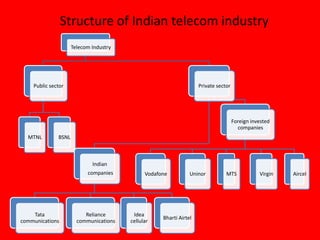
The document provides an overview of the telecom industry in India. It discusses that India has the second largest telecom network in the world with over 800 million connections. The telecom industry is growing rapidly with over 15 million new connections added each month. It is dominated by private operators who have an 84.6% market share. The document outlines the structure of the industry, major players like Bharti Airtel and Reliance, and provides SWOT analyses of the industry and Vodafone.