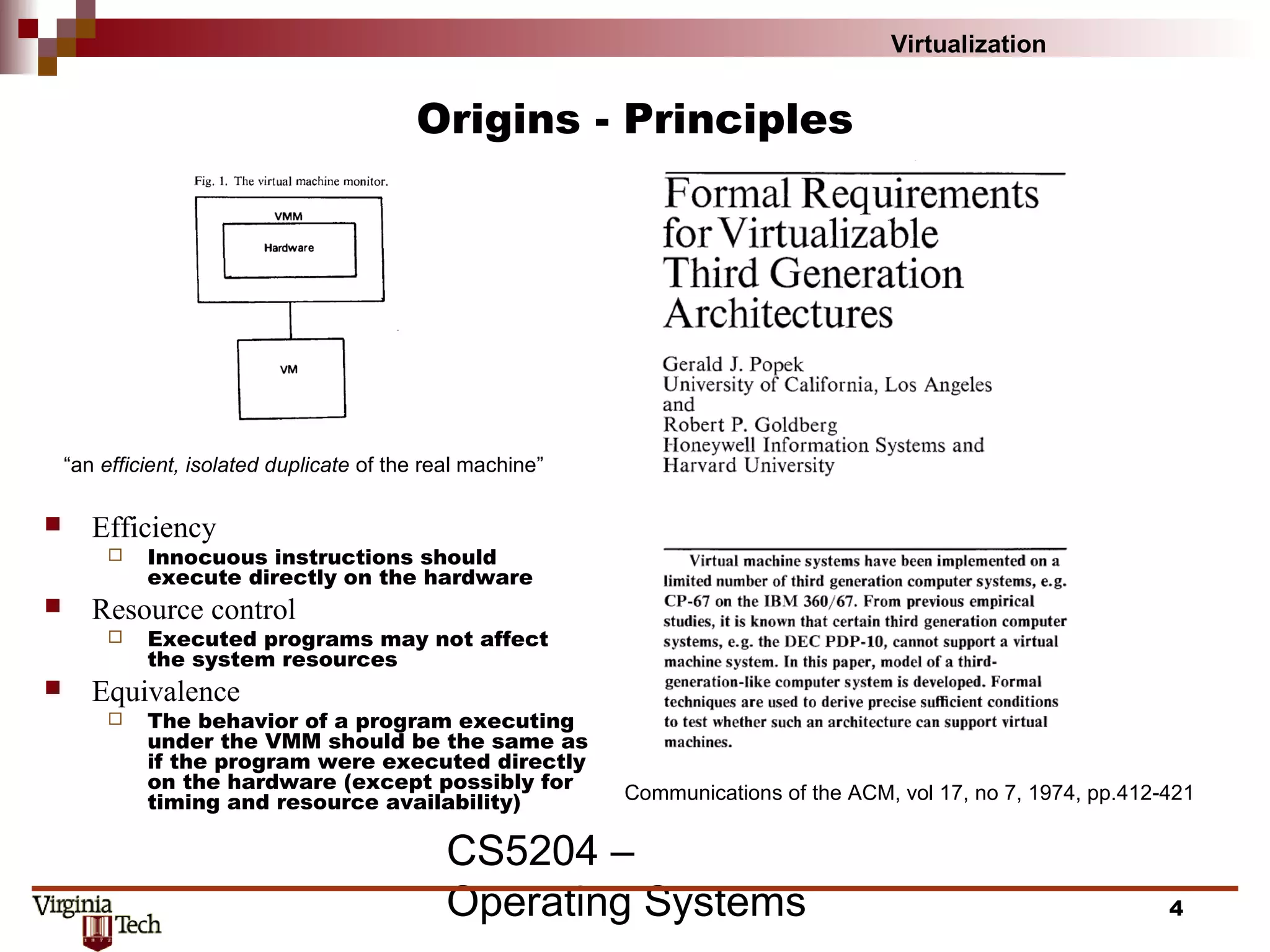
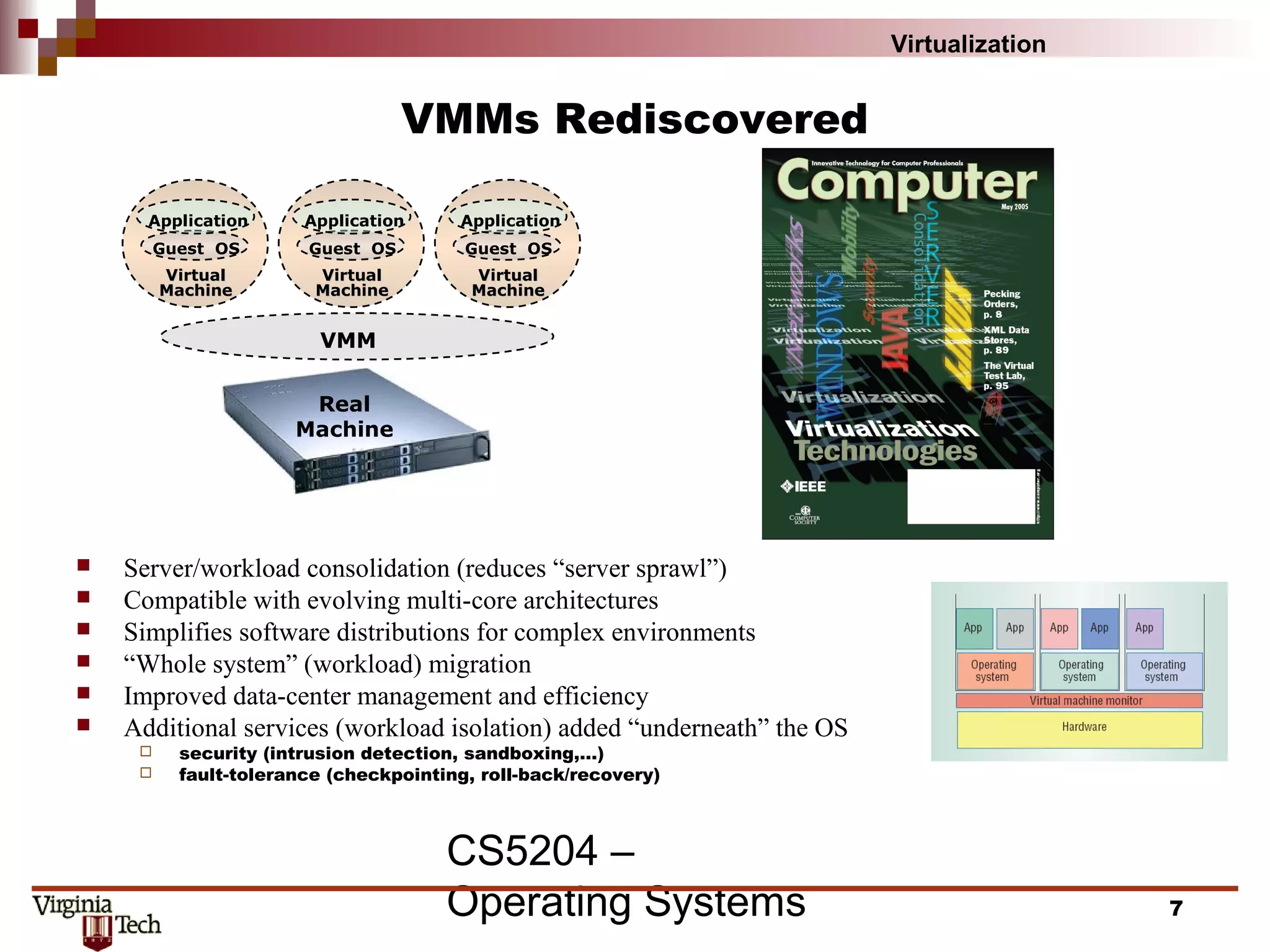
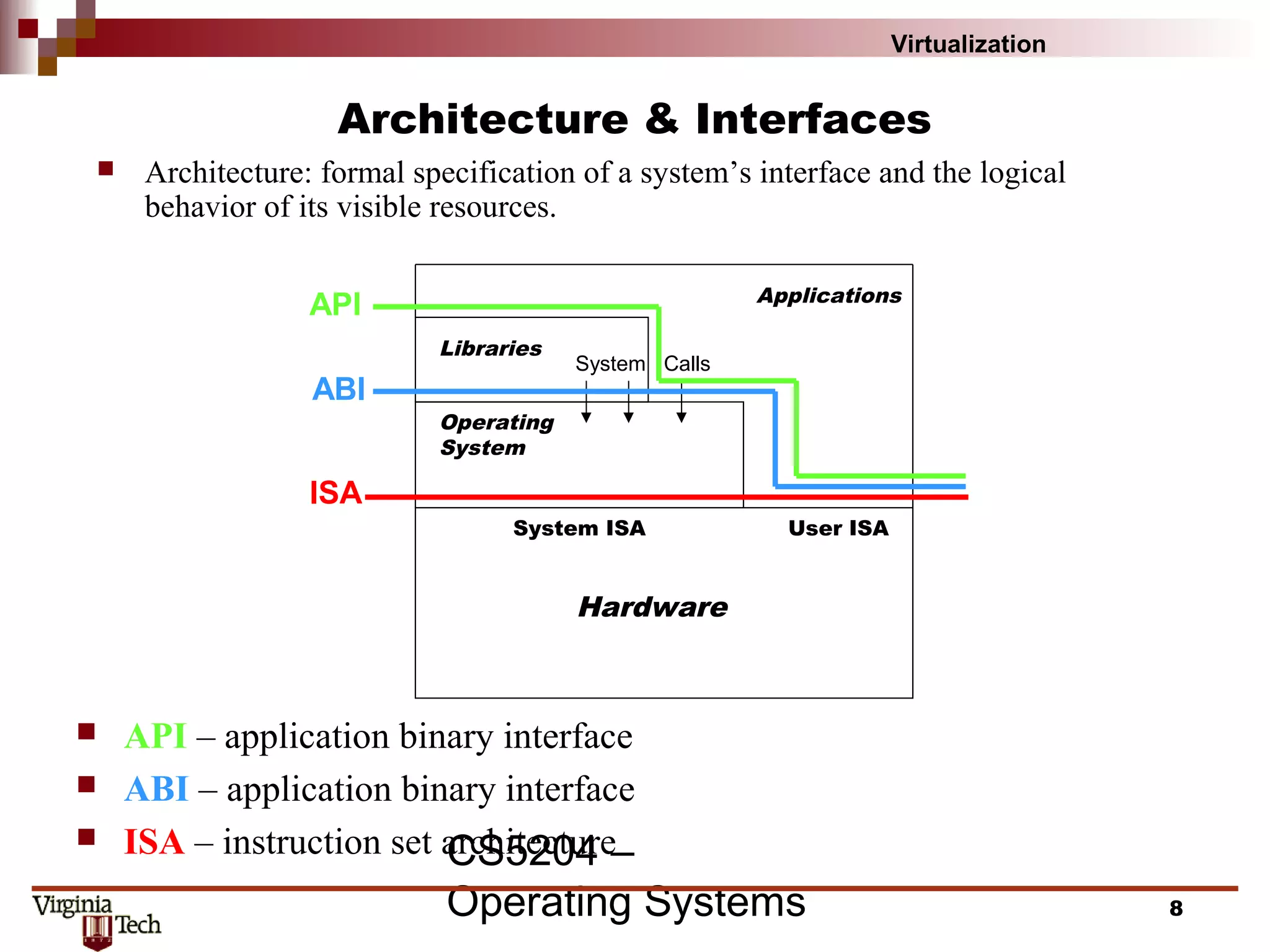
