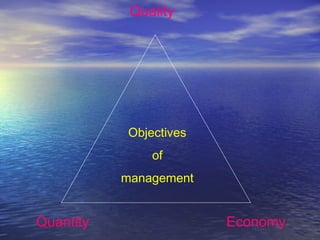
This document discusses waste and abuse in anaesthesiology. It identifies many forms of waste including inaccurate scheduling, unrealistic schedules, and inefficient use of operating room time. This leads to unnecessary costs and frustration among staff. The document provides definitions and outlines steps to improve efficiency such as creating accurate schedules, minimizing turnover times between cases, and addressing delays. Reducing waste in scheduling and operations can help deliver high quality medical services in a more cost effective manner.