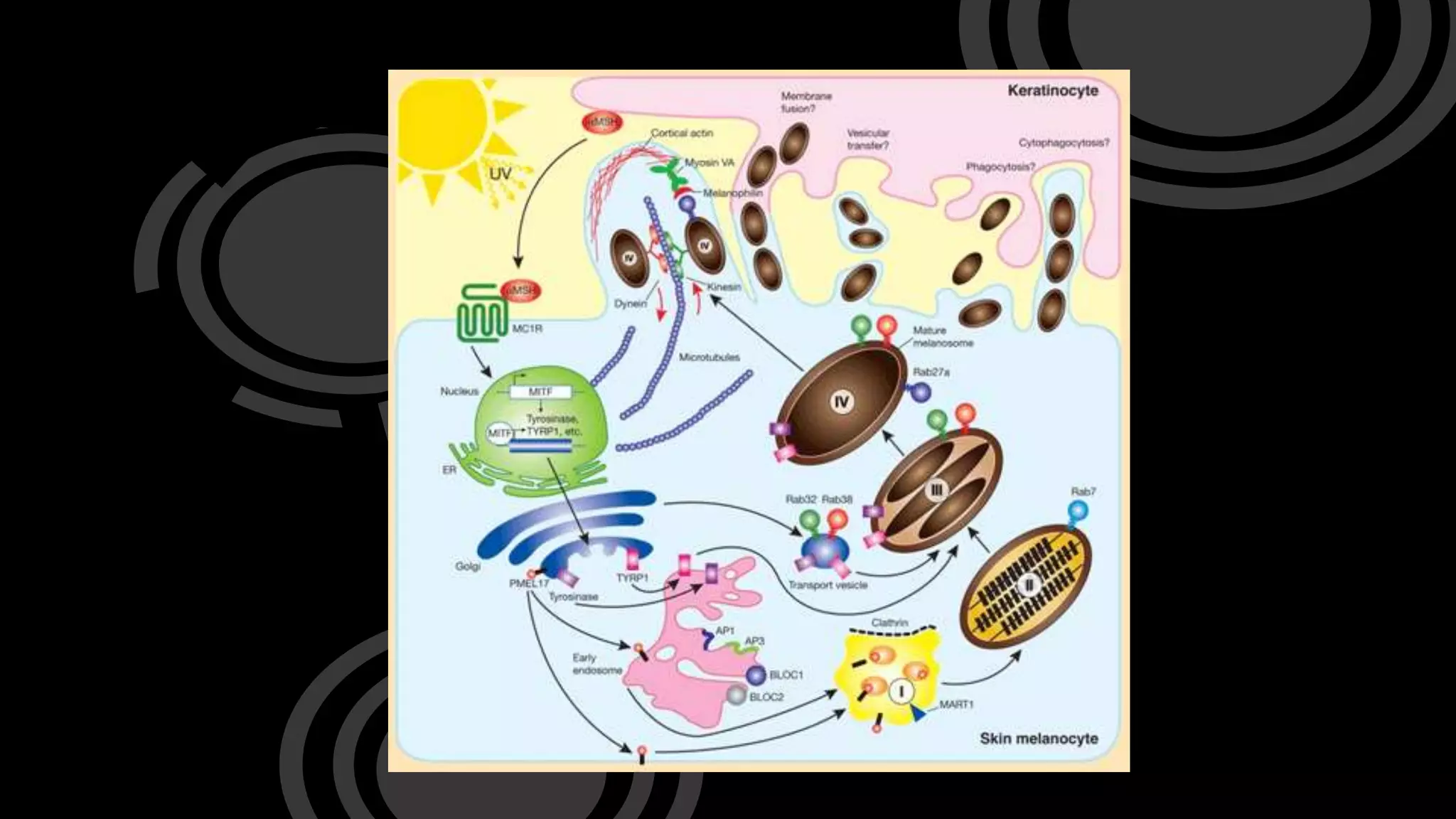
Melanocyte-stimulating hormone (MSH) is a group of hormones produced by the pituitary gland, hypothalamus, and skin cells in response to ultraviolet radiation. It plays a key role in producing skin, hair, and eye color by inducing melanocytes to produce melanin, which protects cells from UV-induced DNA damage and skin cancer. In some animals like frogs, MSH production increases in dark locations, causing skin darkening for camouflage from predators. MSH levels rise after UV exposure and stimulate melanocytes to make melanin, which transfers to skin cells forming caps over nuclei to shield DNA from UV damage.