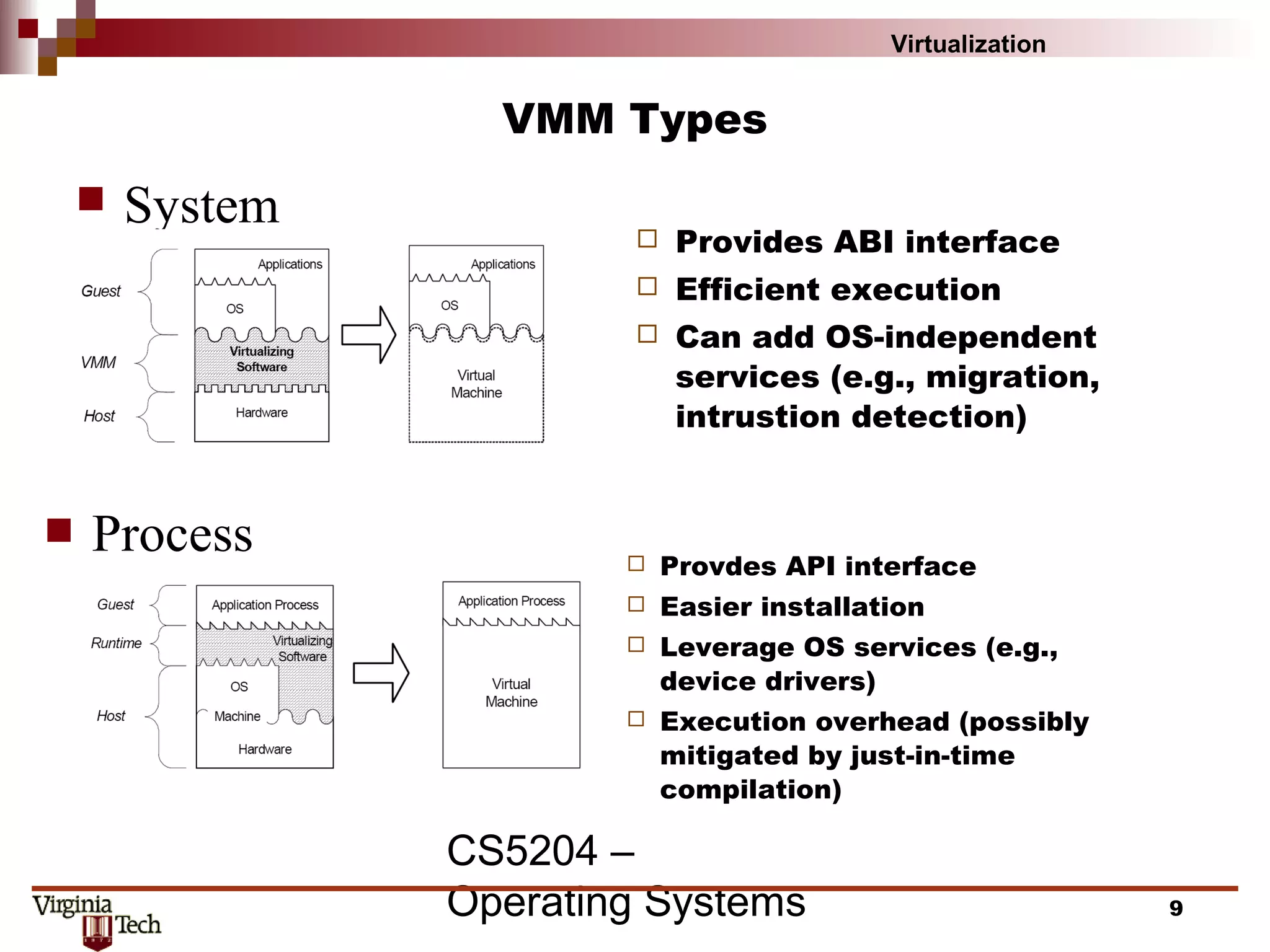
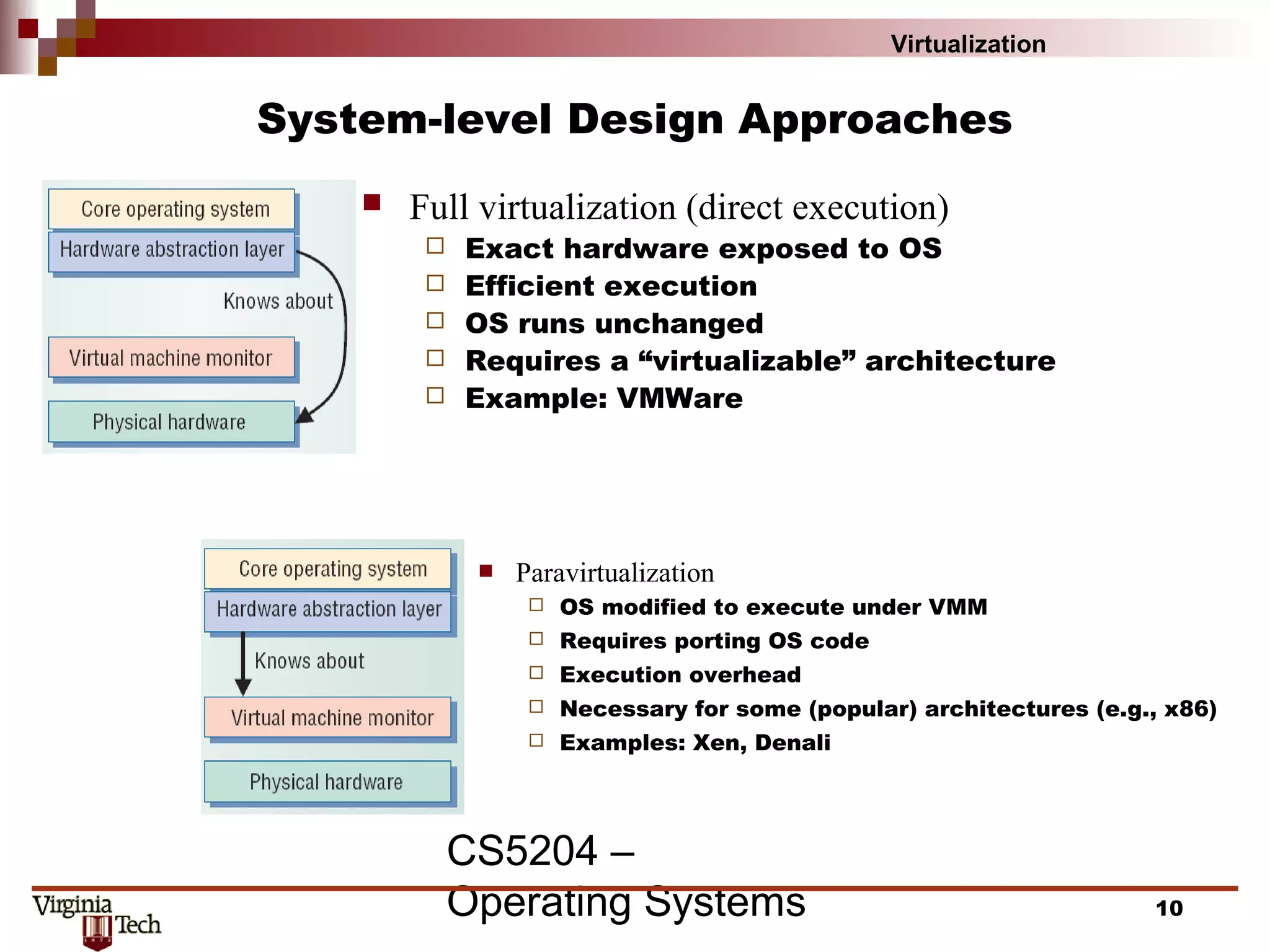
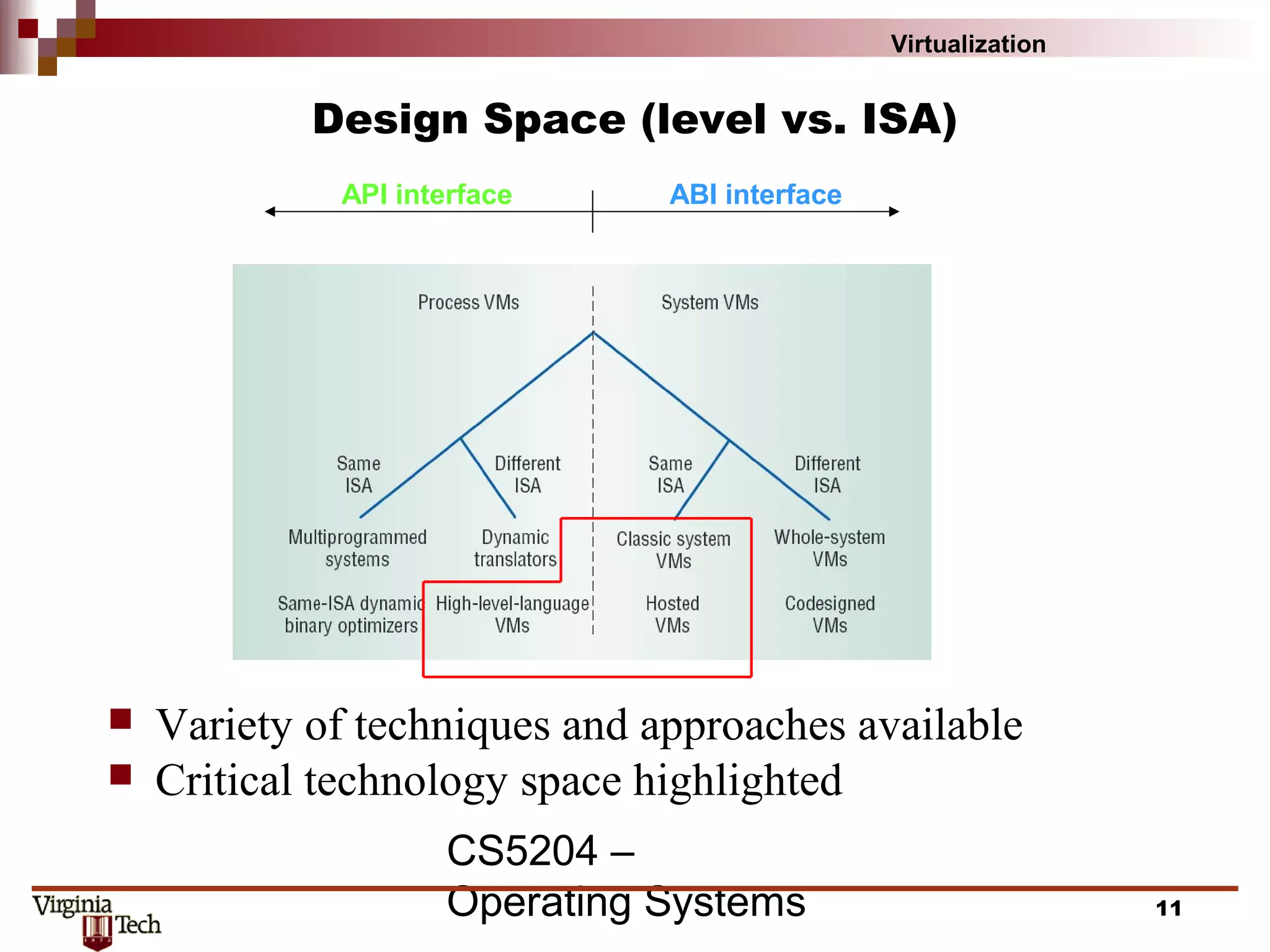
