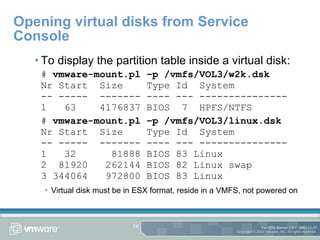
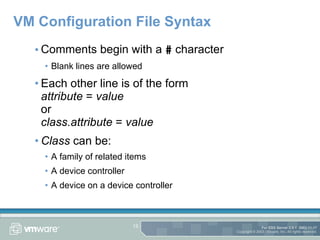
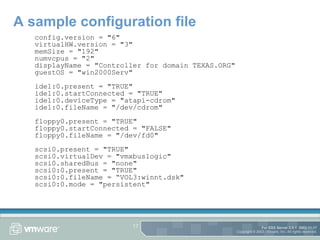
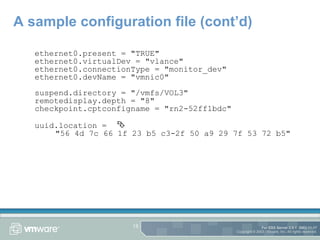
The document provides an overview of using the command line on an ESX Server, including working with disks, virtual machines, and configuration files. It discusses commands for partitioning and managing disks using fdisk and vmkfstools, as well as creating and modifying virtual machines and their configuration files. Tips are also provided for tasks like copying disks between servers and extending disk sizes.





![vmkfstools Syntax The option flag governs the action of the command Either a single letter with one hyphen or a word with two The last argument is always a path using the VMkernel’s device space Either a VMFS name (physical or friendly) vmhba0:1:0:5 /vmfs/vmhba0:1:0:5 myvmfs /vmfs/myvmfs Or a VMFS name followed by a virtual disk file name vmhba0:1:0:5:a.dsk /vmfs/vmhba0:1:0:5/a.dsk myvmfs:a.dsk /vmfs/myvmfs/a.dsk vmkfstools -? [ otherarg otherarg … ] VMkernel-path](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vmware-commandline-091129014253-phpapp01/85/Vmware-Command-Line-6-320.jpg)