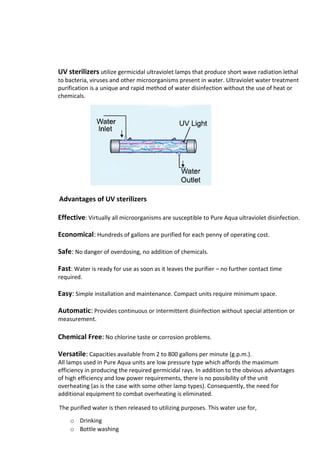
This document summarizes the key components of a water purification system used in industry. It discusses the various steps involved: deep well water collection, pumping, storage, sand filtration, carbon filtration, resin filtration, and UV sterilization. The goal is to remove contaminants and produce clean water suitable for uses like drinking, bottle washing, cleaning, and boilers. Stainless steel pipes, appropriate filter media like sand, activated carbon, ion exchange resins, and UV lamps are used to purify the water through physical and chemical processes.