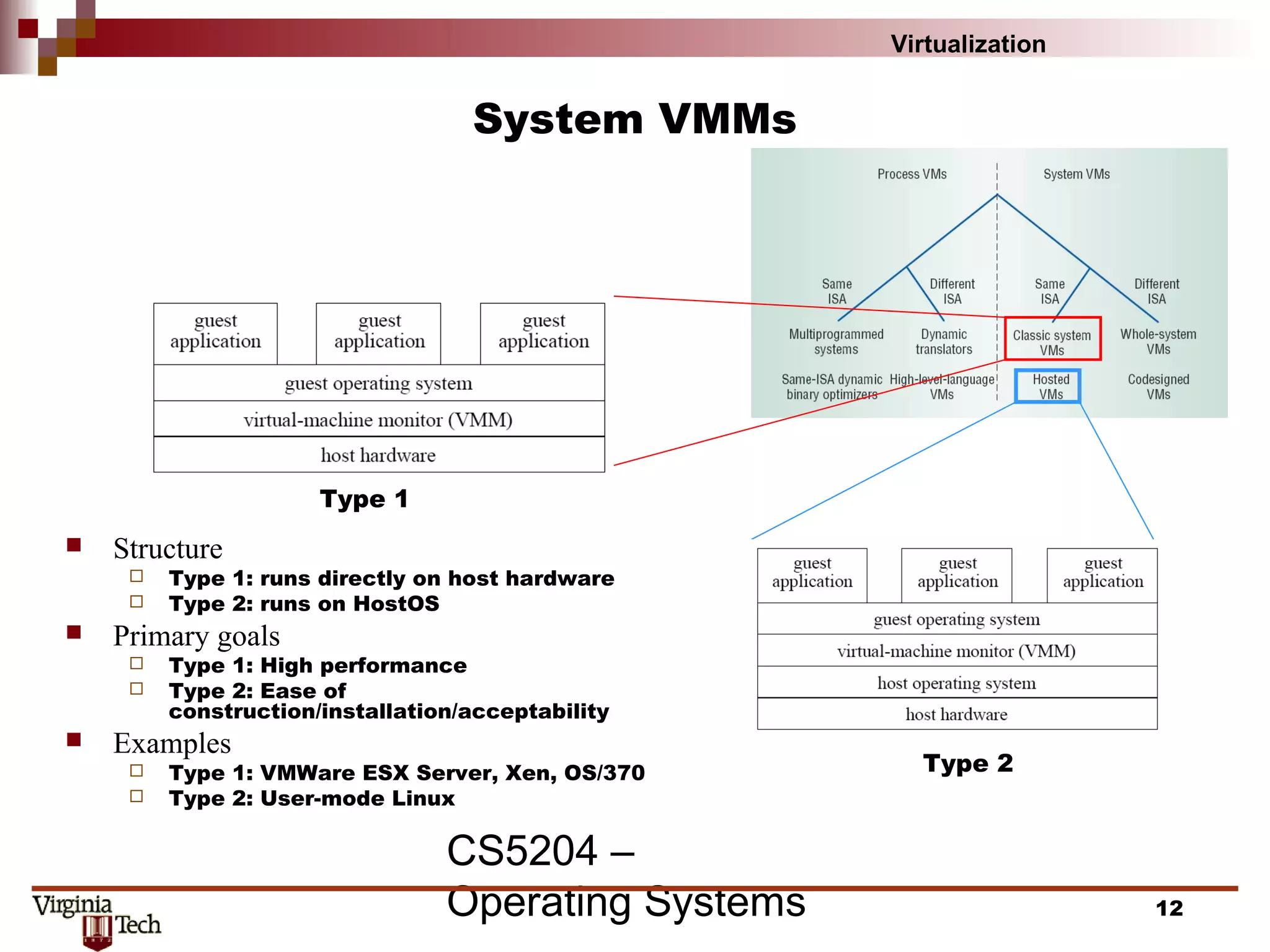
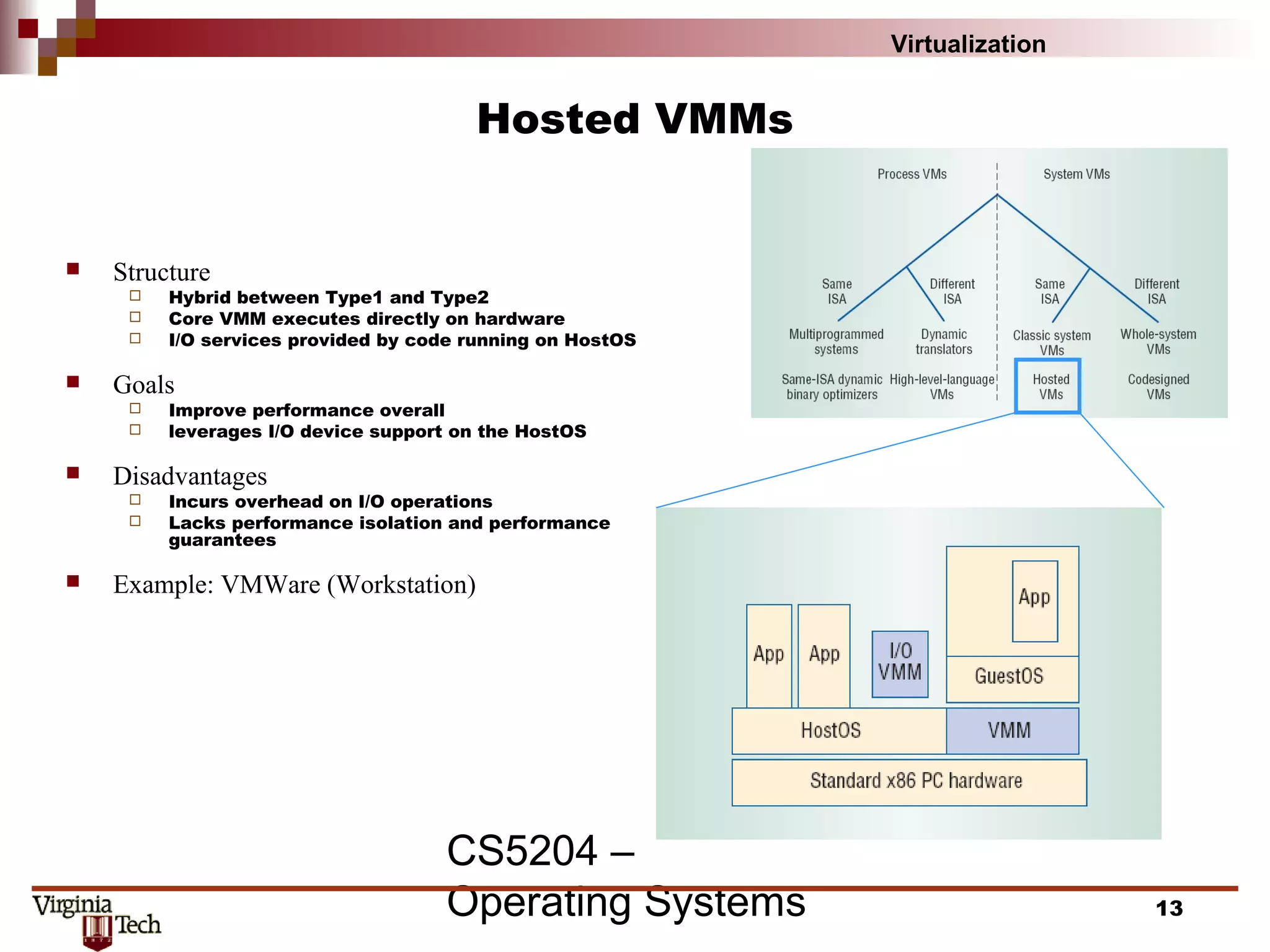
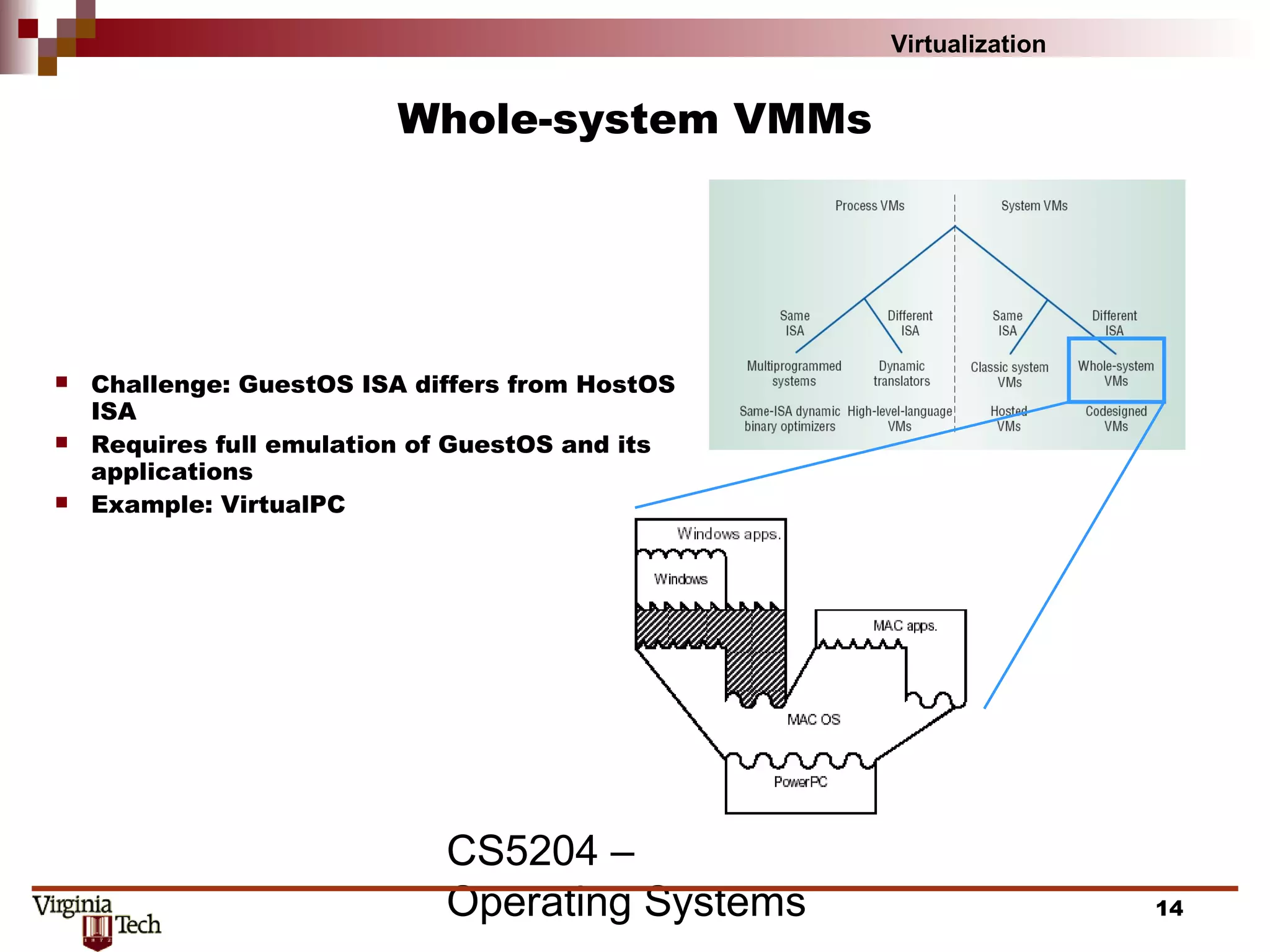
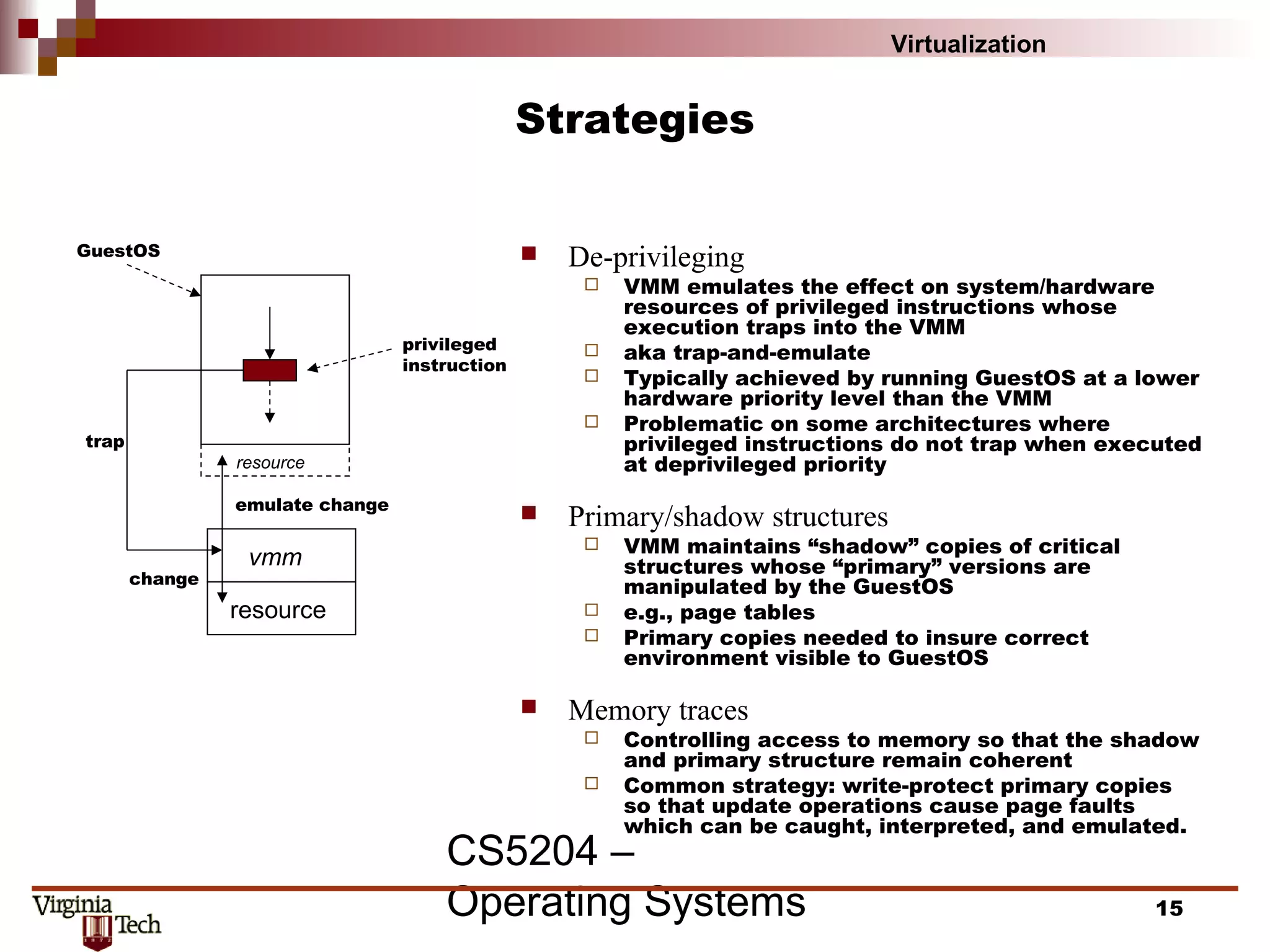
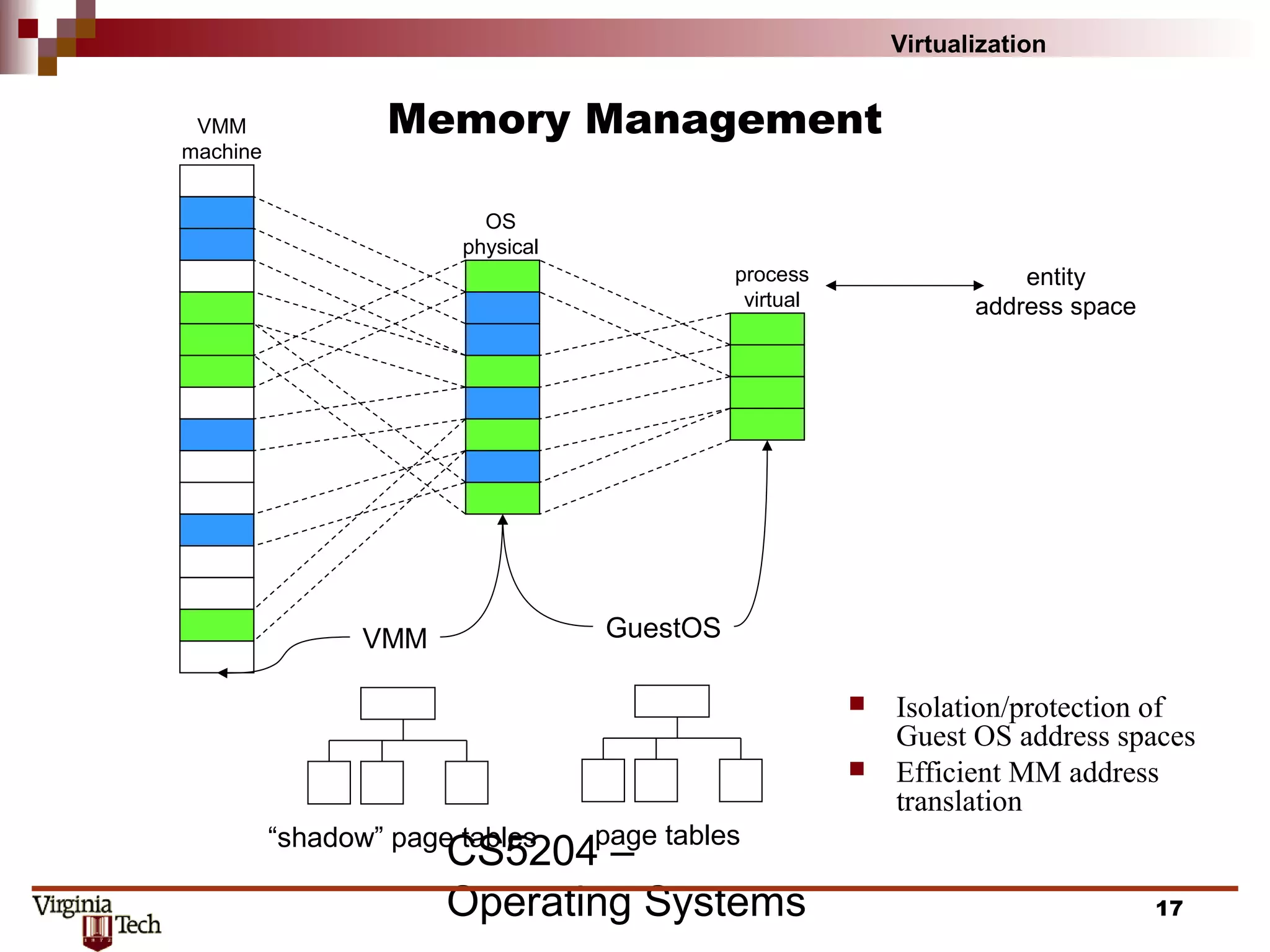
This document discusses virtualization concepts and provides definitions and background information. It begins with references and sources on virtualization. It then defines virtualization and key terms like virtual machine monitor and guest/host. It covers the origins and principles of virtualization, how virtualization was rediscovered, and discusses various virtualization architectures, interfaces, types of virtual machine monitors, and strategies for virtualizing systems like the IA-32 architecture. It concludes by discussing memory management challenges in virtualization.